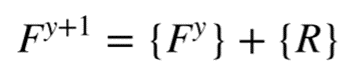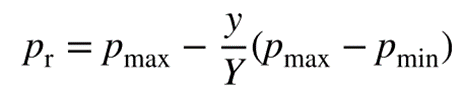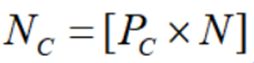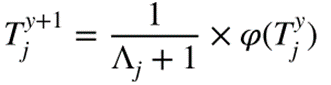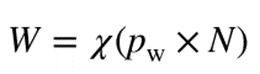智能优化算法之季节优化算法(SOA),原理公式详解,附matlab代码
季节优化算法(Seasons optimization algorithm,SOA)是一种新的随机仿生优化算法,该算法的灵感来自于树木在一年中不同季节的生长周期。该成果于2020年发表在知名SCI期刊Engineering with Computers上。目前谷歌学术上查询被引13次。
SOA算法通过更新、竞争、播种和移除四个主要操作对森林中的树木进行更新,最后选取最强树作为最优解。
算法原理
(1)树木更新阶段
算法首先创建一个随机分布的森林F,定义为F=[T1,T2,...,Tn],更新算子用于模拟树木在春季的行为,该更新算子的数学模型如下式表示:
其中Fy为第y次迭代时的森林,R为新生成的幼苗集合,如下所示:
其中Pr表示更新速率,Ay表示去年秋天落在土地上的种子数。函数Φ在森林的不同区域随机生成Pr×Ay新幼苗。Φ模拟了几种种子的自然发芽并长成幼苗的过程。在自然界中,只有少数种子有机会成长为一棵树,Pr的数学模型如下式表示:
其中Y为最大迭代次数,y为当前迭代次数。经实证检验,Pmin和Pmax分别设为0.4和0.6。
(2)树木竞争阶段
竞争阶段模拟了夏季对树木生长的影响。首先,树木按照其强度递减的顺序进行排序。然后选择最强树的Nc,形成核心树列表Γ=[T1, T2,…,TNc]。Nc的数学模型如下式表示:
其中PC是一个随机数,它识别出要作为核心树的树的分数,然后从相邻树中随机选取Zi树,形成核心树Ti∈Γ的邻域区。在每个邻域i内,为了数学模拟竞争对一棵树Tj的影响,提出如下方程:
其中Tjy为树Tj在迭代y中的位置。Λj为度量拥挤度或竞争指数,计算相邻树对树Tj的影响。
(3)树木播种阶段
为了模拟树木在秋季播种过程的行为,首先随机选取几棵树形成播种列表Υ={T1, T2,…,TA}。这些树就有机会在森林里传播它们的种子。种子数(A)的数学模型如下式表示:
其中Ps为随机数,表示播种速率。函数 从森林中选择Ps×N最强的树。
(4)树木移除阶段
为模拟冬季对树木的影响,该操作符从森林中移除弱树。强度最小的树被认为是弱树,移除工作对森林的影响模型如下:
其中W是将从森林中移除的弱树集合,W的数学模型如下式表示:
其中函数x(.)从森林中去除Pw×N棵树,Pw为抗性率,其数学模型如下式表示:
其中x为负值,表示树木可能受损和倒塌的临界温度。实际上,x的取值范围为[−100,0),但为了保持一致性,它的值被映射为[−1,0)。
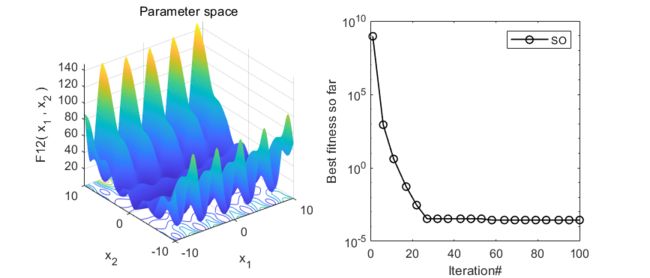
结果展示
以为CEC2005函数集为例,进行结果展示:
MATLAB核心代码
% 季节优化算法(POA)
clear all;
clc;
%% Problem Statement
func_name = 'F12';
ProblemParams.CostFuncName = func_name;
[lowerbound, upperbound, dimension,fobj]=fun_info(ProblemParams.CostFuncName);
ProblemParams.CostFuncName=fobj;
ProblemParams.lb=lowerbound;
ProblemParams.ub=upperbound;
ProblemParams.NPar = dimension;
ProblemParams.VarMin =ProblemParams.lb;
ProblemParams.VarMax = ProblemParams.ub;
if numel(ProblemParams.VarMin)==1
ProblemParams.VarMin=repmat(ProblemParams.VarMin,1,ProblemParams.NPar);
ProblemParams.VarMax=repmat(ProblemParams.VarMax,1,ProblemParams.NPar);
end
ProblemParams.SearchSpaceSize = ProblemParams.VarMax - ProblemParams.VarMin;
AlgorithmParams.NumOfTrees = 8;
AlgorithmParams.NumOfYears = 100;
AlgorithmParams.Pmin = 0.1;
AlgorithmParams.Pmax = 0.8;
%% Main Loop
for year= 1:AlgorithmParams.NumOfYears
p=AlgorithmParams.Pmax-(year/AlgorithmParams.NumOfYears)*(AlgorithmParams.Pmax-AlgorithmParams.Pmin); %pr, ps and pw are in the range [0.4, 0.6]
AlgorithmParams.RenewRate=p;
AlgorithmParams.SeedingRate=p;
AlgorithmParams.ColdThreshold=p;
AlgorithmParams.CompetitionRate = p;
%% Spring Season
if (year==1)
InitialTrees = CreateForest(AlgorithmParams, ProblemParams);
Forest=InitialTrees;
InitialCost = feval(ProblemParams.CostFuncName,InitialTrees');
Forest(:,end+1) = InitialCost';
else
Forest = Renew(Forest, Seeds, AlgorithmParams, ProblemParams);
end
%% Summer Season (Growth & Competition)
[Forest] = Competition (Forest, AlgorithmParams, ProblemParams, year);
%% Autumn Season
Seeds = Seeding(Forest,AlgorithmParams, ProblemParams);
s=size(Seeds,1);
AlgorithmParams.s=s;
%% Winter Season
Forest = Resistance(Forest,AlgorithmParams, ProblemParams);
Costs = Forest(:,end);
MinimumCost(year) = min(Costs);
fprintf('Minimum Cost in Iteration %d is %3.16f \n', year,MinimumCost(year));
end参考文献
[1] Emami H. Seasons optimization algorithm[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2022, 38(2): 1845-1865.
完整代码获取方式:后台回复关键字:TGDM827