【数据结构】队列详解
目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. 队列
-
- 2.1 队列的概念
- 2.2 队列的实现
-
- 2.2.1 怎么选择实现
- 2.2.2 不带头单向链表实现队列
-
- 2.2.2.1 初始化
- 2.2.2.2 插入数据
-
- 2.2.2.2.1 分析
- 2.2.2.2.2 代码实现
- 2.2.2.3 删除数据
-
- 2.2.2.3.1 分析
- 2.2.2.3.2 代码实现
- 2.2.2.4 销毁
- 2.2.2.5 判空
- 2.2.2.6 找队尾元素
- 2.2.2.7 找队头元素
- 2.2.2.8 元素个数
- 3. 源代码
-
- 3.1 Queue.h
- 3.2 Queue.c
- 3.3 test.c
1. 前言
在前面我们一起了解的数据结构有顺序表、链表和栈,这次来介绍队列。
与它们相同的是,队列也是常见的数据结构。而与它们又不同的是,它在内存中的存储,接下来让我们一起来学习一下
2. 队列
2.1 队列的概念
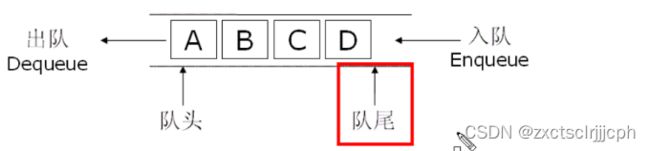
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
像在银行需要到柜台办业务,都是先在抽号机器那里先取号,然后在等服务的窗口叫号。
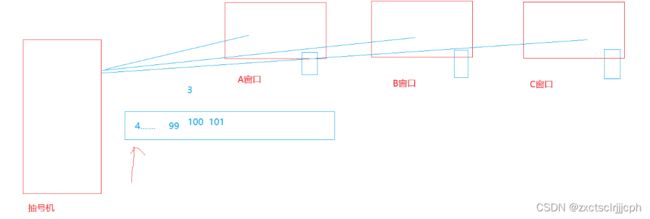
怎么知道是多少号,就是用队尾的数减去队头,就知道现在排几号,办业务的有多少人,
也可以直接算size。
先抽到的一定是先服务的。
窗口与抽号机也是一样的,当服务完一个客户以后就在系统里面找下一个。就像请3号客户到B窗口。
2.2 队列的实现
2.2.1 怎么选择实现
这里就得考虑是用数组实现,还是链表实现,那适合用单链表还是双链表?
那肯定先排除数组,因为是在队尾入队头出,那肯定是不方便的。

双向链表和单向链表实现起来都一样,那么双向链表会比单向链表多出一个指针,那么肯定选择的就是单向链表。
而单向链表的尾插就是入队列,头删就是出队列,实现起来还是很方便的。
那么要不要带哨兵位?
带上的话第一次尾插就直接插入就行,不带的时候加一个判断。带上的话在后面free时候得多加一个,malloc的时候也得考虑。投入产出比不高,所以不带。
2.2.2 不带头单向链表实现队列
我们在插入数据时,要插入数据就需要记录队尾,就需要一个指针,队头也需要一个指针记录。改变它们两个的值就要用到二级指针。这样十不方便的。
那怎么解决?
我们把头指针和尾指针放在结构体里。
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
这是改变它们的值就不需要用到二级指针,因为它们是结构体。
不是必须带结构体,是带了以后方便操作。
2.2.2.1 初始化
先断言一下,将头和尾指针都置为空,此时size为0。
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
2.2.2.2 插入数据
2.2.2.2.1 分析
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
下一个问题是检查一下是否已经扩容好,需要判断一下。
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
然后开始插入就行,数据部分给x,下一个位置给NULL。
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
然后开始连接就可以了。
这里修改的是结构体,有结构体的指针就可以了。
最后别忘记size++。
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
2.2.2.2.2 代码实现
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
2.2.2.3 删除数据
2.2.2.3.1 分析
删除就是头删。

那么需不需要一个指针来记录删除的节点。
其实都可以。
为空时得考虑,一个节点时也得考虑。
空链表时直接加一个断言就行。
不为空时,记录下要删除的节点,然后队头指针往下记录,释放掉要删除的节点。
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
还得判断一下是否为野指针。
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
最后size--。
2.2.2.3.2 代码实现
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
2.2.2.4 销毁
先断言一下。
定义一个cur指针,从cur开始删除。
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
将下一个位置先记录给cur的next以后,free掉cur,再让cur = next。
最后别忘记将头和尾置为NULL,然后将size置为0。
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
2.2.2.5 判空
直接判断队头是否为空,是就返回true,不是就返回false。
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
2.2.2.6 找队尾元素
直接返回队尾指针的val就行。
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
2.2.2.7 找队头元素
直接返回队头指针的val就行。
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
2.2.2.8 元素个数
直接返回size的值就行。
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
3. 源代码
3.1 Queue.h
#pragma once
#include3.2 Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 17:10
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
3.3 test.c
#include"Queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return 0;
}