【权限管理】使用spring security 实现默认登录,源码解析
【权限管理】使用spring security 实现默认登录,源码解析
其他文章可以通过菜单查看:【BookCase 菜单】
1、前言
在springboot 之前使用shiro实现权限管理的比较多,现在使用springboot 整合spring security 更方便。
2、实现
- 创建子项目 bookcase-auth
- 添加配置
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymingroupId>
<artifactId>knife4j-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
dependency>
在springboot 中实现spring sercurity 只需要增加 spring-boot-starter-security 即可,里面已经包含所需的所有依赖。
- 增加knife4j 配置
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2WebMvc
public class Knife4jConfig {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String moduleName;
@Bean(value = "defaultApi2")
public Docket defaultApi2() {
Docket docket = new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(new ApiInfoBuilder()
//.title("swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo RESTful APIs")
.description("# swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo RESTful APIs")
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.xx.com/")
.contact("[email protected]")
.version("1.0")
.build())
//分组名称
.groupName(moduleName)
.select()
//这里指定Controller扫描包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.fans.auth.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
return docket;
}
}
- 增加spring security 配置
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 覆盖此方法来配置HttpSecurity。
* 通常子类不应该通过调用super调用这个方法,因为它可能会覆盖它们的配置
*
* The default configuration is:
* http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().and().formLogin().and().httpBasic();
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//取消CSRF保护
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
//默认的HTTP Basic Auth认证
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
//默认的表单登录
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
//对 /api 路径下的所有接口进行验证,需要权限`ROLE_USER`
.authorizeRequests(req -> req
.antMatchers("/auth/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
);
}
/**
* 覆盖此方法来配置WebSecurity。 例如,如果您希望忽略某些请求。
* 在这个方法中指定的端点将被Spring Security忽略,这意味着它不会保护它们免受CSRF、XSS、Clickjacking等的影响。
* 相反,如果您想保护端点免受常见漏洞的侵害,请参阅configure(HttpSecurity)和HttpSecurity
*
* @param web
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web
.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/error",
"/resources/**",
"/static/**",
"/public/**",
"/h2-console/**",
"/swagger-ui.html",
"/swagger-ui/**",
"/v3/api-docs/**",
"/webjars/**",
"/v2/api-docs/**",
"/doc.html",
"/swagger-resources/**")
.requestMatchers(PathRequest.toStaticResources().atCommonLocations());
}
}
这里配置的两个方法主要作用是 :
1、configure(WebSecurity web) 配置无需拦截的URL,主要是一些静态资源访问和swagger的配置相。
2、void configure(HttpSecurity http) 配置对鉴权方法的管理,这里使用默认的鉴权页面和默认的表单提交方式。鉴权的URL为/auth 下子路径。其他的访问都需要进行权限验证。
- 编写测试方法
无需登录验证:
@RestController
@Api(value = "登录验证")
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/auth")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
@ApiOperation("hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,security";
}
}
登录验证:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@Api(value = "测试验证")
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
@ApiOperation("hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,test security";
}
}
- 其他配置
application.yml 中配置端口号进行访问:
server:
port: 8083
spring:
application:
name: bookcase-auth
3、执行测试
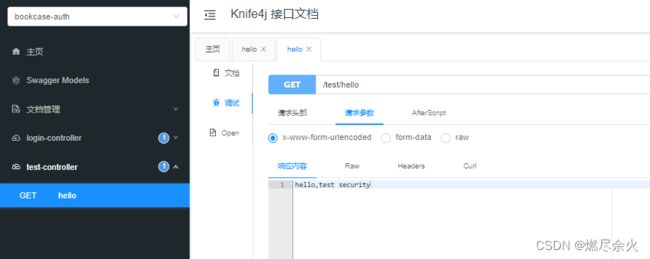
访问swagger并进行测试:
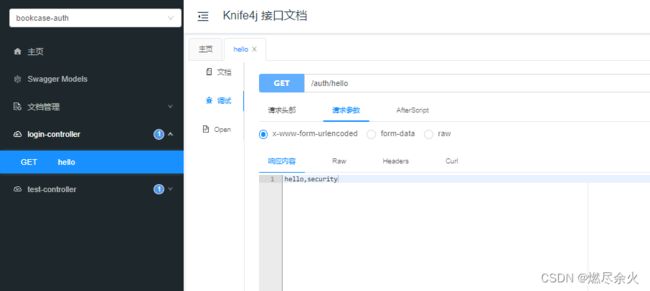
其中login 无需登录可以直接得到结果。
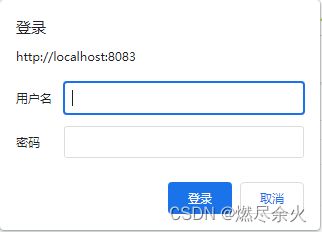
test 需要登录会进行弹窗:
4、原理分析
spring security 是怎么实现默认的登录功能?
假如按照原生的cookie/session 如何实现权限管理,我们会使用filter 进行拦截,并进行权限验证。spring security 也是这样实现的。
Spring Security 使用 AOP思想,基于Sevlet过滤器为核心的安全框架。
我们想要完成访问服务器资源的请求,首先就需要spring security的过滤器链。而默认的过滤器链中实现登录验证的class就是 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter。
查看源码:
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
通过构造器我们可以看到默认的访问时POST方式,URL为 /login。
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
// 获取用户名 username
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
// 获取密码 password
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
// 封装token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
// 验证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
这个时候就发现从封装token到验证就比较复杂,跳过来跳过去。
我们想要明白就需要知道spring security 的结构:

图片来自网络。
当我们访问资源的时候,首先经过过滤器链,找到匹配的过滤器之后,封装token,并交给权限管理器authenticationManger 管理,遍历所有的认证方式,找到对应的认证方式,通过UserDetailService 找到正确的密码进行比对,相等即可验证成功,否则验证失败。
5、断点调试(断点调试不要使用Swagger)
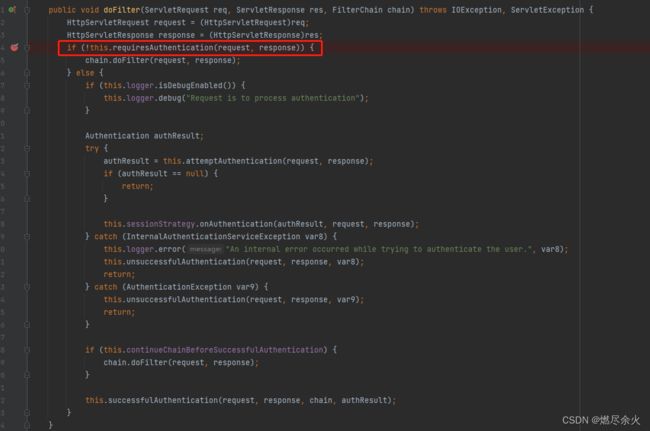
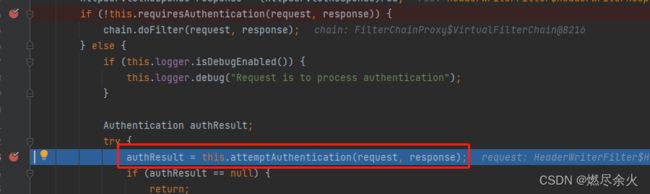
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 中并没有filter的方法,我们通过查找父类
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware 找到 了 doFilter方法,此处打断点:
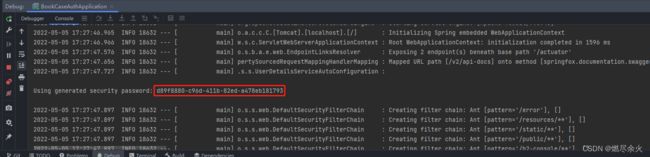
当我们再次测试以上/test/hello 访问的时候,可以看到断点到达此处。
直接执行,这里我们不是登录的url,会重定向到访问页面。
输入账号密码后就可以判断通过:
进入UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,
1、这里首先封装 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
2、然后获取 this.getAuthenticationManager() ,其实就是 AuthenticationManager 实现 ProviderManager;
3、在后鉴权 ProviderManager :: authenticate 方法,这里会遍历所有的 AuthenticationProvider ,当前只有一个DaoAuthenticationProvider,但是实际鉴权是在父抽象类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider中,通过 retrieveUser 方法找回用户信息。
4、UserDetailsService 的实现类 InMemoryUserDetailsManager (其实是实现 UserDetailsManager,UserDetailsManager继承了 UserDetailsService),然后拿到UserDetails ,并重新 new User(…),这里是封装原始生成的账号密码信息。
5、检查当前账号是否开启,是否过期,是否锁定。
6、比较用户名密码是否一致,一致验证成功。
7、之后再次检查是否过期,并放入缓存。
8、再后createSuccessAuthentication对密码重新加密,并使用父类方法createSuccessAuthentication 重新封装 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken。这里设置鉴权成功 super.setAuthenticated(true);
9、以上已鉴权成功,之后放入SecurityContext,SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
10、记录登录成功 RememberMeServices,但是这个是NullRememberMeServices ,所以没有记录。

最终鉴权位置:
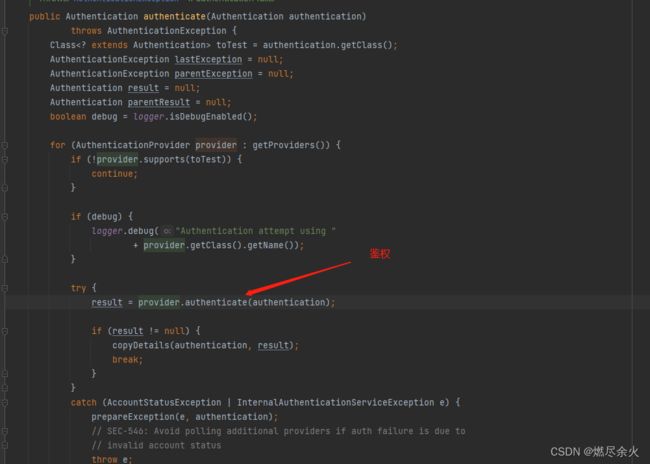
有点多就不截图了,此处为AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider authenticate 方法:
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// ...
// 查询缓存
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 获取用户信息
user = retrieveUser(username,(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
// 5、检查是否禁用,锁定,是否开启
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 6、比较是否相等
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 7、放入缓存
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
// 8、成功后重新封装token,并设置鉴权成功
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
拓展:由于是遍历所有的 AuthenticationProvider ,我们需要其他方式鉴权的时候,其实只需要添加AuthenticationProvider即可。
以上为默认鉴权的解析。谢谢观看