[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1
目录:
- 手工启动热部署
- 自动启动热部署
- 热部署范围配置
- 关闭热部署功能
- 第三方bean属性绑定
- 松散绑定
- 常用计量单位应用
- bean属性校验
- 进制数据转换规则
- 加载测试专用属性
- 加载测试专用配置
- 测试类中启动web环境
- 发送虚拟请求
- 匹配响应执行状态
- 匹配响应体
- 匹配响应体(json)
- 匹配响应头
- 业务层测试事务回滚
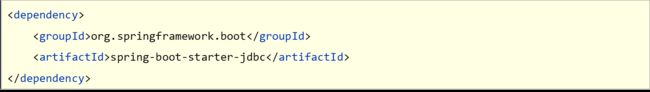
- 测试用例设置随机数据
- 内置数据源
- JdbcTemplate
- H2数据库
- redis下载安装与基本使用
- SpringBoot整合Redis
- Springboot读写Redis的客户端
- Sprintboot操作Redis客户端实现技术切换(jedis)
1.手工启动热部署
开启开发者工具
激活热部署:Ctrl + F9
- 重启(Restart):自定义开发代码,包含类、页面、配置文件等,加载位置restart类加载器
- 重载(ReLoad):jar包,加载位置base类加载器
小结:
- 开启开发者工具后启用热部署
- 使用构建项目操作启动热部署(Ctrl+F9)
- 热部署仅仅加载当前开发者自定义开发的资源,不加载jar资源
2.自动启动热部署
ctrl+alt+shift+/
激活方式:Idea失去焦点5秒后启动热部署
热部署Idea专业版spring boot(spring mvc)项目_idea springmvc 热部署-CSDN博客
3.热部署范围配置
默认不触发重启的目录列表
- /META-INF/maven
- /META-INF/resources
- /resources
- /static
- /public
- /templates
自定义不参与重启排除项
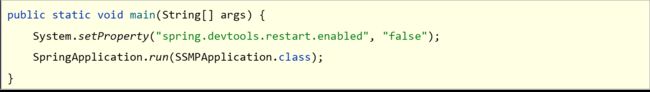
4.关闭热部署功能
属性加载优先顺序
设置高优先级属性禁用热部署
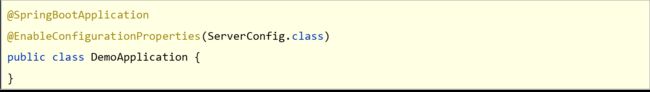
5.第三方bean属性绑定
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解可以将使用@ConfigurationProperties注解对应的类加入Spring容器
注意事项
- @EnableConfigurationProperties.与@Component不能同时使用
解除使用@ConfigurationProperties注释警告
![]()
6.松散绑定
注意事项
- 宽松绑定不支持注解@Value引用单个属性的方式
@ConfigurationProperties绑定属性支持属性名宽松绑定
注意事项
- 绑定前缀名命名规范:仅能使用纯小写字母、数字、下划线作为合法的字符
7.常用计量单位应用
JDK8支持的时间与空间计量单位
8.bean属性校验
数据校验
- 开启数据校验有助于系统安全性,J2EE规范中7SR303规范定义了一组有关数据校验相关的API
添加JSR3日3规范坐标与Hibernate校验框架对应坐标
对Bean开启校验功能
设置校验规则
9.进制数据转换规则
字面值表达方式
application.yml
servers:
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
# ipaddress: 192.168.0.1
# ip_address: 192.168.0.1
# ip-address: 192.168.0.1
# IPADDRESS: 192.168.0.1
# IP_ADD_R-E_SS: 192.168.0.1
port: 4444
timeout: -1
serverTimeOut: 3
dataSize: 10240
dataSource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver456
password: 0127ApplicationTests
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Value("${dataSource.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${servers.ipAddress}")
private String msg;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println(password);
}
}
运行结果:(0127)转换成了8进制
10.加载测试专用属性
在启动测试环境时可以通过properties参数设置测试环境专用的属性
优势:比多环境开发中的测试环境影响范围更小,仅对当前测试类有效
在启动测试环境时可以通过args参数设置测试环境专用的传入参数
Sprintboot14TestApplicationTests
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
//@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
//@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"}, args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
class Sprintboot14TestApplicationTests {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
application.yml
test:
prop: testValue
11.加载测试专用配置
使用@Import注解加载当前测试类专用的配置
MsgConfig.class
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MsgConfig {
@Bean
public String msg() {
return "bean msg";
}
}
ConfigurationTest.class
package com.example;
import com.example.config.MsgConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootTest
@Import({MsgConfig.class})
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Autowired
private String msg;
@Test
void testConfiguration() {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
运行结果:
12.测试类中启动web环境
模拟端口
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
public class WebTest {
@Test
void test() {
}
}
13.发送虚拟请求
虚拟请求测试
BookController.class
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById() {
System.out.println("getById is running...");
return "sprintboot";
}
}
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void test() {
}
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
mvc.perform(builder);
}
}
运行结果:
14.匹配响应执行状态
虚拟请求状态匹配
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
mvc.perform(builder);
}
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
}
}
15.匹配响应体
虚拟请求响应体匹配
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.ContentResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
mvc.perform(builder);
}
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
}
@Test
void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
action.andExpect(result);
}
}
16.匹配响应体(json)
虚拟请求响应体(json)匹配
BookController.class
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// @GetMapping
// public String getById() {
// System.out.println("getById is running...");
// return "springboot";
// }
@GetMapping
public Book getById() {
System.out.println("getById is running...");
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("springboot");
book.setType("springboot");
book.setDescription("springboot");
return book;
}
}
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.ContentResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
mvc.perform(builder);
}
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
}
@Test
void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
action.andExpect(result);
}
@Test
void testJson(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot\"}");
action.andExpect(result);
}
}
17.匹配响应头
虚拟请求响应头匹配
WebTest.class+
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.ContentResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.HeaderResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
mvc.perform(builder);
}
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
}
@Test
void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
action.andExpect(result);
}
@Test
void testJson(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot\"}");
action.andExpect(result);
}
@Test
void testContentType(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "application/json");
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
@Test
void testGetById(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "application/json");
action.andExpect(contentType);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot\"}");
action.andExpect(result);
}
}
18.业务层测试事务回滚
为测试用例添加事务,SpringBoot会对测试用例对应的事务提交操作进行回滚
如果想在测试用例中提交事务,可以通过@Rollback注解设置
19.测试用例设置随机数据
测试用例数据通常采用随机值进行测试,使用SpringBoot提供的随机数为其赋值
- ${random.int}表示随机整数
- ${random.int(10)}表示10以内的随机数
- ${random.int(10,20)}表示10到20的随机数
- 其中()可以是任意字符,例如[],!!均可
20.内置数据源
现有数据层解决方案技术选型
- 数据源:DruidDataSource
- 持久化技术:MyBatis-Plus /MyBatis
- 数据库:MySQL
格式一
格式二
SpringBoot提供了3种内嵌的数据源对象供开发者选择
- HikariCP.
- Tomcat提供DataSource.
- Commons DBCP
通用配置无法设置具体的数据源配置信息,仅提供基本的连接相关配置,如需配置,在下一级配置中设置具体设定
21.JdbcTemplate
现有数据层解决方案技术选型
- 数据源:DruidDataSource
- 持久化技术: MyBatls-Plus / MyBatis
- 数据库:MySQL
内置持久化解决方案——JdbcIemplate
JdbcTemplate配置
22.H2数据库
SpringBoot提供了3种内嵌数据库供开发者选择,提高开发测试效率
- H2
- HSQL
- Derby
导入H2相关坐标
设置当前项目为web工程,并配置H2管理控制台参数
访问用户名sa,默认密码123456
操作数据库(创建表)
设置访问数据源
H2数据库控制台仅用于开发阶段,线上项目请务必关闭控制台功能
SpringBoot可以根据url地址自动识别数据库种类,在保障驱动类存在的情况下,可以省略配置
现有数据层解决方案技术选型
BookDao.interface
package com.example.springboot_15_sql.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.springboot_15_sql.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper {
}
Book.class
package com.example.springboot_15_sql.domain;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String description;
}
Sprintboot15SqlApplication.class
package com.example.springboot_15_sql;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot15SqlApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot15SqlApplication.class, args);
}
}
application.yml
#server:
# port: 8080
#
#spring:
# datasource:
# url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/test_db
# hikari:
# driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# username: root
# password: 666666
# maximum-pool-size: 50
#mybatis-plus:
# global-config:
# db-config:
# table-prefix: tbl_
# id-type: auto
# configuration:
# log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
server:
port: 8080
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
hikari:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
id-type: auto
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplpom.xml
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.7.17
com.example
springboot_15_sql
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
springboot_15_sql
springboot_15_sql
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
com.h2database
h2
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.4.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest
org.projectlombok
lombok
Sprintboot15SqlApplicationTests.class
package com.example.springboot_15_sql;
import com.example.springboot_15_sql.dao.BookDao;
import com.example.springboot_15_sql.domain.Book;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot15SqlApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void test() {
bookDao.selectById(1);
}
@Test
void testJdbcTemplate(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
String sql = "select * from tbl_book";
// List> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
// System.out.println(maps);
RowMapper rm = new RowMapper() {
@Override
public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book temp = new Book();
temp.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
temp.setName(rs.getString("name"));
temp.setType(rs.getString("type"));
temp.setDescription(rs.getString("description"));
return temp;
}
};
List list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm);
System.out.println(list);
}
// @Test
// void testJdbcTemplateSave(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
// String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(null,'springboot','springboot','springboot')";
// jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
// }
@Test
void testJdbcTemplateSave(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(3,'springboot3','springboot3','springboot3')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
}
}
23.redis下载安装与基本使用
市面上常见的NoSQL解决方案
- Redis
- Mongo
- ES
Redis是一款key-value存储结构的内存级NoSQL数据库
- 支持多种数据存储格式
- 支持持久化
- 支持集群
Redis下载(Windows版)
- https://github.com/tporadowski/redis/releases
Redis安装与启动( Windows版)
- Windows解压安装或一键式安装
- 服务端启动命令
- 客户端启动命令
24.SpringBoot整合Redis
导入SpringBoot整合Redis坐标
配置Redis(采用默认配置)
- 主机: localhost(默认)
- 端口:6379(默认)
RedisTemplate提供操作各种数据存储类型的接口API
客户端:RedisTemplate
pom.xml
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.5.4
com.example
sprintboot_16_redis
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sprintboot_16_redis
sprintboot_16_redis
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest
application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
Springboot16RedisApplicationTests.class
package com.example.sprintboot_16_redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
class Sprintboot16RedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void set() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age", "41");
}
@Test
void get() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object age = ops.get("age");
System.out.println(age);
}
@Test
void hset() {
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
ops.put("info", "a", "aa");
}
@Test
void hget() {
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Object val = ops.get("info", "a");
System.out.println(val);
}
}
25.Springboot读写Redis的客户端
客户端:RedisTemplate以对象作为key和value,内部对数据进行序列化
客户端: StringRedisTemplate以字符串作为key和value,与Redis客户端操作等效
StringRedisTemplateTest.class
package com.example.sprintboot_16_redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get1() {
ValueOperations ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
@Test
void get2() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
26.Sprintboot操作Redis客户端实现技术切换(jedis)
客户端选择:jedis
配置客户端
配置客户端专用属性
lettcus与jedis区别
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响。
- lettcus基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnectian。StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然lettcus也支持多连接实例一起工作.
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1cb7bfbe1d3949988cdf2f3f45a3aabc.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e01fbcb6346949fabc612235367dc3e3.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/66d271cf339d405e811a195c905b22cf.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6afc2c113a604a2985842d64719dc025.png)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/178af99559424053bc4498937b9512d9.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2255af3a0e9f4db1add6bbd7c5face11.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/78b396081ac044e89c7e64d33338123a.png)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/387a637ea46e4fe88be43acf4a40d36c.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9464e4ce884d44428e07380cf82bf635.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51abcd53917d45988936e040505a0655.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2c1264f8f7c74951907dd03cb1a357c8.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ace3169bc41b42d4aafc970c6e245d5d.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8f4fd0158af9439989b92c14312bfdc5.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fe65552fc77d424ca54d01fdb17d079b.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/cf027dcbfbc14d15a93d2c932b1db61d.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第16张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1a91762e41eb46a9a25a879bb3dda384.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第17张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/96feebf59eea465ab07ff730ad518f42.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第18张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4acb23aec826478b99e3051b3033f388.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第19张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/90a2c386efa2482e895e079df101fccd.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第20张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1f91f6c7e86f48fb928c71b55816c89d.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第21张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7725a5670791421ca93799deb2fabb93.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第22张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/bb8d54785a5d42078ef7134b42aa4419.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第23张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e8822d76ba474e988c0a1656c38476de.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第24张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f05d52b6c5f54689a200e20c6ad5ecb4.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第25张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/116e3f525e0349629cfb4d1ee2bfd1b6.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第26张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2a8fbe553e394b9aa92a7f3f82c02228.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第27张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/57589c2343f7438ca06a907f27102ba6.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第28张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c2e0eaaac0e24570a1f881fc6f052cf0.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第29张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/24771a72e6894ea5991fb22f9e8bdb34.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第30张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4185cf8aa39b4091b528de8b59e90ef4.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第31张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5909bdf9c2734701b9f35c7acebe62c2.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第32张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b0f4fc1444184cd8abaa3ded88564f73.jpg)

![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第33张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2909a5c0030f43c6bfe66052a25c63fb.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第34张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8248e297d8084ef98d28fc46b6aeeee0.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第35张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f0cda1cd596d431780589dc8ef9a0f07.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第36张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/529d1ee6f02f46cd9d432ad17378dfa5.jpg)

![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第37张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a8286c3f082c49df82bdafb2d64e6508.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第38张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/60eb585d5f5a49ea965180398b15c19c.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第39张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/99a4855046fc48a5b2af125088551e5a.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第40张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/65f6275d12ac43bd83f0dbb1fd693988.jpg)
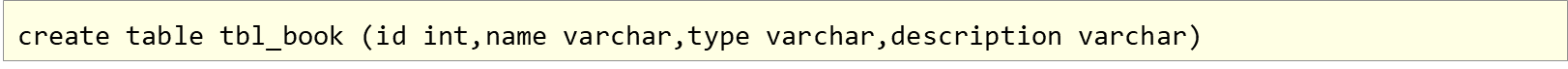
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第41张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b1cc6115f2fa46b6bc93c1ee77b3575a.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第42张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7ad0cebc52ea42efa3f755b5f30cdc3f.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第43张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3f115a32ac40409cbac9a4a5ee9bf50f.jpg)

![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第44张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3e423ce270bf46d8bb60fae2206474e7.jpg)


![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第45张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d0e4817a621544dd8176e047aa2d4f67.png)

![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第46张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/346bb98f7933460c934e38f193cc1a5c.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第47张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/eb6eb43e6deb4ff0b0f7745d19ea02ea.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第48张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fa1049221d83420ebed2e6ede8ca9557.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第49张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b9a607aea4054666a056b68c2aa520b6.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第50张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4892f2045df845f1a263e0e60d89b3ce.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第51张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e707e2253ac142b383544c15fd463d50.png)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第52张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d23c43ca353549d592fea28bf5652ac8.jpg)
![[黑马程序员SpringBoot2]——开发实用篇1_第53张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/90f7bdb8ab3e444d92dbbcd52fdc05f4.jpg)