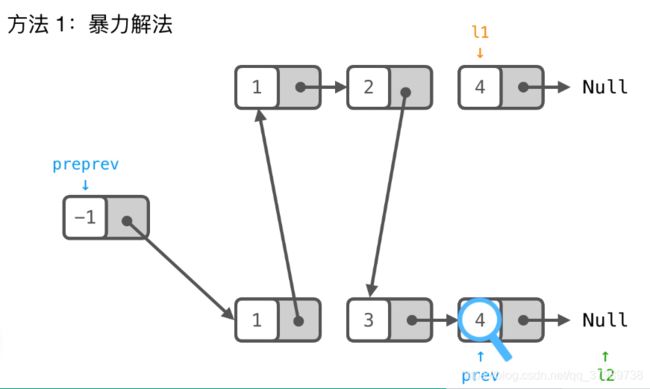
Leetcode经典题目----链表
1. 找出两个链表的交点
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists (Easy)

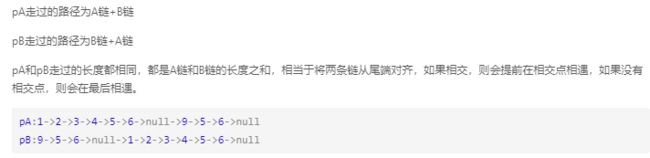
代码实现:
注意:不会出现死循环,因为等到他们都走到末尾的时候,l1=l2=null,会退出循环从而返回null
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode l1 = headA, l2 = headB;
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
while (l1 != l2) {
l1 = (l1 == null) ? headB : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? headA : l2.next;
}
return l1;
}
}
2. 链表反转
206. Reverse Linked List (Easy)
方法一:迭代法
代码实现:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//pre可理解为新链表的头结点
ListNode pre = null, nextTemp = null;
while(head != null){
nextTemp = head.next;//保存下一个节点的元素,比如第一次保存2,为了遍历原来的链表
head.next = pre;//比如1->2->3,刚开始将1的next置为null,即为尾节点
pre = head; //pre往前进一步,比如现在pre指向1这个节点
head = nextTemp;//原链表元素继续往后遍历
}
return pre;
}
}
方法二:递归
代码实现:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
ListNode newHead = reverseList(next);
next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
3. 归并两个有序的链表
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists (Easy)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead= new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = dummyHead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
方法二:递归
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}
else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
4. 从有序链表中删除重复节点
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List (Easy)
方法一:直接法
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null && cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val == cur.val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
方法二:递归
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head.val == head.next.val ? head.next : head;
}
5. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List (Medium)
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode preNode = head;
ListNode finalNode = head;
//第一次遍历求出链表长度
int k = 0;
while(preNode != null){
preNode = preNode.next;
k++;
}
//特殊情况1:如果链表为空或者链表只有一个元素则返回null
if(finalNode == null || finalNode.next == null){
return null;
}
//特殊情况2:如果删除头结点则直接将头结点指向头结点的下一个指针并返回
if(n == k){
head = head.next;
return head;
}
//第二次遍历:定位出要删除的节点并删除
int j=1;
while(finalNode != null){
if(j == k-n){
finalNode.next = finalNode.next.next;
break;
}
finalNode = finalNode.next;
j++;
}
return head;
}
}
方法二:快慢指针
上述算法可以优化为只使用一次遍历。我们可以使用两个指针而不是一个指针。第一个指针从列表的开头向前移动 n+1 步,而第二个指针将从列表的开头出发。现在,这两个指针被 n 个结点分开。我们通过同时移动两个指针向前来保持这个恒定的间隔,直到第一个指针到达最后一个结点。此时第二个指针将指向从最后一个结点数起的第 n个结点。我们重新链接第二个指针所引用的结点的 next 指针指向该结点的下下个结点。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); //这里搞个哑巴节点为了处理边界情况,如果为两个节点,而n也为2fast应该移动3会造成空指针异常
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
for(int i=1;i<=n+1;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
6. 交换链表中的相邻结点
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs (Medium)
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
方法一:非递归写法
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// Dummy node acts as the prevNode for the head node
// of the list and hence stores pointer to the head node.
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
while ((head != null) && (head.next != null)) {
// Nodes to be swapped
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head.next;
// Swapping
prev.next = second;
first.next = second.next;
second.next = first;
// Reinitializing the head and prevNode for next swap
prev = first;
head = first.next; // jump
}
// Return the new head node.
return dummy.next;
}
}
方法二:递归写法
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(next.next);
next.next = head;
return next;
}
}
7. 链表求和
445. Add Two Numbers II (Medium)
方法:使用栈保存链表数据
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
while(l1!=null){
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while(l2!=null){
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode head = null;
while(!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry>0){ //carry>0,当栈里面元素为空时,但是还有进位没算进去,需要加上这个条件
int sum = carry; //本次相加的进位赋给下次相加的初始值
carry = 0;
sum += stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
sum += stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
if(sum>=10){
sum = sum-10;
carry = 1;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(sum);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
return head;
}
}
8. 回文链表
234. Palindrome Linked List (Easy)
方法一:使用栈
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
while(head!=null){
stack.push(head.val);
s.append(stack.pop()+",");
head = head.next;
}
return isPalindrome2(s.toString());
}
public boolean isPalindrome2(String s){
String[] splitString = s.split(",");
int high = splitString.length-1;
int low = 0;
while(low <= high){
if(!splitString[low].equals(splitString[high])){
return false;
}
low++;
high--;
}
return true;
}
}
9. 分隔链表
725. Split Linked List in Parts(Medium)
输入:
root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], k = 3
输出: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10]]
解释:
输入被分成了几个连续的部分,并且每部分的长度相差不超过1.前面部分的长度大于等于后面部分的长度。
方法:创建新列表
如果链表有 NN个结点,则分隔的链表中每个部分中都有 n/k 个结点,且前 N%k 部分有一个额外的结点。我们可以用一个简单的循环来计算 N。现在对于每个部分,我们已经计算出该部分有多少个节点:width + (i < remainder ? 1 : 0)。我们创建一个新列表并将该部分写入该列表。
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
ListNode cur = root;
int N = 0;
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
N++;
}
int width = N / k, rem = N % k;
ListNode[] ans = new ListNode[k];
cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0), write = head;
for (int j = 0; j < width + (i < rem ? 1 : 0); ++j) {
write = write.next = new ListNode(cur.val);
if (cur != null) cur = cur.next;
}
ans[i] = head.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
10. 链表元素按奇偶聚集
328. Odd Even Linked List (Medium)
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL,
return 1->3->5->2->4->NULL.
思路:
一个 LinkedList 需要一个头指针和一个尾指针来支持双端操作。我们用变量 head 和 odd 保存奇链表的头和尾指针。 evenHead 和 even 保存偶链表的头和尾指针。算法会遍历原链表一次并把奇节点放到奇链表里去、偶节点放到偶链表里去。遍历整个链表我们至少需要一个指针作为迭代器。这里 odd 指针和 even 指针不仅仅是尾指针,也可以扮演原链表迭代器的角色。
public class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode odd = head, even = head.next, evenHead = even;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}