MyBatis - 初始化(九)加载Mapper接口与XML映射文件
MyBatis - 初始化(九)加载Mapper接口与XML映射文件
该系列文档是本人在学习 Mybatis 的源码过程中总结下来的,可能对各位读者会不太友好,阅读前需要对 MyBatis 和 Spring 有一定的了解。比较适合刚接触,会使用但是一直没去探究底层的同学。
MyBatis 版本:3.5.6
MyBatis-Spring 版本:2.0.3
MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 版本:2.1.4
该系列其他文档请查看:《 MyBatis 系列 - 导读》
一、MyBatis的初始化
在MyBatis初始化过程中,大致会有以下几个步骤:
- 创建
Configuration全局配置对象,会往TypeAliasRegistry别名注册中心添加Mybatis需要用到的相关类,并设置默认的语言驱动类为XMLLanguageDriver - 加载
mybatis-config.xml配置文件、Mapper接口中的注解信息和XML映射文件,解析后的配置信息会形成相应的对象并保存到Configuration全局配置对象中 - 构建
DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,通过它可以创建DefaultSqlSession对象,MyBatis中SqlSession的默认实现类
因为整个初始化过程涉及到的代码比较多,所以拆分成了四个模块依次对MyBatis的初始化进行分析:
- 《MyBatis - 初始化(八)加载 mybatis-config.xml 》
- 《MyBatis - 初始化(九)加载Mapper接口与XML映射文件》
- 《MyBatis - 初始化(十)SQL初始化(上)》
- 《MyBatis - 初始化(十一)SQL初始化(下)》
由于在MyBatis的初始化过程中去解析Mapper接口与XML映射文件涉及到的篇幅比较多,XML映射文件的解析过程也比较复杂,所以才分成了后面三个模块,逐步分析,这样便于理解
初始化(二)之加载Mapper接口与映射文件
在上一个模块已经分析了是如何解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件的,在最后如何解析
解析XML映射文件生成的对象主要如下图所示:
主要包路径:org.apache.ibatis.builder、org.apache.ibatis.mapping
主要涉及到的类:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder:根据配置文件进行解析,开始Mapper接口与XML映射文件的初始化,生成Configuration全局配置对象org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry:Mapper接口注册中心,将Mapper接口与其动态代理对象工厂进行保存,这里我们解析到的Mapper接口需要往其进行注册org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder:解析Mapper接口,主要是解析接口上面注解,其中加载XML映射文件内部会调用XMLMapperBuilder类进行解析org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder:解析XML映射文件org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder:解析XML映射文件中的Statement配置(org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant:Mapper构造器小助手,用于创建ResultMapping、ResultMap和MappedStatement对象org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMapping:保存org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMap:保存了org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement:保存了解析
解析入口
我们回顾上一个模块,在org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder中会解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的parse()->parseConfiguration(XNode root)->mapperElement(XNode parent)方法,那么我们来看看这个方法,代码如下:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// <0> 遍历子节点
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// <1> 如果是 package 标签,则扫描该包
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 获得包名
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 添加到 configuration 中
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else { // 如果是 mapper 标签
// 获得 resource、url、class 属性
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// <2> 使用相对于类路径的资源引用
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
// 获得 resource 的 InputStream 对象
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建 XMLMapperBuilder 对象
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 执行解析
mapperParser.parse();
// <3> 使用完全限定资源定位符(URL)
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
// 获得 url 的 InputStream 对象
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
// 创建 XMLMapperBuilder 对象
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url,configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 执行解析
mapperParser.parse();
// <4> 使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 获得 Mapper 接口
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
// 添加到 configuration 中
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException( "A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
遍历
- 如果是
package属性,对该包路径下的Mapper接口进行解析 - 否的的话,通过子节点的
resource属性或者url属性解析该映射文件,或者通过class属性解析该Mapper接口
通常我们是直接配置一个包路径,这里就查看上面第1种对Mapper接口进行解析的方式,第2种的解析方式其实在第1 种方式都会涉及到,它只是抽取出来了,那么我们就直接看第1种方式
首先将package包路径添加到Configuration全局配置对象中,也就是往其内部的MapperRegistry注册表进行注册,调用它的MapperRegistry的addMappers(String packageName)方法进行注册
我们来看看在MapperRegistry注册表中是如何解析的,在之前文档的Binding模块中有讲到过这个类,该方法如下:
public class MapperRegistry {
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
/**
* 用于扫描指定包中的Mapper接口,并与XML文件进行绑定
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
// <1> 扫描指定包下的指定类
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
// <2> 遍历,添加到 knownMappers 中
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// <1> 判断,必须是接口。
if (type.isInterface()) {
// <2> 已经添加过,则抛出 BindingException 异常
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// <3> 将Mapper接口对应的代理工厂添加到 knownMappers 中
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the mapper parser.
// If the type is already known, it won't try.
// <4> 解析 Mapper 的注解配置
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析 Mapper 接口上面的注解和 Mapper 接口对应的 XML 文件
parser.parse();
// <5> 标记加载完成
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// <6> 若加载未完成,从 knownMappers 中移除
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
<1>首先必须是个接口
<2>已经在MapperRegistry注册中心存在,则会抛出异常
<3>创建一个Mapper接口对应的MapperProxyFactory动态代理工厂
<4>【重要!!!】通过MapperAnnotationBuilder解析该Mapper接口与对应XML映射文件
MapperAnnotationBuilder
org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder:解析Mapper接口,主要是解析接口上面注解,加载XML文件会调用XMLMapperBuilder类进行解析
我们先来看看他的构造函数和parse()解析方法:
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
/**
* 全局配置对象
*/
private final Configuration configuration;
/**
* Mapper 构造器小助手
*/
private final MapperBuilderAssistant assistant;
/**
* Mapper 接口的 Class 对象
*/
private final Class<?> type;
public MapperAnnotationBuilder(Configuration configuration, Class<?> type) {
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".java (best guess)";
this.assistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.configuration = configuration;
this.type = type;
}
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 加载该接口对应的 XML 文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 解析 Mapper 接口的 @CacheNamespace 注解,创建缓存
parseCache();
// 解析 Mapper 接口的 @CacheNamespaceRef 注解,引用其他命名空间
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) { // 如果不是桥接方法
// 解析方法上面的注解
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
// #1347
InputStream inputStream = type.getResourceAsStream("/" + xmlResource);
if (inputStream == null) {
// Search XML mapper that is not in the module but in the classpath.
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e2) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
}
if (inputStream != null) {
// 创建 XMLMapperBuilder 对象
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(),
xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
// 解析该 XML 文件
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
}
在构造函数中,会创建一个MapperBuilderAssistant对象,Mapper 构造器小助手,用于创建XML映射文件中对应相关对象
parse()方法,用于解析Mapper接口:
- 获取Mapper接口的名称,例如
interface xxx.xxx.xxx,根据Configuration全局配置对象判断该Mapper接口是否被解析过 - 没有解析过则调用
loadXmlResource()方法解析对应的XML映射文件 - 然后解析接口的@CacheNamespace和@CacheNamespaceRef注解,再依次解析方法上面的MyBatis相关注解
注解的相关解析这里就不讲述了,因为我们通常都是使用XML映射文件,逻辑没有特别复杂,都在MapperAnnotationBuilder中进行解析,
loadXmlResource()方法,解析Mapper接口对应的XML映射文件:
- 根据Configuration全局配置对象判断该Mapper接口对应的XML映射文件是否被解析过,例如判断
namespace:xxx.xxx.xxx是否在已加载的资源中 - 获取XML映射文件资源,例如:获取
xxx/xxx/xxx.xml文件流,与接口名称对应 - 创建
XMLMapperBuilder对象,调用其parse()方法解析该XML映射文件
那么接下来我们来看看XMLMapperBuilder是如何解析XML映射文件的
XMLMapperBuilder
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder:解析XML映射文件
继承org.apache.ibatis.builder.BaseBuilder抽象类,该基类提供了类型转换以及一些其他的工具方法,比较简单,这里就不做展述了
构造方法
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
/**
* 基于 Java XPath 解析器
*/
private final XPathParser parser;
/**
* Mapper 构造器助手
*/
private final MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant;
/**
* 可被其他语句引用的可重用语句块的集合,实际上就是 Configuration 全局配置中的 sqlFragments
*
* 例如: ${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password
* - 首先会进入
XPathParser的构造方法,将XML映射文件解析成org.w3c.dom.Document对象,这里传入了XMLMapperEntityResolver作为解析实例对象,其中使用到本地的DTD文件 - 然后创建一个 Mapper 构造器助手
MapperBuilderAssistant对象 - 其中一些属性都是从Configuration全局配置对象中获取的,例如:
typeAliasRegistry、typeHandlerRegistry、sqlFragments
parse方法
parse()方法用于解析XML映射文件,在MapperAnnotationBuilder中被调用,代码如下:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parse() {
// <1> 判断当前 Mapper 是否已经加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// <2> 解析 `<1> 根据Configuration全局配置判断当前XML映射文件是否已经加载过,例如resource为:xxx/xxx/xxx.xml
<2> 解析 configurationElement方法中讲解
<3> 标记该XML映射文件已经加载过,往Configuration全局配置添加该字段文件,例如添加:xxx/xxx/xxx.xml
<4> 绑定 Mapper 到该命名空间,避免在MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource方法中重复加载该XML映射文件
<5> 解析待定的
这里我们来看一下configurationElement(XNode context)方法是如何解析XML映射文件中的
configurationElement方法
configurationElement(XNode context)方法就是来解析XML映射文件中我们定义的SQL相关信息,代码如下:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// <1> 获得 namespace 属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// <2> 解析 <1> 获得 namespace 属性,如果 XML 映射文件中定义的 namespace 和接口名称不相等会抛出异常<2> 解析 cacheRefElement方法 <3> 解析 cacheElement方法 <4> 解析 resultMapElements方法 <5> 解析 sqlElement方法 <6> 解析 节点,调用`buildStatementFromContext方法
cacheRefElement方法
cacheRefElement(XNode context)方法用于解析XML映射文件中的
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// <1> 获得指向的 namespace 名字,并添加到 configuration 的 cacheRefMap 中
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
// <2> 创建 CacheRefResolver 对象
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
// 执行解析,获取引用的缓存对象到自己这里
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}
解析当前XML映射文件的缓存配置,将当前namespace缓存引用其他的namespace的缓存形成映射关系保存在Configuration全局配置对象中
获取引用的namespace的缓存实例,将其设置到MapperBuilderAssistant构造器助手中,在后续构建相关对象时使用
cacheElement方法
cacheElement(XNode context)方法用于XML映射文件中的
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// <1> 获得负责存储的 Cache 实现类
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// <2> 获得负责过期的 Cache 实现类
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
// <3> 获得 flushInterval、size、readWrite、blocking 属性
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// <4> 获得 Properties 属性
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// <5> 创建 Cache 对象
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
解析该节点的相关配置,然后通过MapperBuilderAssistant构造器小助手创建一个Cache缓存实例,添加到Configuration全局配置对象中,并设置到构造器助手中,在后续构建相关对象时使用
resultMapElements方法
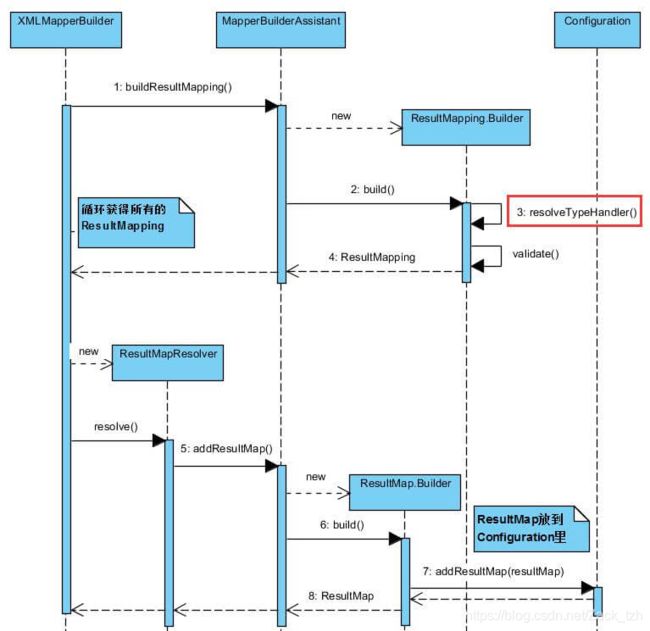
resultMapElements(List方法用于解析
resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List方法逐个解析生成ResultMap对象
整体的流程图:
例如这样配置RresultMap:
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="StudentResult" type="Student">
<result column="id" property="studentId" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result column="teacher_id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="teacher_name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="teacher_age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
association>
resultMap>
mapper>
resultMapElement方法代码如下:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings, Class<?> enclosingType) throws Exception {
// 获取当前线程的上下文
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// <1> 获得 type 属性
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type", resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType", resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 获得 type 对应的类
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
if (typeClass == null) {
// 从 enclosingType Class 对象获取该 property 属性的 Class 对象
typeClass = inheritEnclosingType(resultMapNode, enclosingType);
}
Discriminator discriminator = null;
// 创建 ResultMapping 集合
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加父 ResultMap 的 ResultMapping 集合
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// <2> 遍历 关于
resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List方法的入参分别是:
- 当前节点Node的封装,封装成
XNode便于操作 - 继承的ResultMap所对应的ResultMapping的集合,可以通过extend属性配置继承哪个ResultMap,没有继承的话就是空集合
- 所属的ResultMap的类型,例如
处理逻辑:
- 获得 type 属性,生成该ResultMap对应Class对象,如果没有定义type属性,则可能是
- 遍历
- 如果是
processConstructorElement方法进行解析,再获取它的子节点生成对应的RequestMapping对象,这些RequestMapping对象会添加ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR标记,如果是ResultFlag.ID标记,这些对象会在实例化类时,注入到构造方法中 - 如果是
processDiscriminatorElement方法进行解析,创建一个Discriminator选择器对象,用于可以使用结果值来决定这个属性使用哪个ResultMap,基于 - 其他节点,则调用
buildResultMappingFromContext方法进行解析,如果是
- 如果是
- 创建
ResultMapResolver对象,调用其resolve()方法执行解析,内部调用MapperBuilderAssistant构造器小助手的addResultMap来生成ResultMap对象的
上面的2.1和2.2并不复杂,感兴趣的小伙伴可以查看相关方法,我们来看下2.3是如何解析成ResultMapping对象的
buildResultMappingFromContext方法
buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class resultType, List方法将
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags)
throws Exception {
String property;
// 解析各种属性
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
// 解析 依次从该节点中获取相关属性
- 这里我们看到
nestedResultMap的获取,如果这个是processNestedResultMappings方法解析成ResultMap对象,然后返回该对象的id(没有定义会自动生成),这样这个RequestMapping对象就会关联这个ResultMap对象了,这个方法内部也是调用resultMapElement方法生成ResultMap对象的,可以回过头再看下这个方法 - 最后通过
MapperBuilderAssistant构造器小助手的buildResultMapping方法根据这些属性构建一个ResultMapping对象并返回
整个的ResultMap对象的解析过程到这里就结束了,关于MapperBuilderAssistant在后续会讲到,接下来我们来看看
sqlElement方法
sqlElement(List方法用于解析所有的sqlElement(List方法,代码如下:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// <1> 遍历所有 这里仅仅是将该Map对象中(该对象保存与Configuration全局配置对象中),后续解析其他SQL语句中会使用到,例如查询语句中使用了
buildStatementFromContext方法
buildStatementFromContext(List方法用于解析 节点
内部调用buildStatementFromContext(List方法逐个解析生成MappedStatement对象,代码如下:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// <1> 遍历 为该节点创建XMLStatementBuilder对象,然后调用其parseStatementNode()解析成MappedStatement对象,解析过程在下面的XMLStatementBuilder中讲到
XMLStatementBuilder
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder:解析XML映射文件中的Statement配置
也就是解析 节点,解析过程在parseStatementNode()方法中
构造方法
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private final MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant;
/**
* 当前 XML 节点,例如:、parseStatementNode方法
parseStatementNode()方法用于解析 Statement 对应节点,也就是 节点,代码如下:
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 获得 id 属性,编号。
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// 获得 databaseId , 判断 databaseId 是否匹配
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// 获取该节点名称
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// <1> 根据节点名称判断 SQL 类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 是否为 Select 语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// <2> 是否清空缓存
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// <3> 是否使用缓存
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
// <4> 将该节点的子节点 and were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
/*
* <8>
* 1. 如果上面存在 解析方法有点长,我们一步一步来看
- 根据节点名称设置SQL语句类型,SqlCommandType:
UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH - 获取
flushCache属性,是否清空缓存,非查询语句默认都是true - 获取
useCache属性,是否开启缓存,查询语句默认为true - 创建
XMLIncludeTransformer对象,调用其applyIncludes方法将sqlFragments(前面已经将所有的 - 获取
parameterType属性,参数类型,转换成Class对象 - 获取
lang属性,LanguageDriver语言驱动器,默认为XMLLanguageDriver - 将该节点的
processSelectKeyNodes方法中可以看到,该过程也会生成一个MappedStatement对象,生成的对象的 id 为statementId+'!selectKey' - 解析
useGeneratedKeys属性,获取 SelectKeyGenerator 生成器,如果第7步没有生成才会进入这里,直接返回Jdbc3KeyGenerator单例 - 根据
XMLLanguageDriver语言驱动创建SqlSource对象,通过这个对象可以获取到对应的SQL语句,在后面的《MyBatis初始化之SQL初始化》分析该创建过程 - 获取
statementType属性,Statement类型,默认PREPARED - 获取其他的一下相关信息,例如:
timeout、resultMap、keyProperty、keyColumn等属性,其中配置的resultType也会转换成ResultMap对象 - 通过
MapperBuilderAssistant构造器小助手根据这些属性信息构建一个MappedStatement对象
MapperBuilderAssistant
org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant:Mapper构造器小助手,在前面整个XML映射文件的解析过程中,所需要创建ResultMapping、ResultMap和MappedStatement对象都是通过这个助手来创建的,那么我们来看看它提供了哪些功能
构造方法
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
/**
* 当前 Mapper 命名空间
*/
private String currentNamespace;
/**
* 资源引用的地址
* 解析Mapper接口:xxx/xxx/xxx.java (best guess)
* 解析Mapper映射文件:xxx/xxx/xxx.xml
*/
private final String resource;
/**
* 当前 Cache 对象
*/
private Cache currentCache;
/**
* 是否未解析成功 Cache 引用
*/
private boolean unresolvedCacheRef; // issue #676
public MapperBuilderAssistant(Configuration configuration, String resource) {
super(configuration);
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
this.resource = resource;
}
}
这个小助手是为了 XMLMapperBuilder 和 MapperAnnotationBuilder 都能调用到一些公用方法
useCacheRef方法
前面在XMLMapperBuilder的cacheRefElement方法解析
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true; // 标记未解决
// <1> 获得 Cache 对象
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
// 获得不到,抛出 IncompleteElementException 异常
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.");
}
// 记录当前 Cache 对象
currentCache = cache;
unresolvedCacheRef = false; // 标记已解决
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.", e);
}
}
入参namespace:所引用的缓存所在的namespace
根据该namespace获取到其缓存实例对象,然后设置为当前需要使用的缓存实例
useNewCache方法
前面在XMLMapperBuilder的cacheElement方法解析
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval,
Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) {
// <1> 创建 Cache 对象
// 缓存实例默认为 PerpetualCache 类型,Cache 装饰器默认为 LruCache
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace).implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval).size(size).readWrite(readWrite).blocking(blocking).properties(props)
.build();
// <2> 添加到 configuration 的 caches 中
configuration.addCache(cache);
// <3> 赋值给 currentCache
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
- 根据节点中的相关信息通过
CacheBuilder构造器创建一个缓存实例(被装饰的Cache实例),如何构建的代码有点长,这里就不讲述了,感兴趣的小伙伴可以查看相关方法,都已经注释好了 - 将缓存实例添加到
Configuration全局对象中 - 设置为当前需要使用的缓存实例
buildResultMapping方法
前面在XMLMapperBuilder的resultMapElement方法调用的buildResultMappingFromContext方法中有调用这个方法,用来创建一个RequestMapping对象,代码如下:
public ResultMapping buildResultMapping(Class<?> resultType, String property, String column, Class<?> javaType,
JdbcType jdbcType, String nestedSelect, String nestedResultMap, String notNullColumn, String columnPrefix,
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler, List<ResultFlag> flags, String resultSet, String foreignColumn,
boolean lazy) {
// <1> 解析对应的 Java Type
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveResultJavaType(resultType, property, javaType);
// 解析对应的 TypeHandler ,一般不会设置
TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler);
List<ResultMapping> composites;
// <2> 解析组合字段名称成 ResultMapping 集合,涉及「关联的嵌套查询」
if ((nestedSelect == null || nestedSelect.isEmpty()) && (foreignColumn == null || foreignColumn.isEmpty())) {
composites = Collections.emptyList();
} else {
// RequestMapping 关联了子查询,如果 column 配置了多个则一一再创建 RequestMapping 对象
composites = parseCompositeColumnName(column);
}
// <3> 创建 ResultMapping 对象
return new ResultMapping.Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass).jdbcType(jdbcType)
.nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true))
.nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true)).resultSet(resultSet)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance).flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList<>() : flags)
.composites(composites).notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn))
.columnPrefix(columnPrefix).foreignColumn(foreignColumn).lazy(lazy).build();
}
入参有点多,不过根据名称可以知道其意思,大致逻辑如下:
-
解析对应的 Java Type 和 TypeHandler 的 Class 对象
-
如果嵌套的子查询存在组合字段,则一一解析成 ResultMapping 对象,例如需要在返回的结果集中取多个列作为嵌套查询的入参,那么你需要配置多个映射关系
例如子查询的入参对象有两个属性,分别是name和age,而上一层查询从数据库返回的列名是studentName和studentAge,那么你需要在嵌套查询配置column属性为:{name=studentName,age=studentAge},不然没有映射关系无法设置子查询的入参,这样就会为该属性创建两个ResultMapping添加到
composites集合中 -
调用
applyCurrentNamespace方法,拼接命名空间 -
调用
parseMultipleColumnNames方法,将字符串(以逗号分隔)解析成集合,作用: 默认情况下,在至少一个被映射到属性的列不为空时,子对象才会被创建。 -
通过
ResultMapping.Builder构建一个ResultMapping对象
addResultMap方法
前面在XMLMapperBuilder的resultMapElement方法使用ResultMapResolver生成ResultMap对象时会调用这个方法,用来解析生成ResultMap对象,代码如下:
public ResultMap addResultMap(String id, Class<?> type, String extend, Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings, Boolean autoMapping) {
// <1> 获得 ResultMap 编号,即格式为 `${namespace}.${id}`
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
// <2.1> 获取完整的父 ResultMap 属性,即格式为 `${namespace}.${extend}`。从这里的逻辑来看,貌似只能获取自己 namespace 下的 ResultMap 。
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
// <2.2> 如果有父类,则将父类的 ResultMap 集合,添加到 resultMappings 中。
if (extend != null) {
// <2.2.1> 获得 extend 对应的 ResultMap 对象。如果不存在,则抛出 IncompleteElementException 异常
// 所以说 - 调用
applyCurrentNamespace方法拼接namespace与id,获得ResultMap的唯一编号,格式为${namespace}.${id} - 获得父ResultMap的唯一编号
extend,格式为${namespace}.${extend}extend为null则直接忽略- 否则获取对应的ResultMap对象,则将
extend的ResultMapping集合和自己的ResultMapping集合进行合并
- 通过
ResultMap.Builder构建一个ResultMap对象,并添加到Configuration全局配置中
addMappedStatement方法
在XMLStatementBuilder的parseStatementNode方法中会调用该方法,用来构建一个MappedStatement对象,代码如下:
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(String id, SqlSource sqlSource, StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Integer fetchSize, Integer timeout, String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType, String resultMap, Class<?> resultType, ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache, boolean useCache, boolean resultOrdered, KeyGenerator keyGenerator, String keyProperty,
String keyColumn, String databaseId, LanguageDriver lang, String resultSets) {
// <1> 如果的指向的 Cache 未解析,抛出异常
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
// <2> 获得 id 编号,格式为 `${namespace}.${id}`
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
// 是否为查询语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// <3> 创建 MappedStatement.Builder 对象
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource,
sqlCommandType).resource(resource).fetchSize(fetchSize).timeout(timeout).statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator).keyProperty(keyProperty).keyColumn(keyColumn).databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang).resultOrdered(resultOrdered).resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id)).resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect)).cache(currentCache);
// <4> 生成 ParameterMap 对象
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
// <5> 创建 MappedStatement 对象
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// <6> 添加到 configuration 中
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
入参有点多,这里就不一一进行说明了,通过其名称大致可以知道其意思
-
如果的指向的 Cache 未解析,抛出异常
-
获得
MappedStatement的唯一编号id,格式为${namespace}.${id} -
创建
MappedStatement.Builder对象 -
创建
ParameterMap对象,进入getStatementParameterMap方法可以看到,ParameterMap的Class type属性设置为入参类型,String id设置为statementIdparameterMap属性 -
通过MappedStatement.Builder构建一个MappedStatement对象,并添加到Configuration全局配置中
RequestMapping
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMapping:保存ResultMap相关子节点的信息,也就是 Java Type 与 Jdbc Type 的映射信息
内部定义了Builder构造器,使用构建者模式创建实例对象,有以下属性:
public class ResultMapping {
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* Java 字段
*/
private String property;
/**
* JDBC 列名
*/
private String column;
/**
* Java 类型
*/
private Class<?> javaType;
/**
* JDBC 类型
*/
private JdbcType jdbcType;
/**
* 类型处理器
*/
private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler;
/**
* 对应的 resultMapId
* 例如 构建过程这里就不列出来了,最终会生成以上这些属性
ResultMap
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMap:保存了
内部定义了Builder构造器,使用了构建者模式创建实例对象,构建的时候进行了相关属性的分类,有以下属性:
public class ResultMap {
/**
* Configuration 对象
*/
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* ResultMap 对象
*/
private String id;
/**
* 类型
*/
private Class<?> type;
/**
* ResultMapping 集合
*/
private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
/**
* ID ResultMapping 集合
*
* 当 idResultMappings 为空时,使用 {@link #resultMappings} 赋值
*/
private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;
/**
* 构造方法的入参 ResultMapping 集合
* 根据参数名称已经排序好了
*
* 和 {@link #propertyResultMappings} 不存在相同元素
*/
private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;
/**
* 属性 ResultMapping 集合
*/
private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;
/**
* 数据库的字段集合(全部大写)
*/
private Set<String> mappedColumns;
/**
* Java 对象的属性集合
*/
private Set<String> mappedProperties;
/**
* Discriminator 选择器对象
*/
private Discriminator discriminator;
/**
* 是否有内嵌的 ResultMap
*/
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
/**
* 是否有嵌套关联的子查询
*/
private boolean hasNestedQueries;
/**
* 是否开启自动匹配
*
* 如果设置这个属性,MyBatis将会为这个ResultMap开启或者关闭自动映射。这个属性会覆盖全局的属性
* autoMappingBehavior。默认值为:unset。
*/
private Boolean autoMapping;
private ResultMap() {
}
}
构建过程这里就不列出来了,最终会生成以上这些属性
MappedStatement
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement:保存了解析 标签内的SQL语句所生成的所有信息
内部定义了Builder构造器,使用了构建者模式构建对象,有以下属性:
public final class MappedStatement {
/**
* XML 映射文件路径,例如:xxx/xxx/xxx.xml
*/
private String resource;
/**
* 全局配置对象
*/
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* 唯一编号:`${namespace}.${id}`
*/
private String id;
/**
* 这是一个给驱动的建议值,尝试让驱动程序每次批量返回的结果行数等于这个设置值
* 默认值为未设置(unset)(依赖驱动)
*/
private Integer fetchSize;
/**
* 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数
* 默认值为未设置(unset)(依赖数据库驱动)
*/
private Integer timeout;
/**
* Statement 的类型:STATEMENT PREPARED CALLABLE,默认 PREPARED
* 分别对应:Statement PreparedStatement CallableStatement
*/
private StatementType statementType;
private ResultSetType resultSetType;
/**
* SQL 相关信息
*/
private SqlSource sqlSource;
/**
* 缓存对象
*/
private Cache cache;
private ParameterMap parameterMap;
/**
* ResultMap对象
* 配置多个时需要加上 namespace 并以逗号分隔
*/
private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;
/**
* 是否清空缓存
*/
private boolean flushCacheRequired;
/**
* 是否使用缓存
*/
private boolean useCache;
/**
* 这个设置仅针对嵌套结果 select 语句,默认值:false
* 如果为 true,将会假设包含了嵌套结果集或是分组,当返回一个主结果行时,就不会产生对前面结果集的引用
* 这就使得在获取嵌套结果集的时候不至于内存不够用
*/
private boolean resultOrdered;
/**
* SQL 语句类型
*/
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
/**
* key 的生成器
*/
private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
/**
* key 的生成器的 Java 属性
*/
private String[] keyProperties;
/**
* key 的生成器的 column 列名
*/
private String[] keyColumns;
/**
* 是否有内嵌的 ResultMap
*/
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
/**
* 数据库表示
*/
private String databaseId;
/**
* 日志对象
*/
private Log statementLog;
/**
* 语言驱动,默认为XMLLanguageDriver
*/
private LanguageDriver lang;
/**
* 这个设置仅适用于多结果集的情况
* 它将列出语句执行后返回的结果集并赋予每个结果集一个名称,多个名称之间以逗号分隔
*/
private String[] resultSets;
MappedStatement() {
// constructor disabled
}
}
构建过程这里就不列出来了,最终会生成以上这些属性
其中SqlSource是通过XMLLanguageDriver语言驱动创建的,可以回到XmlStatementBuilder的**parseStatementNode()**方法看看,在后面的《MyBatis初始化之SQL初始化》分析整个创建过程
总结
本分分析了MyBatis在初始化时加载Mapper接口与XML映射文件的整个过程
- 在
XMLConfigBuilder中将用户配置的Mapper接口所在包路径package添加到MapperRegistry注册表中 - 在
MapperRegistry注册表中会对包下的所有Mapper接口进行解析,每个接口都会创建对应的MapperProxyFactory动态代理对象工厂,并保存,也会通过MapperAnnotationBuilder对该接口进行解析,解析过程:- 首先通过该Mapper接口的名称获取对应的XML映射文件,获取到该文件资源进行加载解析,解析后的对象都会跟XML映射文件中配置的
namespace属性关联,所以XML映射文件的名称要与Mapper接口的名称保持一致,配置的namespace属性要与接口的全名保持一致 - 然后解析Mapper接口的MyBatis相关注解
- 首先通过该Mapper接口的名称获取对应的XML映射文件,获取到该文件资源进行加载解析,解析后的对象都会跟XML映射文件中配置的
- 解析XML映射文件的过程中是在
XMLMapperBuilder中进行的,会使用到MapperBuilderAssistant小助手用于创建ResultMapping、ResultMap和MappedStatement对象 - 其中解析
XMLStatementBuilder对象中进行
在XMLStatementBuilder解析上面标签的时候需要通过XMLLanguageDriver语言驱动创建SqlSource对象,这个过程涉及到的篇幅有点多,会在接下来的《MyBatis初始化(三)之SQL初始化(上)》中开始分析
最终所有的MyBatis配置、Mapper接口和XML映射文件生成的相应对象都保存在了Configuration全局配置对象中,那么接下来我们来看看SQL语句在MyBatis中是如何初始化的
参考文章:《MyBatis 源码分析》
--------------最后感谢大家的阅读,愿大家技术越来越流弊!--------------
![]()
--------------也希望大家给我点支持,谢谢各位大佬了!!!--------------