(六)什么是Vite——热更新时vite、webpack做了什么
vite分享ppt,感兴趣的可以下载:
Vite分享、原理介绍ppt
什么是vite系列目录:
(一)什么是Vite——vite介绍与使用-CSDN博客
(二)什么是Vite——Vite 和 Webpack 区别(冷启动)-CSDN博客
(三)什么是Vite——Vite 主体流程(运行npm run dev后发生了什么?)-CSDN博客
(四)什么是Vite——冷启动时vite做了什么(源码、middlewares)-CSDN博客
(五)什么是Vite——冷启动时vite做了什么(依赖、预构建)-CSDN博客
(六)什么是Vite——热更新时vite、webpack做了什么-CSDN博客
(七)什么是Vite——vite优劣势、命令-CSDN博客
热更新时 webpack 做了什么:
打包工具实现热更新的思路都大同小异:主要是通过WebSocket,创建浏览器和服务器的通信,监听文件的改变,当文件被修改时,服务端发送消息通知客户端修改相应的代码,客户端对应不同的文件进行不同的操作的更新。
webpack的热更新就是,当我们对代码做修改并保存后,webpack会对修改的代码块进行重新打包,并将新的模块发送至浏览器端,浏览器用新的模块代替旧的模块,从而实现了在不刷新浏览器的前提下更新页面。相比起直接刷新页面的方案,HMR的优点是可以保存应用的状态。当然,随着项目体积的增长,热更新的速度也会随之下降。
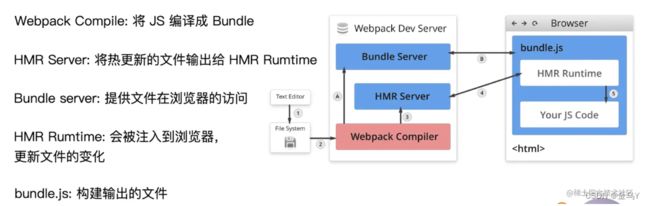
其中,使用webpack冷启动项目的流程是1 -> 2 -> A -> B,热更新的流程是1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5。热更新的大致流程如下:
- 编辑文件并保存后,webpack就会调用Webpack-complier对文件进行编译;
- 编译完后传输给HMR Server,HMR得知某个模块发生变化后,就会通知HMR Runtime;
- HMR Runtime就会加载要更新的模块,从而让浏览器实现更新并不刷新的效果。
热更新时 vite 做了什么:
Webpack: 重新编译,请求变更后模块的代码,客户端重新加载。
Vite: 请求变更的模块,再重新加载。
Vite 通过 chokidar 来监听文件系统的变更,只用对发生变更的模块重新加载, 只需要精确的使相关模块与其临近的 HMR边界连接失效即可,这样HMR 更新速度就不会因为应用体积的增加而变慢而 Webpack 还要经历一次打包构建。所以 HMR 场景下,Vite 表现也要好于 Webpack。
Vite的HMR在构建过程中有以下优势:
Vite的HMR使得前端开发者在开发阶段能够更加高效地进行模块修改,快速查看结果并保持应用程序的状态,极大地提升了开发体验和开发效率。
Vite中主要依赖以下几个步骤来实现HMR的功能:Vite介绍和原理解析
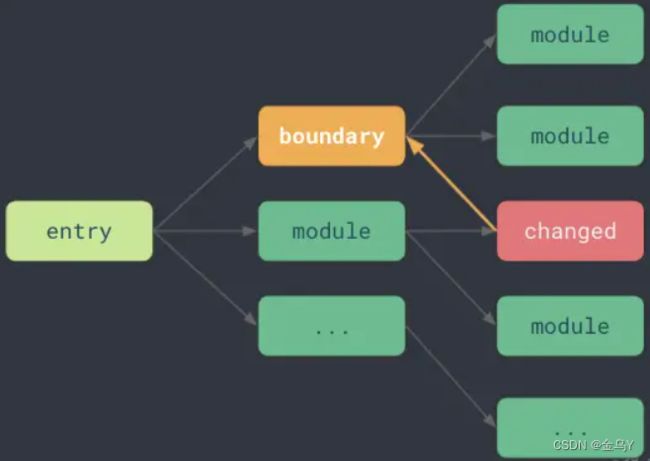
1、在重写模块地址的时候,记录模块依赖链 importMaps 。这样在后续更新的时候,可以知道哪些文件需要被热更新。
代码中可以使用 import.meta.hot 接口来标记"HMR Boundary"。
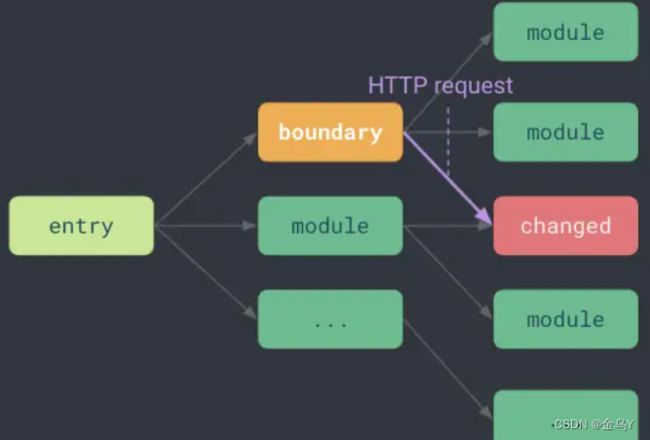
2、接着,当文件更新的时候,会沿着之前记录下 模块依赖链 imoprtMaps 链式结构找到对应的"HMR Boundary", 再从此处重新加载对应更新的模块。
3、如果没有遇到对应的boundary, 则整个应用重新刷新。
热更新的实现:
热更新主要与项目编写的源码有关。前面提到,对于源码,vite使用原生esm方式去处理,在浏览器请求源码文件时,对文件进行处理后返回转换后的源码。vite对于热更新的实现,大致可以分为以下步骤:
- 服务端基于 watcher 监听文件改动,根据类型判断更新方式,并编译资源
- 客户端通过 WebSocket 监听到一些更新的消息类型
- 客户端收到资源信息,根据消息类型执行热更新逻辑
1、创建一个websocket服务端: HMR机制的实践与原理
vite执行 createWebSocketServer 函数,创建webSocket服务端,并监听 change 等事件。
const { createServer } = await import('./server');
const server = await createServer({
root,
base: options.base,
mode: options.mode,
configFile: options.config,
logLevel: options.logLevel,
clearScreen: options.clearScreen,
optimizeDeps: { force: options.force },
server: cleanOptions(options),
})
...
const ws = createWebSocketServer(httpServer, config, httpsOptions)
...
const watcher = chokidar.watch(
// config file dependencies might be outside of root
[path.resolve(root), ...config.configFileDependencies],
resolvedWatchOptions,
)
watcher.on('change', async (file) => {
file = normalizePath(file)
...
// 热更新调用
await onHMRUpdate(file, false)
})
watcher.on('add', onFileAddUnlink)
watcher.on('unlink', onFileAddUnlink)
...
2、创建一个 client 来接收 webSocket 服务端 的信息
const clientConfig = defineConfig({
...
output: {
file: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist/client', 'client.mjs'),
sourcemap: true,
sourcemapPathTransform(relativeSourcePath) {
return path.basename(relativeSourcePath)
},
sourcemapIgnoreList() {
return true
},
},
})
vite会创建一个 client.mjs 文件,合并 UserConfig 配置,通过 transformIndexHtml 钩子函数,在转换 index.html 的时候,把生成 client 的代码注入到 index.html 中,这样在浏览器端访问 index.html 就会加载 client 生成代码,创建 client 客户端与 webSocket 服务端建立 connect 链接,以便于接受 webScoket 服务器信息。
3、服务端监听文件变化,给 client 发送 message ,通知客户端。
同时服务端调用 onHMRUpdate 函数,该函数会根据此次修改文件的类型,通知客户端是要刷新还是重新加载文件。
const onHMRUpdate = async (file: string, configOnly: boolean) => {
if (serverConfig.hmr !== false) {
try {
// 执行热更新
// 服务端调用handleHMRUpdate函数,该函数会根据此次修改文件的类型,通知客户端是要刷新还是重新加载文件。
await handleHMRUpdate(file, server, configOnly)
} catch (err) {
ws.send({
type: 'error',
err: prepareError(err),
})
}
}
}
// 创建hmr上下文
const hmrContext: HmrContext = {
file,
timestamp,
modules: mods ? [...mods] : [],
read: () => readModifiedFile(file), // 异步读取文件
server,
}
// 根据文件类型来选择本地更新还是hmr,把消息send到client
if (!hmrContext.modules.length) {
if (file.endsWith('.html')) { // html文件不能被hmr
config.logger.info(colors.green(`page reload `) + colors.dim(shortFile), {
clear: true,
timestamp: true,
})
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload', // 全量加载
path: config.server.middlewareMode
? '*'
: '/' + normalizePath(path.relative(config.root, file)),
})
} else {
...
}
return
}
// --------
// function updateModules
if (needFullReload) { // html 文件更新 // 需要全量加载
config.logger.info(colors.green(`page reload `) + colors.dim(file), {
clear: !afterInvalidation,
timestamp: true,
})
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload', // 发给客户端
})
return
}
// 不需要全量加载就是hmr
config.logger.info(
colors.green(`hmr update `) +
colors.dim([...new Set(updates.map((u) => u.path))].join(', ')),
{ clear: !afterInvalidation, timestamp: true },
)
ws.send({
type: 'update',
updates,
})
这段代码阐述的意思就是:
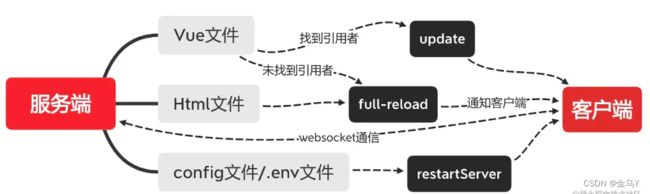
- html文件不参与热更新,只能全量加载。
- 浏览器客户端接收 'full-reload' , 表示启动本地刷新,直接刷新通过 http 请求,加载全部资源,这里做了协商缓存。(vite对于node_modules 的文件做了强缓存,而对我们编写的源码做了协商缓存。)
- 浏览器客户端接收 'update', 表示启动 hmr,浏览器只需要去按需加载对应的模块就可以了。
使用方法如下:
import foo from './foo.js'
foo()
if (import.meta.hot) {
import.meta.hot.accept('./foo.js', (newFoo) => {
newFoo.foo()
})
}下面将以具体代码进行介绍其原理。
客户端逻辑:https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/plugins/importAnalysis.ts#L399
// record for HMR import chain analysis
// make sure to normalize away base
importedUrls.add(url.replace(base, '/'))浏览器文件是几时被注入的?在 importAnalysis 插件中:
if (hasHMR && !ssr) {
debugHmr(
`${
isSelfAccepting
? `[self-accepts]`
: acceptedUrls.size
? `[accepts-deps]`
: `[detected api usage]`
} ${prettyImporter}`
)
// 在用户业务代码中注入Vite客户端代码
str().prepend(
`import { createHotContext as __vite__createHotContext } from "${clientPublicPath}";` +
`import.meta.hot = __vite__createHotContext(${JSON.stringify(
importerModule.url
)});`
)
}https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/client/client.ts#L70
case 'update':
notifyListeners('vite:beforeUpdate', payload)
// 发生错误的时候,重新加载整个页面
if (isFirstUpdate && hasErrorOverlay()) {
window.location.reload()
return
} else {
clearErrorOverlay()
isFirstUpdate = false
}
payload.updates.forEach((update) => {
if (update.type === 'js-update') {
// js更新逻辑, 会进入一个缓存队列,批量更新,从而保证更新顺序
queueUpdate(fetchUpdate(update))
} else {
// css更新逻辑, 检测到更新的时候,直接替换对应模块的链接,重新发起请求
let { path, timestamp } = update
path = path.replace(/\?.*/, '')
const el = (
[].slice.call(
document.querySelectorAll(`link`)
) as HTMLLinkElement[]
).find((e) => e.href.includes(path))
if (el) {
const newPath = `${path}${
path.includes('?') ? '&' : '?'
}t=${timestamp}`
el.href = new URL(newPath, el.href).href
}
console.log(`[vite] css hot updated: ${path}`)
}
})
break
break
服务端处理HMR模块更新逻辑: https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/server/hmr.ts#L42
export async function handleHMRUpdate(
file: string,
server: ViteDevServer
): Promise {
const { ws, config, moduleGraph } = server
const shortFile = getShortName(file, config.root)
const isConfig = file === config.configFile
const isConfigDependency = config.configFileDependencies.some(
(name) => file === path.resolve(name)
)
const isEnv = config.inlineConfig.envFile !== false && file.endsWith('.env')
if (isConfig || isConfigDependency || isEnv) {
// 如果配置文件或者环境文件发生修改时,会触发服务重启,才能让配置生效。
// auto restart server 配置&环境文件修改则自动重启服务
await restartServer(server)
return
}
// (dev only) the client itself cannot be hot updated.
if (file.startsWith(normalizedClientDir)) {
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload',
path: '*'
})
return
}
const mods = moduleGraph.getModulesByFile(file)
// check if any plugin wants to perform custom HMR handling
const timestamp = Date.now()
const hmrContext: HmrContext = {
file,
timestamp,
modules: mods ? [...mods] : [],
read: () => readModifiedFile(file),
server
}
// modules 是热更新时需要执行的各个插件
// Vite 会把模块的依赖关系组合成 moduleGraph,它的结构类似树形,热更新中判断哪些文件需要更新也会依赖 moduleGraph
for (const plugin of config.plugins) {
if (plugin.handleHotUpdate) {
const filteredModules = await plugin.handleHotUpdate(hmrContext)
if (filteredModules) {
hmrContext.modules = filteredModules
}
}
}
if (!hmrContext.modules.length) {
// html file cannot be hot updated
// html 文件更新时,将会触发页面的重新加载。
if (file.endsWith('.html')) {
[config.logger.info](http://config.logger.info/)(chalk.green(`page reload `) + chalk.dim(shortFile), {
clear: true,
timestamp: true
})
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload',
path: config.server.middlewareMode
? '*'
: '/' + normalizePath(path.relative(config.root, file))
})
} else {
// loaded but not in the module graph, probably not js
debugHmr(`[no modules matched] ${chalk.dim(shortFile)}`)
}
return
}
updateModules(shortFile, hmrContext.modules, timestamp, server)
}
// Vue 等文件更新时,都会进入 updateModules 方法,正常情况下只会触发 update,实现热更新,热替换;
function updateModules(
file: string,
modules: ModuleNode[],
timestamp: number,
{ config, ws }: ViteDevServer
) {
const updates: Update[] = []
const invalidatedModules = new Set()
let needFullReload = false
// 遍历插件数组,关联下面的片段
for (const mod of modules) {
invalidate(mod, timestamp, invalidatedModules)
if (needFullReload) {
continue
}
const boundaries = new Set<{
boundary: ModuleNode
acceptedVia: ModuleNode
}>()
// 查找引用模块,判断是否需要重载页面,找不到引用者则会发起刷新。向上传递更新,直到遇到边界
const hasDeadEnd = propagateUpdate(mod, timestamp, boundaries)
if (hasDeadEnd) {
needFullReload = true
continue
}
updates.push(
...[...boundaries].map(({ boundary, acceptedVia }) => ({
type: `${boundary.type}-update` as Update['type'],
timestamp,
path: boundary.url,
acceptedPath: acceptedVia.url
}))
)
}
if (needFullReload) {
// 重刷页面
} else {
// 向ws客户端发送更新事件, Websocket 监听模块更新, 并且做对应的处理。
ws.send({
type: 'update',
updates
})
}
}
在 createServer 的时候,通过 WebSocket 创建浏览器和服务器通信,使用 chokidar 监听文件的改变,当模块内容修改是,发送消息通知客户端,只对发生变更的模块重新加载。
export async function createServer( inlineConfig: InlineConfig = {} ): Promise {
// 生成所有配置项,包括vite.config.js、命令行参数等
const config = await resolveConfig(inlineConfig, 'serve', 'development')
// 初始化connect中间件
const middlewares = connect() as Connect.Serverconst
httpServer = middlewareMode ? null : await resolveHttpServer(serverConfig, middlewares, httpsOptions)
const ws = createWebSocketServer(httpServer, config, httpsOptions)
// 初始化文件监听
const watcher = chokidar.watch(path.resolve(root), {
ignored: ['**/node_modules/**', '**/.git/**', ...(Array.isArray(ignored) ? ignored : [ignored])],
ignoreInitial: true, ignorePermissionErrors: true, disableGlobbing: true, ...watchOptions
}) as FSWatcher
// 生成模块依赖关系,快速定位模块,进行热更新
const moduleGraph: ModuleGraph = new ModuleGraph((url, ssr) => container.resolveId(url, undefined, { ssr }))
// 监听修改文件内容
watcher.on('change', async (file) => {
file = normalizePath(file)
if (file.endsWith('/package.json')) {
return invalidatePackageDjianata(packageCache, file)
}
// invalidate module graph cache on file
changemoduleGraph.onFileChange(file)
if (serverConfig.hmr !== false) {
try {
// 执行热更新
await handleHMRUpdate(file, server)
} catch (err) { ws.send({ type: 'error', err: prepareError(err) }) }
}
})
// 主要中间件,请求文件转换,返回给浏览器可以识别的js文件
middlewares.use(transformMiddleware(server))
...return server
}
优化策略
由于vite打包是让浏览器一个个模块去加载的,因此,就很容易存在http请求的瀑布流问题(浏览器并发一次最多6个请求)。此次,vite内部为了解决这个问题,主要采取了3个方案。
- 预打包,确保每个依赖只对应一个请求/文件。比如lodash。此处可以参考 https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/optimizer/esbuildDepPlugin.ts#L73
- 代码分割code split。可以借助 rollup 内置的 manualChunks 来实现。
- Etag 304 状态码,让浏览器在重复加载的时候直接使用浏览器缓存。
https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/server/middlewares/transform.ts#L155
// check if we can return 304 early
const ifNoneMatch = req.headers['if-none-match']
if (
ifNoneMatch &&
(await moduleGraph.getModuleByUrl(url))?.transformResult?.etag ===
ifNoneMatch
) {
isDebug && debugCache(`[304] ${prettifyUrl(url, root)}`)
res.statusCode = 304
return res.end()
}
与 webpack 的热更新对比起来,两者都是建立 socket 联系,但是两者不同的是,前者是通过 bundle.js 的 hash 来请求变更的模块,进行热替换。后者是根据自身维护 HmrModule ,通过文件类型以及服务端对文件的监听给客户端发送不同的 message,让浏览器做出对应的行为操作。