python双端队列_中间是头两边是尾_两边是头中间是尾
双端队列的顺序表存储结构以及两种特殊的双端队列
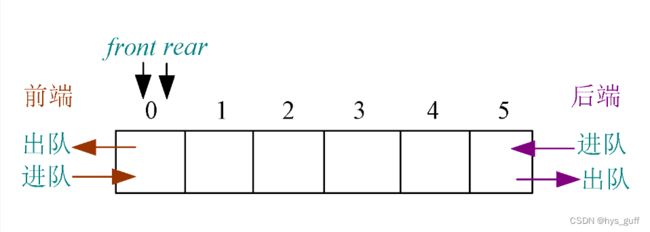
双端队列 是一种允许我们同时从前端和后端添加和删除元素的特殊队列,它是队列和栈的结合体。
双端队列(deque)与队列(queue)就差了两个字,队列里元素只能从头部出来,尾部进去,双端队列也有前端和后端,只不过前后端都能进出数据,元素从哪一端进去或者出来并不是固定的。新的元素可以从头部也可以从尾部进去,已有的元素也可以从头部或者尾部出来。
现实生活中也有应用双端队列的例子:例如我们去电影院排队买票。一个刚刚买完票的人想回来咨询下简单信息,就可以直接回到队伍的头部。某些人正在队尾排队,如果比较赶时间,改变看电影的计划了,就可以从队尾直接离开队伍。
计算机科学中,双端队列常见的应用是存储一系列的撤销操作时。每当用户进行一个操作,操作就会被存,可以撤回到上一步的操作的节点。
以列表为基础的普通双端队列:
class Deque:
"""先进先出"""
def __init__(self):
self.list=[]
def is_empty(self):
return self.list is []
def push_front(self,data):
"""往队首添加一个元素"""
self.list.insert(0,data)
def push_rear(self,data):
"""往队尾添加元素"""
self.list.append(data)
def pop_front(self):
"""弹出队头元素"""
return self.list.pop(0)
def pop_rear(self):
"""弹出队尾元素"""
return self.list.pop()
def getfront(self):
"""获知队头元素"""
return self.list[0]
def size(self):
return len(self.list)双端队列不仅仅可以两边都可以进队出队,也可以中间是头两边是尾,或者两边是头中间是尾。
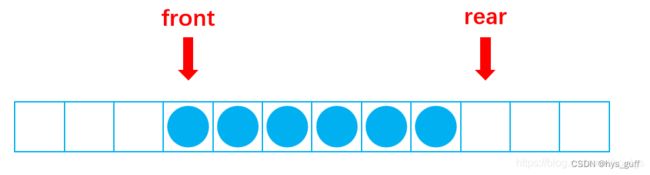
"两边是头中间是尾"的双端队列是一种特殊的数据结构,它的特点是可以在队列的两端进行插入和删除操作,而队列的中间部分保持不变。这种数据结构在实际应用中可能并不常见,但可以根据具体的需求进行实现。
在这种双端队列中,头部和尾部都可以进行插入和删除操作,而队列的中间部分则保持不变。这样的设计可能在某些特定的场景下有用,比如需要保持队列中间部分的顺序不变,而只在两端进行操作。实现这样的双端队列可能需要考虑如何确保中间部分的稳定性,以及如何进行高效的插入和删除操作。具体的实现方式可能需要根据具体的需求和场景来进行设计和优化。
两边是头中间是尾的双端队列:
#两边是头,中间是尾的从两端往中间走的双端队列
class Deque(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.list1 = [None for i in range(size)]
self.size = size
self.zuotou = 0 #尾在抽象层面上的初始位置在头的后一位
self.zuowei = -1
self.youtou = size-1
self.youwei = size
def empty(self):
if self.zuotou-1==self.zuowei and self.youtou+1==self.youwei: #判断条件:两边的尾巴都在头的后一位
return True
else:
return False
def full(self):
if self.zuowei + 1 == self.youwei: #判断条件:两个尾巴相邻
return True
else:
return False
def push(self, flag, data): #flag用来确立往左右哪边队列添加元素
if self.full():
print('无法再添加数据,队列满')
else:
if flag == 1:
self.zuowei += 1 #尾巴后移,然后赋值
self.list1[self.zuowei] = data
else:
self.youwei -= 1 #抽象层面上尾巴后移,然后赋值
self.list1[self.youwei] = data
def pop(self, flag):
if self.empty():
return False
else:
if flag == 1:
self.list1[self.zuotou]=None #让头赋值为None,再指向下一个头
self.zuotou+=1
else:
self.list1[self.youtou]=None #让头赋值为None,再指向下一个头
self.youtou-=1
SS=Deque(10)
print("空",SS.empty())
print("满",SS.full())
print(SS.list1)
SS.push(1, 12)
SS.push(2, 90)
print(SS.list1)
SS.push(1, 13)
SS.push(2, 89)
print(SS.list1)
SS.pop(2)
print(SS.list1)
print("空",SS.empty())
SS.pop(1)
print(SS.list1)
print("空",SS.empty())
SS.push(1,0)
SS.push(1,1)
SS.push(1,2)
SS.push(1,3)
SS.push(1,4)
SS.push(1,5)
print(SS.list1)
print("满",SS.full())
SS.push(1,6)
# 空 True
# 满 False
# [None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None]
# [12, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, 90]
# [12, 13, None, None, None, None, None, None, 89, 90]
# [12, 13, None, None, None, None, None, None, 89, None]
# 空 False
# [None, 13, None, None, None, None, None, None, 89, None]
# 空 False
# [None, 13, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 89, None]
# 满 True
# 无法再添加数据,栈满
#
# Process finished with exit code 0中间是头两边是尾的双端队列可以被理解为一个具有双向操作的队列,可以在队列的两端进行插入和删除操作。这种数据结构在很多应用中都非常有用,例如在实现双向搜索算法、滑动窗口等场景中都可以发挥作用。
中间是头两边是尾的双端队列:
# 中间是头,两边是尾的从两端往两边走的双端队列
class Deque(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.list1 = [None for i in range(size)]
self.size = size
self.middle=(size+1)//2 #用该方法确定size是奇数和偶数两种情况时中间头部位置的选取
self.zuotou = self.middle-1
self.zuowei = self.middle #尾巴在抽象层面初始时在头的后一位
self.youtou = self.middle
self.youwei = self.middle-1
def empty(self):
if self.zuotou+1==self.zuowei and self.youtou-1==self.youwei :#判断条件:两边的尾巴都在头的后一位
return True
else:
return False
def full(self): #判断条件:左边的尾巴到左头,或者右边的尾巴到右头
if self.zuowei==0 or self.youwei==self.size-1:
return True
else:
return False
def push(self, flag, data): #flag用来确立往左右哪个队列添加元素
if self.full():
print('无法再添加数据,队列满')
else:
if flag == 1:
self.zuowei -= 1 #尾巴移动,赋值
self.list1[self.zuowei] = data
else:
self.youwei += 1 #尾巴移动,赋值
self.list1[self.youwei] = data
def pop(self, flag):
if self.empty():
return False
else:
if flag == 1:
self.list1[self.zuotou]=None #头赋值None,再移动
self.zuotou-=1
else:
self.list1[self.youtou]=None #头赋值None,再移动
self.youtou+=1
SS=Deque(10)
print("空",SS.empty())
print("满",SS.full())
print(SS.list1)
SS.push(1, 12)
SS.push(2, 90)
print(SS.list1)
SS.push(1, 13)
SS.push(2, 89)
print(SS.list1)
SS.pop(2)
print(SS.list1)
print("空",SS.empty())
SS.pop(1)
print(SS.list1)
print("空",SS.empty())
SS.push(1,0)
SS.push(1,1)
SS.push(1,2)
SS.push(1,3)
print(SS.list1)
# 空 True
# 满 False
# [None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None]
# [None, None, None, None, 12, 90, None, None, None, None]
# [None, None, None, 13, 12, 90, 89, None, None, None]
# [None, None, None, 13, 12, None, 89, None, None, None]
# 空 False
# [None, None, None, 13, None, None, 89, None, None, None]
# 空 False
# 无法再添加数据,队列满
# [2, 1, 0, 13, None, None, 89, None, None, None]
#
# Process finished with exit code 0