Spring学习③__Bean管理
目录
- IOC接口
-
- ApplicationContext 详解
-
- IOC操作Bean管理
-
- 基于xml方式
-
- 基于xml方式创建对象
- 基于xml方式注入属性
-
- 使用set方法进行注入
- 通过有参数的构造进行注入
- p 名称空间注入(了解)
- 基于xml方式注入其他类型属性
- xml 注入数组类型属性
IOC接口
- IOC思想基于IOC容器完成,IOC容器底层就是对象工厂
- Spring提供IOC容器实现的两种方式:
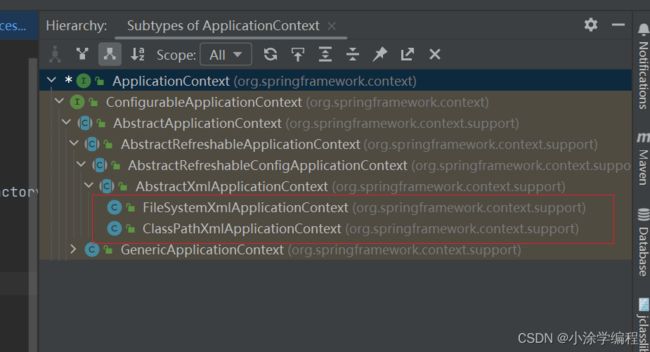
ApplicationContext 详解
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext : 配置文件为系统盘的文件
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext : 配置为类路径下的文件
IOC操作Bean管理
- Bean管理指的是两个操作
- ① Spring创建对象 :Spring通过Xml解析再通过工厂模式来进行创建对象
- ② Spring 注入属性 :Spring可以使用类似于Set对象的操作对对象或者字注入值
- Bean管理操作有两种方式
- ①基于xml配置文件方式实现
- ②基于注解方式实现
基于xml方式
基于xml方式创建对象

① 在spring配置文件中,使用bean标签,标签里面添加对应属性,就可以实现对象创建
② 在bean标签有很多属性,介绍常用的属性
- id属性 : 获取对象中的唯一的标识
- class属性 :类全路径(包类路径)
- name属性 :name的作用与id一样,name属性可以添加特殊符号
③ 创建对象的时候,默认也是执行无参的构造方法完成对象的创建
基于xml方式注入属性
DI : 依赖注入,就是注入属性
使用set方法进行注入
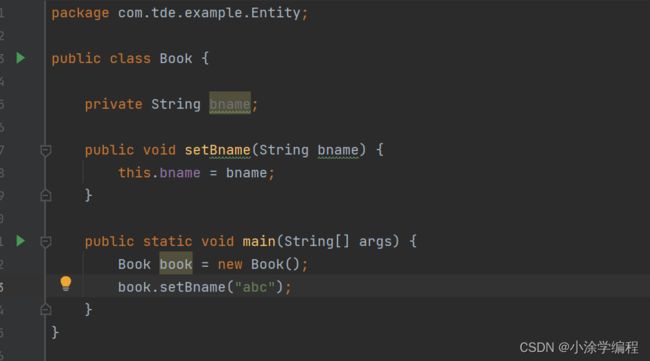
在spring配置文件配置对象创建,配置属性注入(使用Set方式注入)

通过有参数的构造进行注入
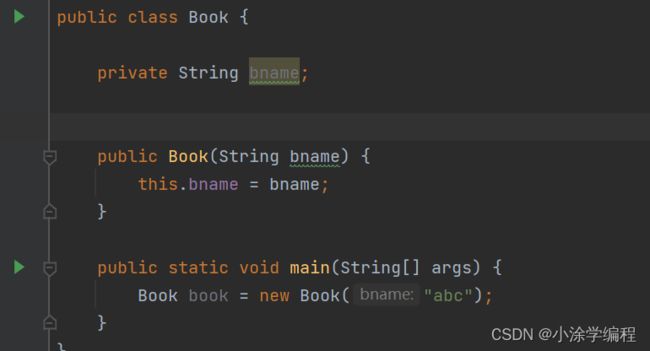
在spring配置文件配置对象创建,配置属性注入(使用有参数构造注入)

p 名称空间注入(了解)
使用 p 名称空间注入,可以简化基于 xml 配置方式
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns: p="http: //www. springframework. org/schema/p //添加 p 名称空间在配置文件中
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
//进行属性注入,在 bean 标签里面进行操作
<bean id="book" class="com. atguigu. spring5.Book" p:bname="九阳神功"
p: bauthor="无名氏">×/bean>
beans>
基于xml方式注入其他类型属性
- 字面量
- null 值
<property name="address">
<null/>
property>
- 属性值包含特殊符号
<property name="address">
<value>>]]>value>
property>
- 注入属性-外部 bean (外部调用对象的方法)
- 创建两个类 ,service 类和 dao 类
- 在 service 调用 dao 里面的方法
- 在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
public class UserService {
//创建UserDao类型属性,生成set方法
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add() {
System.out.println("service add...............");
userDao.update();
}
}
public class UserDao {
public void update() {
System.out.println("dao update...........");
}
}
-
通过springxml配置操作
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.atguigu.spring5.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl">property>
bean>
<bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.atguigu.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl">bean>
beans>
@Test
public void testBean1() {
//1 加载spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
//2 获取配置创建的对象
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
- 注入属性-内部 bean (内部属性包含对象)
① 一对多关系:部门和员工一个部门有多个员工,一个员工属于一个部门部门是一,员工是多
②在实体类之间表示一对多关系,员工表示所属部门,使用对象类型属性进行表示
部门类
//部门类
public class Dept {
private String dname;
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"dname='" + dname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
员工类
//员工类
public class Emp {
private String ename;
private String gender;
//员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示
private Dept dept;
//生成dept的get方法
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void add() {
System.out.println(ename+"::"+gender+"::"+dept);
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="安保部">property>
bean>
property>
bean>
beans>
@Test
public void testBean2() {
//1 加载spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//2 获取配置创建的对象
Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class);
emp.add();
}
- 注入属性-级联赋值 (都可以达到注入的作用)
第一种方法 直接赋值一个对象
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept">property>
bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部">property>
bean>
第二种方法 赋值里面的一个属性值
//生成dept的get方法
public Dept getDept(){
return dept:
}
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept">property>
<property name="dept.dname" value="技术部">property>
bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部">property>
bean>
xml 注入数组类型属性
- 注入数组类型属性
创建类,定义数组、list、map、set 类型属性,生成对应 set 方法
package com.tde.example.Entity;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Student {
//1 数组类型属性
private String[] courses;
//2 list集合类型属性
private List<String> list;
//3 map集合类型属性
private Map<String, String> maps;
//4 set集合类型属性
private Set<String> sets;
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setCourses(String[] courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(courses));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(maps);
System.out.println(sets);
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="stu" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Stu">
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>java课程value>
<value>数据库课程value>
array>
property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三value>
<value>小三value>
list>
property>
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java">entry>
<entry key="PHP" value="php">entry>
map>
property>
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>MySQLvalue>
<value>Redisvalue>
set>
property>
bean>
beans>
@Test
public void testCollection1() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean5.xml");
Stu stu = context.getBean("stu", Stu.class);
stu.test();
}
<bean id="course1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="Spring5 框架">property>
bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="MyBatis 框架">property>
bean>
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1">ref>
<ref bean="course2">ref>
list>
property>
//学生所学多门课程
private List<Course> courseList;
public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) {
this.courseList = courseList;
}
- 把集合注入部分提取出来
- 在 spring 配置文件中引入名称空间 util
- 使用 util 标签完成 list 集合注入提取
Book类
package com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype;
import java.util.List;
public class Book {
private List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>易筋经value>
<value>九阴真经value>
<value>九阳神功value>
util:list>
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Book">
<property name="list" ref="bookList">property>
bean>
beans>
@Test
public void testCollection2() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean6.xml");
Book book1 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
Book book2 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
book1.test();
book2.test();
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book2);
}