基于Netty的WebSocket即时通信系统
一、Netty简介
1.1 什么是Netty
Netty 是一个基于NIO(Nonblocking I/O,非阻塞IO)的客户、服务器端的Java网络编程框架;提供异步的、事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具,用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序。它的健壮性、功能、性能、可定制性和可扩展性在同类框架中都是首屈一指的。
通过对Netty的分析,我们将它的优点总结如下:
-
- API使用简单,开发门槛低;
- 功能强大,预置了多种编解码功能,支持多种主流协议;
- 定制能力强,可以通过ChannelHandler对通信框架进行灵活地扩展;
- 性能高,通过与其他业界主流的NIO框架对比,Netty的综合性能最优;
- 成熟、稳定,Netty修复了已经发现的所有JDK NIO的Bug, 业务开发者无需再为JAVA NIO的Bug而烦恼;
- 社区活跃,版本迭代周期短,发现的Bug可以被及时修复,同时,还有更多的新功能会加入;
- 经历了大规模的商业应用考验,它已经得到成百上千的商用项目验证;
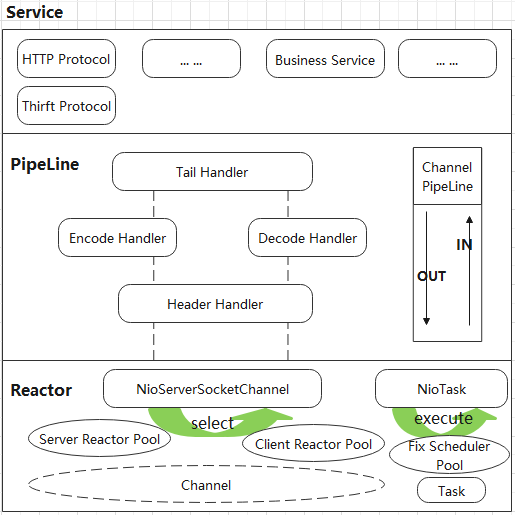
1.2 Netty的逻辑架构
Netty采用经典的三层网络架构进行设计和开发。从上往下依次是业务逻辑编排层、职责链、通信调度层。
1.2.1 Reactor通信调度层
该层的主要职责就是监听网络的读写和连接操作,负责将网络层的数据读取到内存缓冲区中,然后触发各种网络事件,例如连接创建、连接激活、读事件、写事件等,将这些事件触发到PipeLine中,由PipeLine管理的职责链来进行后续的处理。
1.2.2 ChannelPipeLine职责链
该层负责事件在职责链中的有序传播,同时负责动态地编排职责链。职责链可以选择监听和处理自己关系的事件,它可以拦截处理和向后/向前传播事件。不同应用的Handler节点的功能也不同,通常情况下,往往会开发编解码Handler用于消息的编解码,它可以将外部的协议消息转换成内部的POJO对象,这样上层业务只需要关心处理业务逻辑即可,不需要感知底层的协议差异和线程模型差异,实现了架构层面的分层隔离。
1.2.3 Service ChannelHandler业务逻辑编排层
ChannelHandler通常有两类:一类是应用的协议插件,还有一类是纯粹的业务逻辑编排。
架构的不同层面,需要关系和处理的对象都不同,通常情况下,对于业务开发者,只需要关心职责链的拦截和业务的Handler的编排;各种应用协议以插件的形式提供,应用层协议插件往往是开发一次,到处运行,只有协议开发人员需要关注协议插件。这种分层的架构设计理念实现了NIO框架各层之间的解耦,便于上层业务协议栈的开发和业务逻辑的定制。
1.2.4 请求的基本流程
- Channel: 表示一个连接,可以理解为每一个请求,就是一个Channel;
- ChannelHandler: 业务处理器;
- ChannelHandlerContext: 传输业务数据;
- ChannelPipeline: 所有ChannelHandler都会注册到ChannelPipeline中,并按顺序组织起来;
1.3 可以做什么
Netty作为网络通信框架,能通过编程自定义各种协议。Netty内置了多种协议,如HTTP协议,Redis协议,MQTT协议等,我们可以依此来实现自己的HTTP服务器,Redis服务器等。
典型的应用有:阿里分布式服务框架 Dubbo 的 RPC 框架使用Dubbo协议进行节点间通信,Dubbo 协议默认使用 Netty作为基础通信组件。除了 Dubbo 之外,淘宝的消息中间件 RocketMQ 的消息生产者和消息消费者之间,也采用 Netty 进行高性能、异步通信。
二、整合SpringBoot
Spring框架是一个开放源代码的J2EE应用程序框架,由Rod Johnson发起,是针对bean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器(lightweight container),提供了功能强大IOC、AOP及Web MVC等功能。Spring Boot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。将Netty与SpringBoot进行整合的目标:
- 使用SpringBoot管理Netty Server的生命周期;
- Netty Server以及ChannelHandler能使用IOC中的Bean实例;
- Netty Server以及ChannelHandler可以读取全局配置;
2.1 添加依赖
pom.xml
io.netty
netty-all
4.1.20.Final
2.2 通过yml配置基本的属性
2.2.1. application.yml
netty:
# Websocket服务端口
port: 9600
# URI路径
websocket-path: /ws
# boss线程数
boss-thread: 10
# worker线程数
worker-thread: 100
# 当服务器请求处理线程全满时,用于临时存放已完成三次握手的请求的队列的最大长度
backlog: 1002.2.2. NettyConfig配置类
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "netty")
@Data
public class NettyConfig {
int port;
int bossThread;
int workerThread;
boolean keepalive;
int backlog;
String websocketPath;
}boss线程池处理accept事件,不管线程池多大,通常情况下只会使用一个线程,既然只使用一个线程为什么要用线程池呢?主要是异常的情况下,线程挂了,可以再创建一个新线程;当ServerBootstrap bind多个端口时,每个端口都有一个线程eventloop accept事件,此时boss线程池里的多个线程都会被用到。
2.3 编写Netty Server
2.3.1. NettyServer
@Component
public class NettyServer {
@Autowired
NettyConfig nettyConfig;
@Autowired
NettyWebSocketChannelInitializer nettyWebSocketChannelInitializer;
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup;
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup;
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
log.info(NettyServer.class + " 启动正在监听:" + nettyConfig.getPort());
ServerBootstrap sb = new ServerBootstrap();
sb.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, nettyConfig.getBacklog());
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(nettyConfig.getBossThread());
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(nettyConfig.getWorkerThread());
sb.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.localAddress(nettyConfig.getPort())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler())
.childHandler(nettyWebSocketChannelInitializer);
ChannelFuture sync = sb.bind().sync();
}
}上面这段代码展示了服务端的一个基本步骤:
- 初始化ServerBootstrap实例, 此实例是Netty服务端应用开发的入口;
- 初始化用于Acceptor的主"线程池"以及用于I/O工作的从"线程池";
- 设置ServerBootstrap实例的主从“线程池”;
- 设置服务端监听的端口;
- 指定通道Channel的类型,由于是服务端,使用NioServerSocketChannel;
- 设置ServerSocketChannel的处理器,监听Channel的各种动作以及状态的改变,包括连接、绑定、接收消息等。
- 设置子通道也就是SocketChannel的处理器, 其内部是实际业务开发的"主战场";
- 绑定并侦听某个端口
handler在初始化时就会执行,而childHandler会在客户端成功connect后才执行;通过handler添加的handlers是对bossGroup线程组起作用,通过childHandler添加的handlers是对workerGroup线程组起作用。
2.3.2 NettyWebSocketChannelInitializer
ChannelInitializer自身也是一个ChannelHandler, 一开始会被注册到ChannelPipeline里,但是在初始化(initChannel)完成后,ChannelInitializer会将自己从pipeline中移除。
@Component
public class NettyWebSocketChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer {
@Autowired
NettyConfig nettyConfig;
@Autowired
TextMessageHandler textMessageHandler;
@Autowired
PongFrameHandler pongFrameHandler;
@Autowired
InnerEventHandler eventHandler;
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(5, -1, -1));
pipeline.addLast(new HandshakeHandler(nettyConfig.getWebsocketPath()));
pipeline.addLast(pongFrameHandler);
pipeline.addLast(textMessageHandler);
pipeline.addLast(eventHandler);
}
} - HttpServerCodec: 内置的ChannelHandler,集成了HttpRequest解码器以及HttpResponse编码器。
- HttpObjectAggregator: 内置的ChannelHandler, 将HttpMessage和HttpContent集合成FullHttpRequest。
- ChunkedWriteHandler: 内置的ChannelHandler, 实现大数据包的传输。
- IdleStateHandler: 内置的ChannelHandler, 读、写空闲处理器,空闲超时会触发一个IdleStateEvent事件。我们可以通过接受IdleStateEvent事件后会发送PING消息,实现Websocket服务的PING/PONG机制。
- HandshakeHandler: 自定义的ChannelHandler, 接受一个FullHttpRequest对象,处理连接的认证,完成连接的升级以及注册websocket的编码/解码器。Netty有内置的Websocket协议处理器WebSocketServerProtocolHandler,但是没有暴露连接认证的接口;当然我们可以使用WebSocketServerProtocolHandler,再写一个接受FullHttpRequest对象的ChannelHandler来进行连接的认证。
- PongFrameHandler: 自定义的ChannelHandler, 接受TextWebSocketFrame对象,处理客户端的PONG消息。
- TextMessageHandler: 自定义的ChannelHandler, 接受TextWebSocketFrame对象,处理其他文本事件。
- InnerEventHandler: 自定义ChannelHandler, 处理内置的事件,如:channelInactive,IdleStateEvent。
2.3.3 启动类中启动
public class WebsocketApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
try {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(WebsocketApplication.class, args);
NettyServer nettyServer = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(NettyServer.class);
nettyServer.start();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}2.4 Netty中Websocket协议解析
2.3.2中提到我们在HandshakeHandler这个ChannelHandler里会完成连接的升级以及注册websocket的编码/解码器,下面我们来看看具体实现的关键代码。
2.4.1 HandshakeHandler
public class HandshakeHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler{
public HandshakeHandler(String websocketPath) {
this.websocketPath = websocketPath;
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
//连接路由校验
if (isNotWebSocketPath(request)) {
MessageHelper.sendHttpResponse(ctx, request, new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND));
return;
}
// 自动检测正在使用的Web套接字协议的版本 目前是13
WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory wsFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory(getWebSocketLocation(ctx.pipeline(), request, websocketPath), null, false);
//连接认证
...
// server side web socket opening and closing handshakes
WebSocketServerHandshaker handshake = wsFactory.newHandshaker(request);
if (handshake == null) {
WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory
.sendUnsupportedVersionResponse(ctx.channel());
} else {
ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(channelBiz);
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new DefaultHttpHeaders();
responseHeaders.add(SUB_PROTOCOL_KEY, subProtocol);
//进行的逻辑
handshake.handshake(ctx.channel(), request, responseHeaders, ctx.channel().newPromise());
}
}
} 2.4.2 WebSocketServerHandshaker
public abstract class WebSocketServerHandshaker {
// 开始握手
public final ChannelFuture handshake(Channel channel, FullHttpRequest req, HttpHeaders responseHeaders, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
// 创建响应 见2.4.3
FullHttpResponse response = newHandshakeResponse(req, responseHeaders);
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
// 将HttpObjectAggregator,HttpContentCompressor移除。连接建立后就不需要这些处理器了
if (p.get(HttpObjectAggregator.class) != null) {
p.remove(HttpObjectAggregator.class);
}
if (p.get(HttpContentCompressor.class) != null) {
p.remove(HttpContentCompressor.class);
}
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = p.context(HttpRequestDecoder.class);
final String encoderName;
if (ctx == null) {//如果没有HttpRequestDecoder就进入这步
// this means the user use a HttpServerCodec
ctx = p.context(HttpServerCodec.class);
if (ctx == null) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("No HttpDecoder and no HttpServerCodec in the pipeline"));
return promise;
}
//将wsdecoder,wsencoder加到HttpServerCodec前
p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsdecoder", newWebsocketDecoder());
p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsencoder", newWebSocketEncoder());
encoderName = ctx.name();
} else {
...
}
channel.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
ChannelPipeline p = future.channel().pipeline();
// 连接升级后 将HttpServerCodec从channelpipeline里删除
p.remove(encoderName);
promise.setSuccess();
} else {
promise.setFailure(future.cause());
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}2.4.3 WebSocketServerHandshaker13
public class WebSocketServerHandshaker13 extends WebSocketServerHandshaker {
@Override
protected FullHttpResponse newHandshakeResponse(FullHttpRequest req, HttpHeaders headers) {
FullHttpResponse res = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS);
...
// 添加响应头,前端收到这些响应头后会将连接升级为web socket
res.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.UPGRADE, HttpHeaderValues.WEBSOCKET);
res.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaderValues.UPGRADE);
res.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.SEC_WEBSOCKET_ACCEPT, accept);
...
return res;
}
}2.5 自定义事件处理器
在实际业务场景中,肯定会有很多业务逻辑,而所有的业务逻辑都写在一个ChannelHandler会不好维护,而不同的业务逻辑写不同的ChannelHandler又会造成ChannelHandler的类过于庞大,ChannelInitializer里的初始方法会很长。我们可以通过JAVA的反射,在一个ChannelHandler里将任务分发到其他类中。
2.5.1 模块
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
public @interface EventModule {
String appId();
}2.5.2 事件处理器
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Documented
public @interface EventHandler {
String event();
int order() default Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}2.5.3 使用注解
@Service(value = "basicEventService")
@EventModule(appId = "module.basic.app-id")
@Slf4j
public class EventServiceImpl implements IEventService {
/**
* 用户状态变更
*/
@EventHandler(event = "uup", order = 1)
public void updateUserProperty(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, UProperty[] uPropertyArr) {
// TODO
}
}2.5.4 储存/分类
@Component
public class EventHandlerMapping implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static final Map> EVENT_HANDLERS = new HashMap<>();
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
Map beans = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(EventModule.class);
for(Object bean : beans.values()){
Method[] methods = bean.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : methods) {
EventHandler eventHandler = declaredMethod.getAnnotation(EventHandler.class);
if (null == eventHandler) {
continue;
}
String event = eventHandler.event();
List stored = EVENT_HANDLERS.getOrDefault(event, new ArrayList<>());
stored.add(new MethodHandler(bean, declaredMethod, eventHandler.order()));
EVENT_HANDLERS.putIfAbsent(event, stored);
}
}
for (Map.Entry> handlers: EVENT_HANDLERS.entrySet()) {
handlers.getValue().sort((Comparator.comparingInt(MethodHandler::getOrder)));
}
}
public static List listHandlerMappings(String event) {
return EVENT_HANDLERS.get(event);
}
} 2.5.5 ChannelHandler中分发
@Component(value = "textHandler")
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
@Slf4j
public class TextMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
String text = msg.text();
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
ChannelBiz channelBiz = DataStorage.CHANNEL_BIZ.get(ctx.channel());
MessageRequest request = ... ...;
List methods = EventHandlerMapping.listHandlerMappings(request.getEvent());
... ...
try {
for (MethodHandler method: methods) {
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getMethod().getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {
method.getMethod().invoke(method.getBean(), ctx);
} else {
method.getMethod().invoke(method.getBean(), ctx, JSONArray.parseObject(request.getMessage(), parameterTypes[1]));
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
MessageHelper.p2pMessage("error", redis.addAndGetRoomVersion(channelBiz.getAppId(), channelBiz.getRoomId()), incoming, e.getMessage());
log.error("事件处理失败:{}, { }", request.getEvent(), e);
}
}
} 三、自建的新特性
3.1 消息的应答与重试
消息应答:确认客户端已收到服务端的消息,如果超过一定时间未收到客户端的应答, 服务端将会重新发送该消息。
实现原理:每个消息有一个messageId,客户端通过应答这个ID来向服务端确认已收到该消息。消息重试可通过Netty的EventLoop调度任务实现,设定一段时间后去检查某个messageId是否已应答,若未应答则重发这条消息,发送时需保持messageId不变。
1. 发送消息后,向缓存里保存一份,同时添加一个定时任务。
private void writeAndFlush(Channel channel, ChannelBiz channelBiz, MessageResponse messageResponse) {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame(JSONObject.toJSONString(messageResponse)));
redis.addPendingMessage(channelBiz, messageResponse);
channel.eventLoop().schedule(new RetryMessageTask(channelBiz, messageResponse.getVersion(), redis, this), RETRY_PERIOD, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}2. 当服务器收到客户端的ack请求后,会将缓存保存的消息删除。
/**
* 消息应答
* @param ctx
* @param property
*/
@EventHandler(event = "ack")
public void ack(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Property[] property) {
ChannelBiz channelBiz = DataStorage.CHANNEL_BIZ.get(ctx.channel());
List versionList;
try {
versionList = Arrays.stream(property).map(Property::getMessageId).collect(Collectors.toList());
} catch (Throwable e) {
versionList = null;
}
// 进行消息应答
redis.ackPendingMessage(channelBiz, versionList);
} 3. 当设置的时间到后,会执行RetryMessageTask里的run方法,在该方法中会先取缓存中的消息,如果没取到说明该消息已过期或者已被应答,不做后续处理;如果消息还在缓存中,则说明该消息还未被应答,就会重新发送这条消息。
@Override
public void run() {
try {
PendingMessage pendingMessage = redis.getPendingMessage(channelBiz, version);
if (null == pendingMessage) {
return;
}
Channel channel = DataStorage.USER_CHANNEL.get(channelBiz.getUserUniqKey());
if (null != channel) {
messageSender.sendToChannel(channel, channelBiz, pendingMessage.getMessage());
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("执行重推任务失败error: { }", e);
}
}3.2 扩展Socket.io
Socket.IO将WebSocket和轮询(Polling)机制以及其它的实时通信方式封装成了通用的接口,并且在服务端实现了这些实时机制的相应代码。也就是说,WebSocket仅仅是Socket.IO实现实时通信的一个子集。Socket.IO简化了WebSocket API,统一了返回传输的API。参考地址:https://github.com/mrniko/netty-socketio。
3.2.1 使用Netty创建socketio服务端
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SocketioServer {
@Autowired
NettyConfig nettyConfig;
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup;
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup;
@Autowired
SocketioAuthorizationListener authorizationListener;
@Autowired
SocketioConnectListener connectListener;
@Autowired
SocketioDisconnectListener disconnectListener;
SocketIOServer server;
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.setAllowCustomRequests(true);
config.setHostname(nettyConfig.getHostname());
config.setPort(nettyConfig.getPort());
config.setContext(nettyConfig.getWebsocketPath());
config.setBossThreads(nettyConfig.getBossThread());
config.setWorkerThreads(nettyConfig.getWorkerThread());
config.setPingInterval(5000);
config.setPingTimeout(30000);
config.setAuthorizationListener(authorizationListener);
server = new SocketIOServer(config);
server.addConnectListener(connectListener);
server.addDisconnectListener(disconnectListener);
List eventServiceList = EventHandlerMapping.getEventServices();
for (IEventService service: eventServiceList) {
service.setServer(server);
}
Map> eventMappings = EventHandlerMapping.listHandlerMappings();
for (Map.Entry> eventEntry: eventMappings.entrySet()) {
server.addEventListener(eventEntry.getKey(), Object.class, new DataListener 与ServerBootstrap的配置相似,SocketIOServer也需要设置主从“线程池”、服务端口、路由;除此之外,SocketIOServer已经实现了PING/PONG机制、消息应答,还对外暴露了AuthorizationListener接口,方便业务上自定义的连接认证。
四、状态位管理
4.1 版本号
@Data
public class Property {
public Property() {
}
public Property(Object value, Integer version) {
this.value = value;
this.version = version;
}
String key;
Object value;
Integer version;
}- Key: 属性名
- Value: 属性值,可以为任意类型
- Version: 版本号
这里的版本号是由服务端生成传给客户端的,一个房间使用一个值。是客户端判断这个消息是否有效的依据。举个例子:服务端依次向客户端发送消息A、B(同一属性的变更消息),由于网络原因,客户端只收到了消息B, 我们的应答机制发现客户端没有应答消息A,于是又重新发送了消息A,客户端收到消息A后发现A的版本号比当前要小,于是就放弃了消息A。
参考资料:https://www.jianshu.com/nb/7981390
转载自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j1TWqeva4z97HngbAFKeyA