Spring-外置环境变量解析
前言
外置环境变量一般指的是配置文件, 常用的是properties文件, 但其只能表示简单对象(单个变量和数组变量), 后来spring-boot引入了yaml配置文件并提供了自动配置(将配置映射为复杂对象)功能, 使得开发效率大大提升, 本文将从properties和yaml两大方面说说在Spring工程中(部分引入boot的jar包)如何解析放入到环境变量或实例的成员变量中.
Properties
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
启动时读取指定的配置文件并遍历其他所有bean, 只会被加载到引用bean的成员变量中.
@Configuration
public class PropertiesConfig {
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer placeholderConfigurer() {
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
configurer.setIgnoreResourceNotFound(true);
configurer.setFileEncoding(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
// 启动时读取类路径下的boot.properties文件
configurer.setLocations(new ClassPathResource("boot.properties"));
return configurer;
}
}
注:
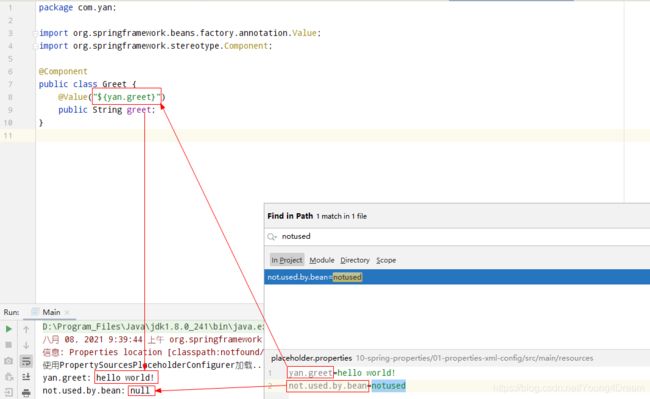
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer只能是static的- 全局只能有一个实例, 如果项目上下文已经有了这个对象,并指定了
Resource, 不能再新增, 因此不推荐使用 - 被
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer加载并读取的变量, 必须被其他bean读取(如使用@Value("${xx.xx}")),直接从Environment中是无法获取的.这里功能的限制体现在PlaceholderConfigurerSupport#doProcessProperties中
- 另外还有个配置类
PropertyOverrideConfigurer, 是用来覆盖已经初始化好了的bean的属性值的, 用法可以参考:Spring占位符PropertyOverrideConfigurer的使用
@PropertySource(s)
PropertySource可以读取指定路径下的一个或多个properties, 不支持通配符*.
PropertySource可以放在@Configuration类下, 也可以与其他实例绑定, 但效果一样, 都是全局性的.
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class JdbcProperties {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
}
如果找不到指定的资源, 会报错, 但可以指定是否忽略:
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:xxx.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
PropertySources可以允许多个PropertySource:
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource("classpath:a.properties"),
@PropertySource("classpath:sceduler/sc-a.properties")
})
Yaml
依赖
确保引入如下依赖, 其中spring-boot和spring-boot-autoconfigure版本保持一致
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-bootartifactId>
<version>2.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigureartifactId>
<version>2.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.yamlgroupId>
<artifactId>snakeyamlartifactId>
<version>1.28version>
dependency>
自动解析
要使用boot的自动解析功能, 最简单的配置就是利用预置好的事件发布, 定义一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent和一个ConfigFileApplicationListener:
/**
* 提供解析{@code application.yaml}的事件发布配置
*/
@Configuration
public class BootEnvironmentConfig implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(applicationContext);
ConfigFileApplicationListener listener = new ConfigFileApplicationListener();
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = context.getEnvironment();
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event = new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(springApplication, null, environment);
context.publishEvent(event);
}
}
如果是springboot-5.3.X及以上版本, 改为:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class BootEnvironmentConfig implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware, ConfigDataEnvironmentUpdateListener {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(applicationContext);
DefaultBootstrapContext defaultBootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = context.getEnvironment();
DeferredLogs deferredLogs = new DeferredLogs();
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor processor = new ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor(deferredLogs, defaultBootstrapContext, this);
processor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, springApplication);
}
}
此时就集成了springboot的配置文件解析功能, 可以自动解析全局配置文件:
application.yamlapplication.ymlapplication.properties- 其他带有
profile后缀的yaml或yml文件的解析.
不足
要注意的是, 这里集成的功能有限, 最严重的是它不支持profile型的对象实例化.
比如, 在application.yaml中指定了spring.profiles.active为dev, 并且定义了一个类:
@Component
@Profile("dev")
public class DevInstance {
// ignore
}
此时可以从environment对象中读取到spring.profiles.active的值为dev, 但无法在上下文中获取DevInstance实例.
对象映射
yaml文件本来就是用来表示复杂对象的, springboot也贴心的集成了对象映射功能, 需要在某个配置类上开启@EnableConfigurationProperties,同时在实例对象上使用@ConfigurationProperties.
比如相关配置文件为:
license:
id: 1
name: test
permission-for: yanwei
items:
a:
- a1
- a2
b:
- b1
- b2
那么可以自动映射为LicenseProperties的实例对象:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("license")
public class LicenseProperties {
private String id;
private String name;
private String permissionFor;
private Map<String, List<String>> items;
}
以上就表示找到前缀为license的环境变量, 将其下属性一一对应放入LicenseProperties的成员变量中.
您可以在Gitee上找到本文的源代码。