【算法】树形DP③ 监控二叉树 ⭐(二叉树染色&二叉树灯饰)!
文章目录
- 前期知识 & 相关链接
- 例题
-
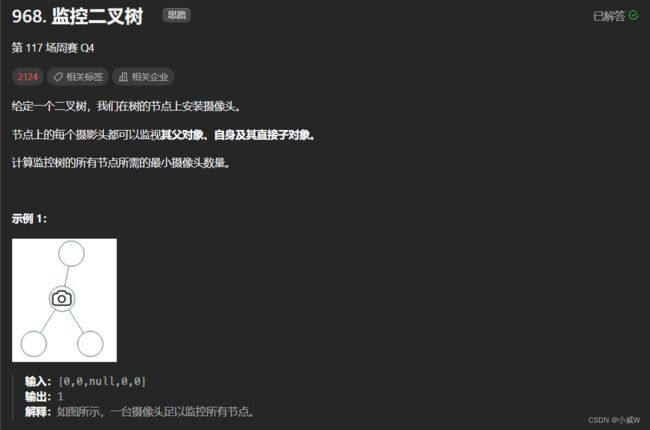
- 968. 监控二叉树
-
- 解法1——标记状态+贪心
- 解法2——动态规划
- 相关练习题目
-
- P2458 [SDOI2006] 保安站岗⭐(有多个儿子节点)
- LCP 34. 二叉树染色⭐(每个节点 单独dp[k + 1]数组)
- LCP 64. 二叉树灯饰⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
前期知识 & 相关链接
树形DP:监控二叉树【基础算法精讲 25】
相关链接:
【算法】树形DP ①(树的直径)
【算法】树形DP ② 打家劫舍Ⅲ(树上最大独立集)
本文中的四道题目都很重要!
例题
968. 监控二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-cameras/solutions/2452795/shi-pin-ru-he-si-kao-shu-xing-dpgai-chen-uqsf/
提示:
给定树的节点数的范围是 [1, 1000]。
每个节点的值都是 0。
解法1——标记状态+贪心
从下到上dfs,标记各个节点的节点。必须使用时就使用一个监控。
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
if (dfs(root) == 0) ans++;
return ans;
}
// 0没有被覆盖,1被覆盖,使用摄像头2
public int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 1;
int l = dfs(root.left), r = dfs(root.right);
if (l == 0 || r == 0) {
ans++;
return 2;
} else if (l == 2 || r == 2) return 1;
return 0;
}
}
解法2——动态规划
同样是后序dfs。
状态分为:该节点上有,该节点父节点上有,该节点子节点上有。
dp 中的数值 表示 花费。
class Solution {
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
int[] res = dfs(root);
return Math.min(res[0], res[2]);
}
// 该节点上有,该节点父节点上有,该节点子节点上有
public int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[]{Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2, 0, 0};
}
int[] l = dfs(root.left), r = dfs(root.right);
int choose = Math.min(l[0], l[1]) + Math.min(r[0], r[1]) + 1; // 自己选
int byFa = Math.min(l[0], l[2]) + Math.min(r[0], r[2]); // 自己不选,用他爹的
int byChildren = Math.min(Math.min(l[0] + r[2], l[2] + r[0]), l[0] + r[0]); // 自己不选,用它儿子的
return new int[]{choose, byFa, byChildren};
}
}
相关练习题目
P2458 [SDOI2006] 保安站岗⭐(有多个儿子节点)
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2458
将节点分成三类:1.靠自己 2.靠父节点 3.靠子节点。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(), root = 0;
int[] cost = new int[n + 1];
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n + 1];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; ++i) {
int x = scanner.nextInt(), c = scanner.nextInt(), m = scanner.nextInt();
if (root == 0) root = x; // 记录根节点标号
cost[x] = c;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
int y = scanner.nextInt();
g[x].add(y);
}
}
int[] res = dfs(root, g, cost);
System.out.println(Math.min(res[0], res[2]));
}
// 自己,父节点,儿子
public static int[] dfs(int x, List<Integer>[] g, int[] cost) {
int c = cost[x], fa = 0, ch = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int y: g[x]) {
int[] res = dfs(y, g, cost);
c += Math.min(res[0], res[1]); // 靠自己:从靠自己和靠爹的转移过来
fa += Math.min(res[0], res[2]); // 靠爹:从靠自己和靠儿子的转移过来
ch = Math.min(ch, res[0] - res[2]); // 靠儿子:子节点不可能靠爹,且至少有一个靠自己.这里处理最少一个靠自己,最后再加上fa
}
return new int[]{c, fa, fa + Math.max(0, ch)};
}
}
主要考虑递推公式的写法。
其中靠儿子的转移:子节点不可能靠爹,且至少有一个靠自己。先去掉这个“至少有一个靠自己”的限制条件,那么 ch 的计算就和 fa 的计算一样了。除此之外,我们要记录 res[0] - res[2] 的最小值,这样最后将其和 0 取最大值,就可以达到将至少一个靠儿子的节点修改成靠自己的节点了。
LCP 34. 二叉树染色⭐(每个节点 单独dp[k + 1]数组)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-shu-ran-se-UGC/description/

提示:
1 <= k <= 10
1 <= val <= 10000
1 <= 结点数量 <= 10000
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-shu-ran-se-UGC/solutions/1427646/by-codesheng-n-ewdf/
后序遍历。
对于每个节点,都有一个 dp[k + 1] 的数组,其中dp[i]表示到该节点连续有i个时的最大价值。
class Solution {
public int maxValue(TreeNode root, int k) {
return dfs(root, k)[k];
}
public int[] dfs(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) return new int[k + 1];
int[] dp = new int[k + 1];
int[] l = dfs(root.left, k), r = dfs(root.right, k);
// dp数组初始化
dp[0] = l[k] + r[k]; // 当前节点不选
// 枚举与当前节点连续的节点数量
for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1];
// 枚举左右子树的分配情况
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], l[j] + r[i - j - 1] + root.val);
}
}
return dp;
}
}
LCP 64. 二叉树灯饰⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/U7WvvU/description/

提示:
1 <= 节点个数 <= 10^5
0 <= Node.val <= 1
https://leetcode.cn/problems/U7WvvU/solutions/1846995/shu-xing-dp-by-endlesscheng-isuo/
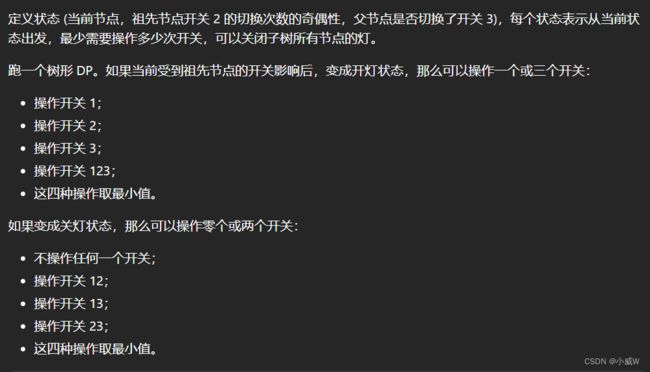
代码按照记忆化搜索来写。Java要用TreeNode当数组下标可以通过Map来实现。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, int[][]> map;
public int closeLampInTree(TreeNode root) {
map = new HashMap<>();
// 当前节点,祖先节点开关2的奇偶性,父节点是否切换了开关3
return dfs(root, false, false);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode node, boolean s2, boolean s3) {
if (node == null) return 0;
int x = s2? 1: 0, y = s3? 1: 0;
int[][] val = new int[2][2];
if (map.containsKey(node)) {
val = map.get(node);
if (val[x][y] > 0) return val[x][y];
} else {
map.put(node, val);
}
if ((node.val == 1) == (s2 == s3)) {
// 需要从开灯变成关灯状态
int res1 = dfs(node.left, s2, false) + dfs(node.right, s2, false)+ 1;
int res2 = dfs(node.left, !s2, false) + dfs(node.right, !s2, false) + 1;
int res3 = dfs(node.left, s2, true) + dfs(node.right, s2, true) + 1;
int res4 = dfs(node.left, !s2, true) + dfs(node.right, !s2, true) + 3;
val[x][y] = min(res1, res2, res3, res4);
} else {
// 需要保持关灯状态
int res1 = dfs(node.left, s2, false) + dfs(node.right, s2, false);
int res2 = dfs(node.left, !s2, false) + dfs(node.right, !s2, false) + 2;
int res3 = dfs(node.left, s2, true) + dfs(node.right, s2, true) + 2;
int res4 = dfs(node.left, !s2, true) + dfs(node.right, !s2, true) + 2;
val[x][y] = min(res1, res2, res3, res4);
}
return val[x][y];
}
public int min(int a, int b, int c, int d) {
if (b < a) a = b;
if (c < a) a = c;
if (d < a) a = d;
return a;
}
}
代码耗时 672 ms。