C++初级项目-webserver(1)
1.引言
Web服务器是一个基于Linux的简单的服务器程序,其主要功能是接收HTTP请求并发送HTTP响应,从而使客户端能够访问网站上的内容。本项目旨在使用C++语言,基于epoll模型实现一个简单的Web服务器。选择epoll模型是为了高效地处理大量并发连接。
2.项目概览
这个项目的目标是实现一个简单的Web服务器,可以处理基本的HTTP请求并发送相应的HTTP响应。项目结构包括服务器初始化、Epoll模型的使用、事件处理循环、HTTP请求处理、文件发送、错误处理等关键模块。技术和工具方面使用了C++语言、epoll模型以及socket编程。
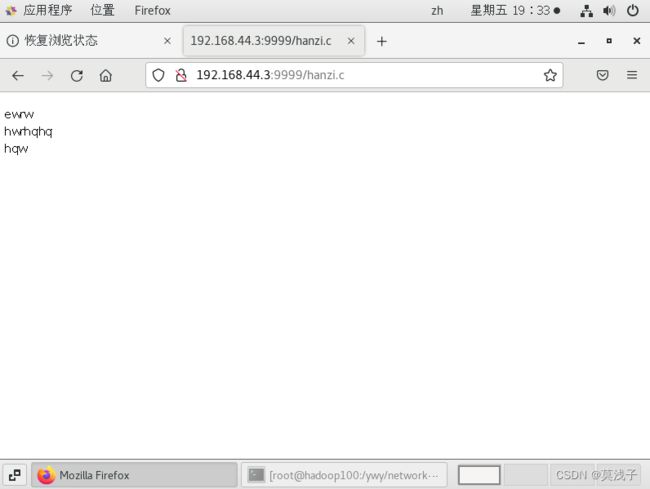
根据这个服务器可以实现下面的功能,打开Linux环境下的文件。
在浏览器上面的搜索栏输入http://192.168.44.3:9999/hanzi.c
192.168.44.3是Linux环境的本机IP地址,9999是端口号,hanzi.c是打开的文件名
3.Epoll模型
1. 基本概念和优势
-
Epoll简介:Epoll(Event Poll)是Linux内核为处理大量文件描述符而设计的一种高效的I/O事件通知机制。它允许程序监视多个文件描述符上的事件状态,而无需轮询这些文件描述符。
-
优势:
- 高效的事件通知机制:Epoll使用基于事件的机制,只有当事件发生时才会通知应用程序,避免了轮询的开销。
- 支持大量并发连接: 适用于处理大量并发连接的场景,能够有效管理数以千计的文件描述符。
- 适用于非阻塞I/O: 与非阻塞模型结合使用,使得应用程序能够同时处理多个连接而不被阻塞。
2. 创建Epoll树和添加文件描述符
// 创建epoll树
int epfd = epoll_create(1024);
if (epfd < 0) {
perror("epoll_create error");
close(lfd);
return -1;
}
// 将监听文件描述符lfd添加到epoll树上
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = lfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, lfd, &ev);
- epoll_create: 创建一个epoll实例,返回一个用于标识该实例的文件描述符。
- epoll_ctl: 控制epoll实例的行为,可以用于注册、修改或删除文件描述符。
3. Epoll事件处理循环
int nready;
struct epoll_event events[1024];
while (1) {
// 等待事件发生
nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
if (nready < 0) {
if (errno == EINTR) {
continue;
}
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
int sockfd = events[i].data.fd;
// 处理监听文件描述符lfd上的事件
if (sockfd == lfd) {
// 接受新的客户端连接
int cfd = Accept(lfd, NULL, NULL);
// 设置cfd为非阻塞
int flag = fcntl(cfd, F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(cfd, F_SETFL, flag);
// 将新的cfd添加到epoll树上
ev.data.fd = cfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, cfd, &ev);
} else {
// 处理客户端数据
http_request(sockfd);
}
}
}
- epoll_wait: 等待事件发生,返回就绪事件的数量。
- events数组: 存储发生事件的文件描述符和事件类型。
- EPOLLIN: 表示文件描述符上有可读数据。
- Accept函数: 用于接受新的客户端连接。
- fcntl函数: 用于设置文件描述符的属性,将其设置为非阻塞。
通过这样的Epoll模型,服务器能够高效地处理并发连接,只在有事件发生时才进行相应的处理,避免了不必要的轮询。
4. 事件处理循环
1. 服务器主循环
服务器的主循环是一个持续运行的事件处理循环,通过调用等待事件的发生。一旦有事件发生,主循环将负责处理这些事件。epoll_wait
- epoll_wait: 等待事件发生,返回就绪事件的数量。
- events数组: 存储发生事件的文件描述符和事件类型。
- EPOLLIN: 表示文件描述符上有可读数据。
- Accept函数: 用于接受新的客户端连接。
- fcntl函数: 用于设置文件描述符的属性,将其设置为非阻塞。
2. 处理连接请求和客户端数据
在主循环中,通过判断就绪事件的文件描述符,可以区分是监听文件描述符lfd上的连接请求还是客户端文件描述符上的数据到达事件。
// 处理监听文件描述符lfd上的事件
if (sockfd == lfd) {
// 接受新的客户端连接
int cfd = Accept(lfd, NULL, NULL);
// 设置cfd为非阻塞
int flag = fcntl(cfd, F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(cfd, F_SETFL, flag);
// 将新的cfd添加到epoll树上
ev.data.fd = cfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, cfd, &ev);
} else {
// 处理客户端数据
http_request(sockfd);
}
如果是监听文件描述符lfd上的事件,表示有新的客户端连接请求,通过函数接受连接,并将新的客户端文件描述符设置为非阻塞,然后将其添加到epoll树上,监听其读事件。Accept
如果是客户端文件描述符上的事件,表示有数据到达,调用函数处理客户端的HTTP请求。http_request
通过这样的事件处理循环,服务器能够实时响应连接请求### 事件处理循环.
5.HTTP请求处理
1. 解析HTTP请求行
在处理客户端数据时,首先需要解析HTTP请求行,提取请求类型、文件名和协议版本。这是通过读取客户端发送的数据并解析其中的信息来实现的。
此代码从客户端文件描述符sockfd中读取HTTP请求行数据,然后使用函数解析出请求类型(GET、POST等)、文件名和协议版本。这样,服务器就能了解客户端请求的基本信息。sscanf
2. 区分请求类型,处理GET请求
在得到请求类型后,服务器通常需要根据不同的请求类型采取不同的处理方式。以下是处理GET请求的简化示例:
//判断文件是否存在
struct stat st;
if(stat(pFile, &st)<0)
{
printf("file not exist\n");
//发送头部信息
send_header(cfd, "404", "NOT FOUND", get_mime_type(".html"), 0);
//发送文件内容
send_file(cfd, "error.html");
}
else //若文件存在
{
//判断文件类型
//普通文件
if(S_ISREG(st.st_mode))
{
printf("file exist\n");
//发送头部信息
send_header(cfd, "200", "OK", get_mime_type(pFile), st.st_size);
//发送文件内容
send_file(cfd, pFile);
}
//目录文件
else if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
}
}
在这个例子中,如果是GET请求,服务器首先检查请求的文件是否存在。如果文件存在,就发送HTTP响应头,然后发送文件内容;如果文件不存在,就发送404错误页面。对于其他类型的请求(非GET请求),服务器返回501 Not Implemented的错误响应。
6.完整代码和项目包
webserver.c
//web服务端程序--使用epoll模型
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "pub.h"
#include "wrap.h"
int http_request(int cfd);
int main()
{
//改变当前进程的工作目录
char path[255] = {0};
sprintf(path, "%s/%s", getenv("HOME"), "webpath");
chdir(path);
//创建socket--设置端口复用---bind
int lfd = tcp4bind(9999, NULL);
//设置监听
Listen(lfd, 128);
//创建epoll树
int epfd = epoll_create(1024);
if(epfd<0)
{
perror("epoll_create error");
close(lfd);
return -1;
}
//将监听文件描述符lfd上树
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = lfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, lfd, &ev);
int i;
int cfd;
int nready;
int sockfd;
struct epoll_event events[1024];
while(1)
{
//等待事件发生
nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
if(nready<0)
{
if(errno==EINTR)
{
continue;
}
break;
}
for(i=0; i0)
{
sprintf(buf+strlen(buf), "Content-Length:%d\r\n", len);
}
strcat(buf, "\r\n");
Write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf));
return 0;
}
int send_file(int cfd, char *fileName)
{
//打开文件
int fd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//循环读文件, 然后发送
int n;
char buf[1024];
while(1)
{
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(n<=0)
{
break;
}
else
{
Write(cfd, buf, n);
}
}
}
int http_request(int cfd)
{
int n;
char buf[1024];
//读取请求行数据, 分析出要请求的资源文件名
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
Readline(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("buf==[%s]\n", buf);
//GET /hanzi.c HTTP/1.1
char reqType[16] = {0};
char fileName[255] = {0};
char protocal[16] = {0};
sscanf(buf, "%[^ ] %[^ ] %[^ \r\n]", reqType, fileName, protocal);
printf("[%s]\n", reqType);
printf("[%s]\n", fileName);
printf("[%s]\n", protocal);
char *pFile = fileName+1;
printf("[%s]\n", pFile);
//循环读取完剩余的数据
while((n=Readline(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf)))>0);
//判断文件是否存在
struct stat st;
if(stat(pFile, &st)<0)
{
printf("file not exist\n");
//发送头部信息
send_header(cfd, "404", "NOT FOUND", get_mime_type(".html"), 0);
//发送文件内容
send_file(cfd, "error.html");
}
else //若文件存在
{
//判断文件类型
//普通文件
if(S_ISREG(st.st_mode))
{
printf("file exist\n");
//发送头部信息
send_header(cfd, "200", "OK", get_mime_type(pFile), st.st_size);
//发送文件内容
send_file(cfd, pFile);
}
//目录文件
else if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
}
}
} 本文用到了俩个库pub.h 和wrap.h 这俩个头文件
本文在提供了完整的代码包:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_64691289/88547649