C++ 使用jsoncpp解析json文件
今天复习一下jsoncpp解析库的用法
文章目录
-
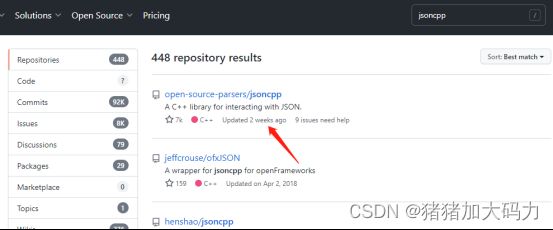
- 1.Github搜jsoncpp下载工程源码
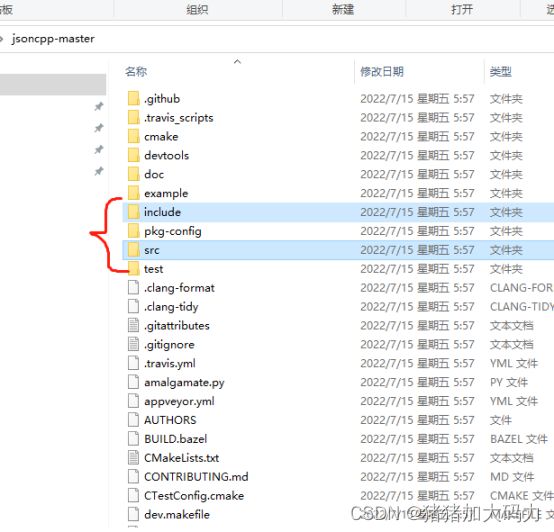
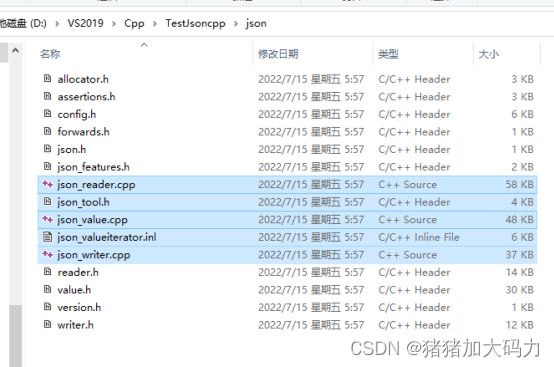
- 2.解压得到需要使用的两个目录include和src
- 3. 创建新测试工程:
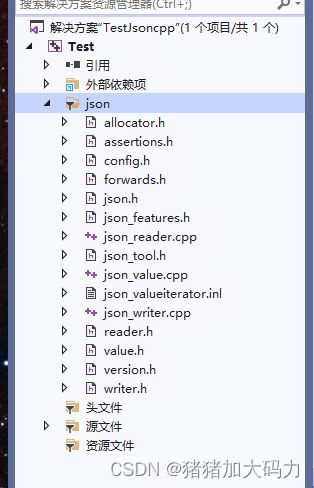
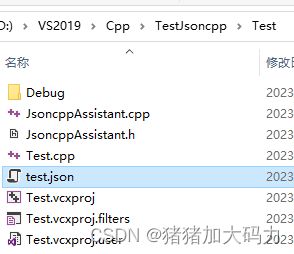
- 4.解决方案目录下创建新目录json,存储上文拿到的json文件:
- 5.测试工程添加筛选器,并且添加进去得到的jsoncpp文件:
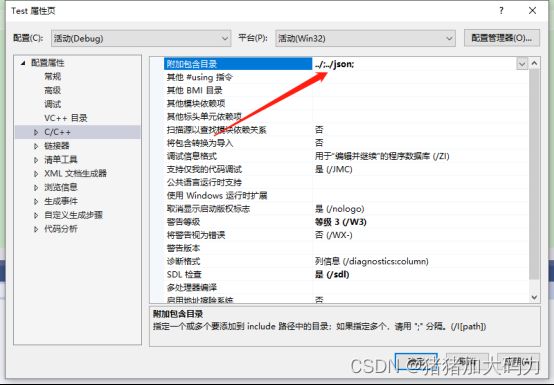
- 6.工程属性,附加包含两个目录:
- 7.添加解析类 JsoncppAssistant
- 8.测试看看:
-
- 8.1写文件
- 8.2读文件:
1.Github搜jsoncpp下载工程源码
2.解压得到需要使用的两个目录include和src
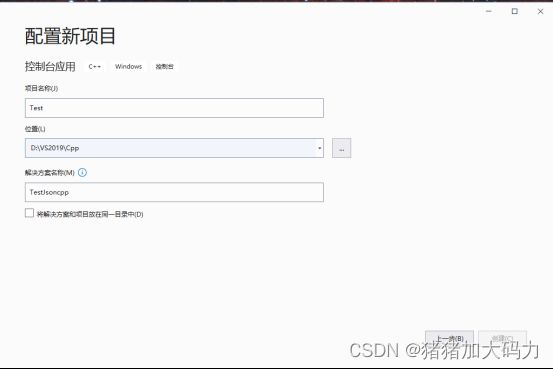
3. 创建新测试工程:
4.解决方案目录下创建新目录json,存储上文拿到的json文件:
5.测试工程添加筛选器,并且添加进去得到的jsoncpp文件:
6.工程属性,附加包含两个目录:
7.添加解析类 JsoncppAssistant
#pragma once
#include "json.h"
#include #include "JsoncppAssistant.h"
#include 8.测试看看:
8.1写文件
void Write()
{
vector<Student> arr;
Student aaa;
aaa.name = "aaa";
aaa.arr.push_back(Score("c", 60.5));
aaa.arr.push_back(Score("cpp", 88.5));
aaa.arr.push_back(Score("python", 99.5));
arr.push_back(aaa);
Student bbb;
bbb.name = "bbb";
bbb.arr.push_back(Score("c", 77.5));
bbb.arr.push_back(Score("cpp", 67));
bbb.arr.push_back(Score("python", 95));
arr.push_back(bbb);
Student ccc;
ccc.name = "ccc";
ccc.arr.push_back(Score("c", 85));
ccc.arr.push_back(Score("cpp", 76.5));
ccc.arr.push_back(Score("python", 69.5));
arr.push_back(ccc);
GetJscppMgr()->Write(arr);
}
8.2读文件:
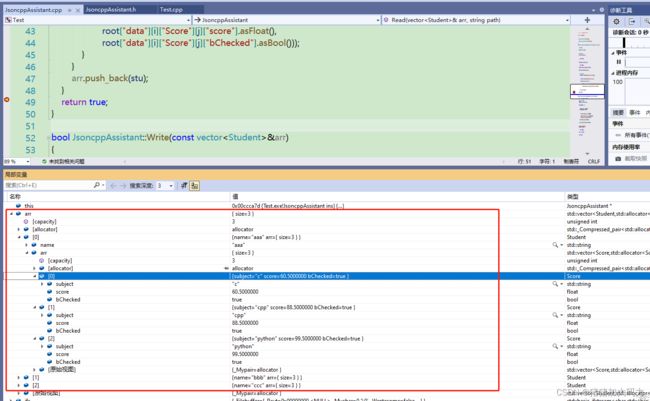
bool JsoncppAssistant::Read(vector<Student>& arr, string path)
{
arr.clear();
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("test.json");
if (!ifs.is_open())
{
return false;
}
if (!reader.parse(ifs, root))
{
return false;
}
if (root["data"].isNull()) return false;
int nSize = root["data"].size();
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; i++)
{
Student stu;
stu.name = root["data"][i]["name"].asString();
if (!root["data"][i]["Score"].isNull())
{
int nSz2 = root["data"][i]["Score"].size();
stu.arr.reserve(nSz2);
for (int j = 0; j < nSz2; j++)
{
stu.arr.push_back(Score(root["data"][i]["Score"][j]["subject"].asString(),
root["data"][i]["Score"][j]["score"].asFloat(),
root["data"][i]["Score"][j]["bChecked"].asBool()));
}
}
arr.push_back(stu);
}
return true;
}