pytorch基本介绍:张量基本操作
写在最前
这里的代码,是在jupyter下运行的。如果需要用于pycharm等运行,只需要将输出行换掉(以第一份代码为例)。
常见的函数
torch.arange(n) :形成一个从 0 0 0到 n − 1 n-1 n−1的一维张量(向量)。
import torch
x = torch.arange (12)
x
# pycharm下运行
print(x)
x.reshape(m,n) :形成一个 m × n m\times n m×n的二维张量(矩阵)
y = x.reshape(3,4)
# y被重塑为3行4列的矩阵
y
torch.randn(m,n):形成一个 m × n m\times n m×n的二维随机张量(矩阵,以概率1的正态分布)
torch.ones(m,n):形成一个 m × n m\times n m×n的二维张量(矩阵,全1)
torch.zeros(m,n):形成一个 m × n m\times n m×n的二维张量(矩阵,全0)
# zeros, ones 可以设置成
z = torch.randn(3, 4)
x = torch.randn(3, 4)
c = torch.randn(3, 4)
z, x, c
运算符
这里的运算符,都是指按元素操作!(这点与julia、matlab都很大不同;一定谨记,很多个bug都是会出现在这里)
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2, 4, 8])
y = torch.tensor([2, 2, 2, 2])
x + y, x - y, x * y, x / y,
x ** y# **运算符是求幂运算
如果a与b的size不同,则以某种方式将a或b进行复制,使得复制后的a和b的size相同,然后再将a和b做element-wise的乘法[1]。
张量的连结:将两个张量连结在一起。要注意:要连结的端是行时,参数给为dim = 0;要连结的端时列,参数给为dim = 1。
X = torch.arange(12, dtype=torch.float32).reshape((3,4))
Y = torch.tensor([[2.0, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]])
torch.cat((X, Y), dim=0), torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1)
线代运算
torch.dot(x,y):点积。点积出现在两个向量之间。注意:维度必须相同。
x = torch.arange(4, dtype = torch.float32)
y = torch.ones(4, dtype = torch.float32)
# dtype参数是指定类型
x, y, torch.dot(x, y)
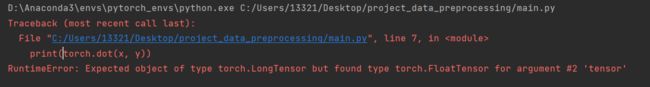
如果没有指定dtype,则会报错。并不会强制类型转换。
x = torch.arange(4)
y = torch.ones(4, dtype = torch.float32)
# dtype参数是指定类型
x, y, torch.dot(x, y)
如果维度错误,则会报错inconsistent tensor size。
torch.mv(A, x) :矩阵向量乘法(matrix-vector)。出现在矩阵-向量之间。保证A的列数与x的维度相等。
x = torch.randn(3,4)
y = torch.ones(4, dtype = torch.float32)
# dtype参数是指定类型
x, y, torch.mv(x, y)
torch.mm(A, B) :矩阵矩阵乘法(matrix-matrix)。出现在矩阵-矩阵之间。保证A的列数与B的维度相等。
x = torch.randn(3,4)
y = torch.randn(4,3)
torch.mm(x, y)
# pycharm下
print(torch.mm(x, y))
范数
范数定义:
∥ x ∥ p = ( ∣ x 1 ∣ p + ∣ x 2 ∣ p + ⋯ + ∣ x n ∣ p ) 1 p \|x\|_{p}=\left(\left|x_{1}\right|^{p}+\left|x_{2}\right|^{p}+\cdots+\left|x_{n}\right|^{p}\right)^{\frac{1}{p}} ∥x∥p=(∣x1∣p+∣x2∣p+⋯+∣xn∣p)p1
torch.norm(input, p='fro', dim=None, keepdim=False, out=None, dtype=None)
参数如下:
input:输入tensorp (int, float, inf, -inf, 'fro', 'nuc', optional):范数计算中的幂指数值。默认为’fro’dim (int,2-tuple,2-list, optional): 指定计算的维度。如果是一个整数值,向量范数将被计算;如果是一个大小为2的元组,矩阵范数将被计算;如果为None,当输入tensor只有两维时矩阵计算矩阵范数;当输入只有一维时则计算向量范数。如果输入tensor超过2维,向量范数将被应用在最后一维keepdim(bool,optional)指明输出tensor的维度dim是否保留。如果dim=None或out=None,则忽略该参数。默认值为False,不保留out(Tensor, optional):tensor的输出。如果dim=None或out=None,则忽略该参数。dtype(torch.dtype,optional):指定返回tensor的期望数据类型。如果指定了该参数,在执行该操作时输入tensor将被转换成 :attr:’dtype’
x = torch.arange(12) # tensor(0,1,...,11)
torch.norm(x) # 默认为2——L2范数
torch.norm(x,1) # 默认为2——L2范数
torch.norm(x,inf) # 默认为2——L2范数
'''
#输出
tensor(22.4944)
tensor(66.)
tensor(11.)
'''
参考文献
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/da_kao_la/article/details/87484403
[2] https://zh.d2l.ai/chapter_preliminaries/linear-algebra.html#sec-linear-algebra