剑指offer 刷题笔记
文章目录
-
- 2020/3/1
- 1.二维数组的查找
- 2.替换空格
- 3.从尾到头打印链表
- 4.重建二叉树
- 5.用两个栈实现队列
- 6.旋转数组的最小值
- 7.斐波那契数列
- 8.青蛙跳台阶
- 9.变态跳台阶
- 10. 矩形覆盖
- 11. 二进制中1的个数
- 12. 数值的整数次方
- 13. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
- 14. 链表中倒数第k个结点
- 15. 反转链表
- 16. 合并两个排序的链表
- 17. 树的子结构(重点再看)
- 18. 二叉树的镜像
- 19.顺时针打印矩阵(重点再看)
- 20.顺时针打印矩阵
- 21.栈的压入弹出序列
- 22.从上往下打印二叉树
- 23.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 24.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 25.复杂链表的复制
- 26.二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 27.字符串的排列
- 28.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
2020/3/1
开始刷剑指offer第二遍,第一遍没有仔细记录。
第二遍将完整记录每道题的解题过程和思路。
tips:刷第一遍题的时候,二叉树的题建议先跳过,最后只剩下的二叉树的题的时候统一刷。
1.二维数组的查找
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
思考
暴力法就不说了,遍历数组进行比较返回即可。
从二维矩阵数组的左下或者右上角开始查找,相对于左上或者右下角考虑的边界条件会简单很多,因为索引只需从向两个方向移动即可。以从右上角开始查找为例子,每次比较目标值和当前位置,如果小于目标值,行索引++,大于目标值,列所索引–,否则返回true,而结束循环的条件就是行索引大于行数或列索引小于0。
代码
class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int rows =array.length;
int cols =array[0].length;
int i=0;
int j=cols-1;
while(i<rows&&j>=0){
if(target>array[i][j]){
i++;
}else if(target<array[i][j]){
j--;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
2.替换空格
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
思考
判断每个元素是否空格就行,字符空格使用Character.isSpace()方法,字符串空格使用==" "即可
代码
class Solution {
// public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
// return str.toString().replaceAll(" ","20%");
// }方法一 使用内置函数直接替换
//-----------------------------------方法二 遍历字符数组
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
StringBuffer strnew =new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if (Character.isSpace(str.charAt(i))){
strnew.append("%20");
}
else {
strnew.append(str.charAt(i));
}
}
return strnew.toString();
}
}
3.从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表,按链表从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
思考
最简单的方法就是直接遍历使用ArrayList的add(0,value)函数,实现数字的倒序插入。
另外,可以使用递归的方法,移动链表指针一直往下找,当找到尾节点时开始往ArrayList中添加数字,得到的结果就是倒序的。
方法1 直接遍历
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode){
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
if(listNode==null) return l;
ListNode p =listNode;
while (p!=null){
l.add(0,p.val);
p=p.next;
}
return l;
}
方法2 递归
ArrayList<Integer> list =new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode){
ReverseInsertOrder(listNode);
return list;
}
public boolean ReverseInsertOrder(ListNode n){
if(n==null) return true;
if(ReverseInsertOrder(n)) {
list.add(n.val);
}
return true;
}
4.重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
思考
看到二叉树的题,就要想到递归。
1.前序遍历的第一个元素是二叉树的根节点,这里找到 1在in中的位置位in[3]
2.将in数组按in[3]切割成左右子树的中序遍历结果{4,7,2},{5,3,8,6}
3.根据切割后的数组长度再切割pre得到左右子树的前序遍历结果{2,4,7},{3,5,6,8},依次类推。数组为空作为终止条件。
通过递归来实现,每次根据pre数组的第一个元素构建根节点,然后进行下次递归找出根节点的左子树和右子树,终止条件成立时返回null。
代码
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre,int[] in){
if(pre.length==0||in.length==0) return null;
TreeNode root =new TreeNode(pre[0]);//根节点是前序遍历的第一个元素
int cutPoint=0;
for(int i=0;i<in.length;i++){
if(in[i]==pre[0]){
cutPoint =i;//找到pre[0]在in中的索引cutPoint
break;
}
}
//递归构建左子树和右子树
root.left =reConstructBinaryTree(
Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,cutPoint+1),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in,0,cutPoint));
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(
Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,cutPoint+1,pre.length),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in,cutPoint+1,in.length)
);
return root;
}
5.用两个栈实现队列
思考
队列的特性是:“先入先出”,栈的特性是:“先入后出”。
关键两点:
1.当插入时,直接插入 stack1
2.当弹出时,当 stack2 不为空,弹出 stack2 栈顶元素,如果 stack2 为空,将 stack1 中的全部数逐个出栈入栈 stack2,再弹出 stack2 栈顶元素
代码
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
6.旋转数组的最小值
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。
输入一个非递减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
思路
暴力法不讨论。这个题实质上是二分法的变种,第二次做又不会…
详细思路参考牛客网答案:
https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/9f3231a991af4f55b95579b44b7a01ba?answerType=1&f=discussion
代码
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
if(array.length==0) return 0;
int low =0;
int high=array.length-1;
int mid =0;
while(low<high){
if(array[low]<array[high]) return array[low];
mid=(low+high)>>2;
if(array[mid]>array[low]) low=mid+1;
else if(array[mid]<array[high]) high=mid;
else low++;
}
return array[low];
}
7.斐波那契数列
大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。n<=39
思考
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2), 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13… 两两一组生成即可,只是需要注意边界条件
代码
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return 1;
int i=0;
int j=1;
int tmp;
int count=1;
while (count<n){
tmp=i+j;
i=j;
j=tmp;
count++;
}
return j;
}
8.青蛙跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
思考
//记得是用回溯法 递归 函数表达式
记错了,不是递归,本质是斐波那契数列,递归会超时。
假设n个台阶对应一共有F(n)种结果,而F(n)是由前一次走的结果决定的,最后一次如果走了1步则是F(n-1),最后一步如果走了2步则是F(n-2)。
即F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),典型的斐波那契数列。
代码
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if(target==0) return 0;
if(target==1) return 1;
if(target==2) return 2;
int m=1;
int n=2;
int tmp;
for(int i=0;i<target-2;i++){
tmp=n;
n+=m;
m=tmp;
}
return n;
}
9.变态跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
思考
同上题类似思路 有
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)+…+f(1)
f(n-1)=f(n-2)+…+f(1)
由上面两式得到 f(n)=2f(n-1) —> f(n)=f(1)*(2^(n-1))
代码
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
return (int)Math.pow(2,target-1);
}
10. 矩形覆盖
我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。
请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
比如n=3时,23的矩形块有3种覆盖方法:
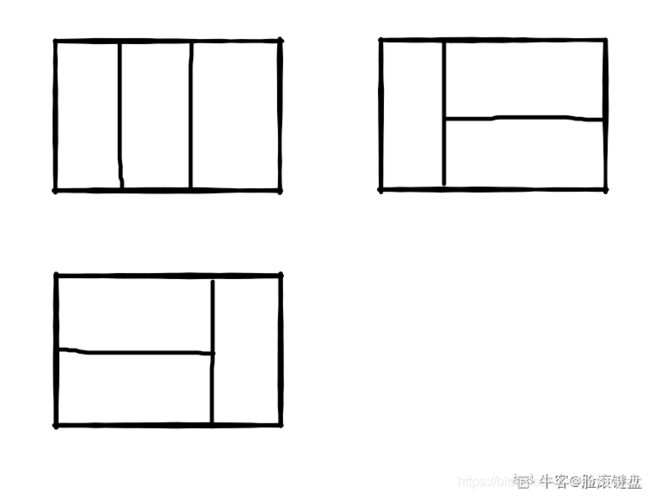
思考
本质还是斐波那契数列 因为一条边长被固定死为2了,
2*n的矩阵 假设它有f(n)中放法,只要看最后的位置,
2 * 1的矩形如果是竖着放 那么剩下的区域放置方法就是f(n-1)
2 * 1的矩形如果是横着放 那么剩下的区域放置方法就是f(n-2)
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)
本质还是斐波那契数列
代码
public int RectCover(int target) {
if(target<3) return target;
int i=1,j=2,tmp=0;
for(int k=0;k<target-2;k++){
tmp=j;
j=i+j;
i=tmp;
}
return j;
}
11. 二进制中1的个数
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
思考
参考牛客网最佳答案。
n&(n-1)会使得n的二进制表达形式的最右边那个1消失。
代码
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count =0;
while (n!=0){
count++;
n=n&(n-1);
}
return count;
}
12. 数值的整数次方
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。保证base和exponent不同时为0。
思路
方法1 Math.pow()
方法2 快速幂算法 将指数用二进制表达 复杂度从O(n)降到O(logn)
代码
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
// return Math.pow(base,exponent);
double sum =1;
boolean flag =false;
if(exponent<0) {
exponent=-exponent;
flag=true;
}
while (exponent!=0){
if((exponent&1)==1){
sum*=base;
}
exponent>>=1;
base*=base;
}
return flag?1/sum:sum;
}
13. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
思考
顺序遍历数组,遇到偶数时,令变量ou=索引位置,下一个数如果是偶数,进行下次循环,如果是奇数,移动数组中的元素交换奇数偶数位置,在移动完之后,ou=ou+1,依次类推。
代码
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
int ou=-1;//每次遇到的第一个偶数 保留索引
int i=0;
while (i<array.length){
boolean flag =(array[i]&1)==0;
if(flag){
if(ou==-1) ou=i;
}
else if(ou!=-1){ //遇到偶数后遇到奇数 交换数组元素顺序
int tmp =array[i];
for(int j=i;j>ou;j--){
array[j]=array[j-1];
}
array[ou]=tmp;
ou=ou+1 ;
continue;
}
i++;
}
}
14. 链表中倒数第k个结点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
思考
双指针法,第一个指针先走k步,然后第二个指针从头部出发,两个指针一起移动,当第一个指针到达终点时,第二个指针刚好到达倒数第k个节点。
代码
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
ListNode t1 =head;
ListNode t2 =head;
while(t1!=null){
t1=t1.next;
if(k!=0) {
k--;
}
else {
t2=t2.next;
}
}
if(k>0) return null;
return t2;
}
15. 反转链表
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
思考
方法1 借助栈进行反转 先入栈 后出栈 利用哑节点
方法2 借助双指针 从链表上移动 两个指针中间隔一个节点
代码
方法1
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode h =head;
Stack<ListNode> stack =new Stack<>();
while (h!=null){
stack.push(h);
h=h.next;
}
ListNode t=new ListNode(0);//哑节点
ListNode nh =t;
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
t.next =stack.pop();
t=t.next;
}
t.next=null;//原来的首节点的next要指向空
return nh.next;
}
方法二
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null) return null;
ListNode l=null;
ListNode r;
ListNode h=head;
while(h.next!=null){
r=h.next;
h.next=l;
l=h;
h=r;
}
h.next=l;
return h;
}
16. 合并两个排序的链表
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
思考
借助哑节点作为头节点,然后依次比较两个链表的节点。
代码
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
ListNode h =new ListNode(0);
ListNode rs=h;
ListNode l1=list1;
ListNode l2=list2;
while (l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val>l2.val) {
h.next=l2;
l2=l2.next;
}
else {
h.next=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}
h=h.next;
}
while (l1!=null){
h.next=l1;
h=h.next;
l1=l1.next;
}
while (l2!=null){
h.next=l2;
h=h.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
return rs.next;
}
17. 树的子结构(重点再看)
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思考
又忘记怎么做了,牛客网排名第一的答案是错的。
其实思路应该分为两步:
1.在大树中找到和小树根节点相同的节点。
2.然后以此节点为根节点,在大树上往下搜索对比小书左右节点是否相同,不同则返回false
大树中找不到的话,从左子树和右子树找,依次递归。
代码
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null||root2==null) return false;
boolean result=false;
if(root1.val==root2.val){
result = HasSubtreeHelper(root1,root2);
}
if(!result) result = HasSubtree(root1.left,root2);
if(!result) result = HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
return result;
}
public boolean HasSubtreeHelper(TreeNode r1,TreeNode r2){
if(r2==null) return true;
if(r1==null) return false;
if(r1.val!=r2.val) return false;
return HasSubtreeHelper(r1.left,r2.left)&&HasSubtreeHelper(r1.right,r2.right);
}
18. 二叉树的镜像
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
思考
交换左右节点+递归
代码
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=tmp;
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
19.顺时针打印矩阵(重点再看)
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
思考
第二次做再次惨败,参考最佳答案的思路,不用考虑太多边界条件。
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/9b4c81a02cd34f76be2659fa0d54342a?answerType=1&f=discussion
代码
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
int rows =matrix.length;
int cols =matrix[0].length;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
HashSet<Integer> set =new HashSet<>();
int up=0,down=matrix.length-1,right=cols-1,left=0;
while(true){
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++) list.add(matrix[up][i]);
if(++up>down) break;
for(int j=up;j<=down;j++) list.add(matrix[j][right]);
if(--right<left) break;
for(int i=right;i>=left;i--) list.add(matrix[down][i]);
if(--down<up) break;
for(int j=down;j>=up;j--) list.add(matrix[j][left]);
if(++left>right) break;
}
return list;
}
20.顺时针打印矩阵
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。 注意:保证测试中不会当栈为空的时候,对栈调用pop()或者min()或者top()方法。
代码
Stack<Integer> dataStack =new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> minStack =new Stack<>();
public void push(int node) {
dataStack.push(node);
if(minStack.isEmpty()||node<=minStack.peek()) minStack.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
if (dataStack.peek().equals(minStack.peek())) minStack.pop();
dataStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return dataStack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
21.栈的压入弹出序列
代码
/* * 输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。
* 假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。
* 例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,
* 但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)*/
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
if(pushA==null||popA==null||pushA.length==0||popA.length==0) return false;
Stack<Integer> stack =new Stack<>();
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<pushA.length;i++){
stack.push(pushA[i]);
while (!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()==popA[j]){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
if(stack.isEmpty()) return true;
else return false;
}
22.从上往下打印二叉树
代码
/*
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
*
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return list;
TreeNode tr=root;
queue.add(tr);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
tr =queue.poll();
list.add(tr.val);
if(tr.left!=null) queue.add(tr.left);
if(tr.right!=null) queue.add(tr.right);
}
return list;
}
23.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
代码
/*
* 输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。
* 如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。
* 假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
*
* 后序遍历是左右中,有个特点就是后序遍历数组中的最后一个元素是根节点
*
* 再次惨败 这道题一定要注意 两个for循环的迭代的变量 一定要再循环外面提前声明,这样每步循环完 变量也会变化
* */
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Offer23().VerifySquenceOfBST(new int[]{4,6,7,5});
}
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0) {
return false;
}
return VerifySquenceOfBSTHelper(sequence,0,sequence.length-1);
}
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBSTHelper(
int [] sequence,int start,int stop){
if(start>=stop) return true;
int rootval =sequence[stop];
int i=start;
for(;i<stop;i++){
if(sequence[i]>rootval) break;
}
int j=i;
for(;j<stop;j++){
if(sequence[j]<rootval) return false;
}
return VerifySquenceOfBSTHelper(sequence,start,i-1)&&
VerifySquenceOfBSTHelper(sequence,i,stop-1);
}
24.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
代码
/*
* 输入一颗二叉树的根节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。
* 路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
* (注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)
* 又忘记怎么做了
* */
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> lists =new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
if(root==null) return lists;
target-=root.val;
list.add(root.val);
if(target==0&&root.left==null&&root.right==null) lists.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
FindPath(root.left,target);
FindPath(root.right,target);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return lists;
}
25.复杂链表的复制
代码
/*
* 输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,
* 以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),
* 返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。
* (注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
*
* 重点是要注意两个边界条件
* */
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
{
if(pHead==null) return null;
RandomListNode h1 =pHead;
RandomListNode h2 =pHead;
RandomListNode h3 =pHead;
RandomListNode tmp;
while(h1!=null){
tmp=h1.next;
RandomListNode insertNode = new RandomListNode(h1.label);
h1.next=insertNode;
insertNode.next=tmp;
h1=tmp;
}
while (h2!=null){
h2.next.random=h2.random==null?null:h2.random.next;
h2=h2.next.next;
}
RandomListNode newNode=h3.next;
while (h3!=null){
RandomListNode tmpNode=h3.next;
h3.next=tmpNode.next;
tmpNode.next=tmpNode.next==null?null:tmpNode.next.next;
h3=h3.next;
}
return newNode;
}
26.二叉搜索树与双向链表
代码
/*
* 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。
* 要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
*
*
* 中序遍历 是关键 左中右
* 从最左边开始,LastNode指向前一个节点,当前节点.left=LastNode,LastNode.right=当前节点,
* 移动LastNode指针,LastNode =当前节点
* 然后回到上一层递归
* */
TreeNode LastNode =null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
ChangeOrder(root);
while (LastNode!=null&&LastNode.left!=null){
LastNode = LastNode.left;
}
return LastNode;
}
public void ChangeOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
ChangeOrder(root.left);
root.left=LastNode;
if(LastNode!=null) LastNode.right=root;
LastNode=root;
ChangeOrder(root.right);
}
27.字符串的排列
代码
/*
*
* 输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。
* 例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
*
* https://blog.csdn.net/pcwl1206/article/details/86352979
* */
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Offer27().Permutation("a");
}
public ArrayList Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList stringList = new ArrayList<>();
if(str==null||str.length()==0) return stringList;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
PermutationHelpr(chars,stringList,0);
Collections.sort(stringList);
return stringList;
}
public void PermutationHelpr(char[] chars, List rs,int index){
if(index==chars.length-1) {
if(!rs.contains(String.valueOf(chars))) rs.add(String.valueOf(chars));
return;
}
for(int i=index;i 28.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
思考
https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/e4290272e9ba42aa96cfd012e17e4c25?f=comment
这个支持者反对者答案写的很好,便于理解。
代码
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
if(array==null||array.length==0) return 0;
int count =1;
int val =array[0];
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
if(val==array[i]) ++count;
else{
--count;
if(count==0){
val=array[i];
++count;
}
}
}
count =0;
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(val==array[i]) ++count;
}
return count>array.length/2?val:0;
}