李沐动手学深度学习第四章-4.5权重衰减(正则化)
1. 高维线性回归
一个简单的例子来演示权重衰减。
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l选择标签是关于输入的线性函数。 标签同时被均值为0,标准差为0.01高斯噪声破坏。 为了使过拟合的效果更加明显,我们可以将问题的维数增加到d=200, 并使用一个只包含20个样本的小训练集。
n_train, n_test, num_inputs, batch_size = 20, 100, 200, 5
true_w, true_b = torch.ones((num_inputs, 1)) * 0.01, 0.05
train_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_train)
train_iter = d2l.load_array(train_data, batch_size)
test_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_test)
test_iter = d2l.load_array(test_data, batch_size, is_train=False)2. 从零开始实现
定义一个函数来随机初始化模型参数
def init_params():
w = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(num_inputs, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
return [w, b]定义L2范数惩罚
def l2_penalty(w):
return torch.sum(w.pow(2)) / 2定义训练代码实现
从 3节以来,线性网络和平方损失没有变化, 所以我们通过d2l.linreg和d2l.squared_loss导入它们。 唯一的变化是损失现在包括了惩罚项。
def train(lambd):
w, b = init_params()
net, loss = lambda X: d2l.linreg(X, w, b), d2l.squared_loss
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
# 增加了L2范数惩罚项,
# 广播机制使l2_penalty(w)成为一个长度为batch_size的向量
l = loss(net(X), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w)
l.sum().backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
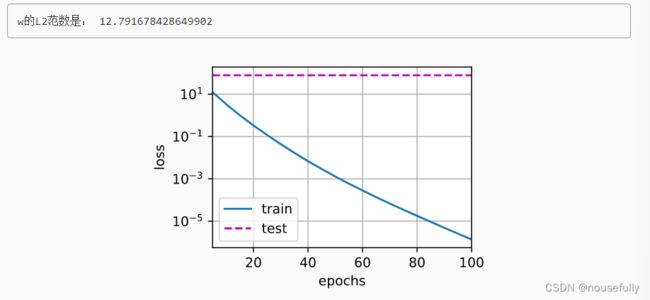
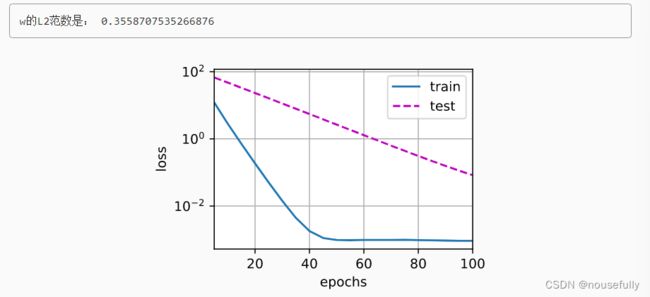
print('w的L2范数是:', torch.norm(w).item())忽略正则化直接训练
train(lambd=0)使用权重衰减
train(lambd=3)3. 简洁实现
在下面的代码中,我们在实例化优化器时直接通过weight_decay指定weight decay超参数。 默认情况下,PyTorch同时衰减权重和偏移。 这里我们只为权重设置了weight_decay,所以偏置参数b不会衰减。
def train_concise(wd):
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
for param in net.parameters():
param.data.normal_()
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
# 偏置参数没有衰减
trainer = torch.optim.SGD([
{"params":net[0].weight,'weight_decay': wd},
{"params":net[0].bias}], lr=lr)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
trainer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.mean().backward()
trainer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1,
(d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('w的L2范数:', net[0].weight.norm().item())这些图看起来和我们从零开始实现权重衰减时的图相同。 然而,它们运行得更快,更容易实现。 对于更复杂的问题,这一好处将变得更加明显。
train_concise(0)train_concise(3)4. 小结
-
正则化是处理过拟合的常用方法:在训练集的损失函数中加入惩罚项,以降低学习到的模型的复杂度。
-
保持模型简单的一个特别的选择是使用L2惩罚的权重衰减。这会导致学习算法更新步骤中的权重衰减。
-
权重衰减功能在深度学习框架的优化器中提供。
-
在同一训练代码实现中,不同的参数集可以有不同的更新行为。