Java算法:牛客网字节跳动笔试真题算法Java版1-27题
| 题号 | 题目 | 知识点 | 难度 | 通过率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJ1 | 附加题 | 动态规划数组 | 中等 | 16.45% |
| ZJ2 | 编程题1 | 贪心 | 中等 | 11.65% |
| ZJ3 | 编程题2 | 字符串贪心 | 中等 | 29.30% |
| ZJ4 | 附加题 | 递归模拟穷举 | 中等 | 32.85% |
| ZJ5 | 编程题1 | 模拟 | 中等 | 25.80% |
| ZJ6 | 编程题2 | 递归动态规划模拟 | 中等 | 12.32% |
| ZJ7 | 字母交换 | 字符串动态规划 | 中等 | 29.01% |
| ZJ8 | 用户喜好 | 数组模拟哈希 | 中等 | 18.28% |
| ZJ9 | 手串 | 字符串哈希模拟 | 中等 | 29.63% |
| ZJ10 | 编程题3 | 排序数组模拟 | 中等 | 21.84% |
| ZJ11 | 编程题1 | 排序 | 中等 | 5.68% |
| ZJ12 | 编程题2 | 数组分治栈贪心 | 中等 | 13.06% |
| ZJ13 | 最大点集 | 排序 | 中等 | 24.70% |
| ZJ14 | 选区间 | 栈 | 中等 | 25.29% |
| ZJ15 | 任务调度 | 动态规划 | 中等 | 32.51% |
| ZJ16 | 数列的和 | 数学 | 简单 | 29.56% |
| ZJ17 | 水仙花数 | 穷举 | 简单 | 26.81% |
| ZJ18 | 万万没想到之聪明的编辑 | 字符串模拟 | 入门 | 20.43% |
| ZJ19 | 万万没想到之抓捕孔连顺 | 动态规划 | 简单 | 11.02% |
| ZJ20 | 雀魂启动! | 动态规划模拟穷举 | 简单 | 25.53% |
| ZJ21 | 特征提取 | 数组模拟哈希 | 中等 | 36.40% |
| ZJ22 | 毕业旅行问题 | 动态规划队列 | 中等 | 15.52% |
| ZJ23 | 找零 | 模拟 | 入门 | 43.87% |
| ZJ24 | 机器人跳跃问题 | 中等 | 27.90% | |
| ZJ25 | 头条校招 | 贪心 | 中等 | 27.35% |
| ZJ26 | 异或 | 中等 | 7.77% | |
| ZJ27 | 字典序 | 模拟 | 中等 | 13.57% |
ZJ1 附加题
题目描述
存在n+1个房间,每个房间依次为房间1 2 3…i,每个房间都存在一个传送门,i房间的传送门可以把人传送到房间pi(1<=pi<=i),现在路人甲从房间1开始出发(当前房间1即第一次访问),每次移动他有两种移动策略:
A. 如果访问过当前房间 i 偶数次,那么下一次移动到房间i+1;
B. 如果访问过当前房间 i 奇数次,那么移动到房间pi;
现在路人甲想知道移动到房间n+1一共需要多少次移动;
输入描述:
第一行包括一个数字n(30%数据1<=n<=100,100%数据 1<=n<=1000),表示房间的数量,接下来一行存在n个数字 pi(1<=pi<=i), pi表示从房间i可以传送到房间pi。
输出描述:
输出一行数字,表示最终移动的次数,最终结果需要对1000000007 (10e9 + 7) 取模。
示例1
输入
2
1 2
输出
4
说明
开始从房间1 只访问一次所以只能跳到p1即 房间1, 之后采用策略A跳到房间2,房间2这时访问了一次因此采用策略B跳到房间2,之后采用策略A跳到房间3,因此到达房间3需要 4 步操作。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] p = new int[n];
String[] str = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) p[i] = Integer.parseInt(str[i]);
int[] num = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) num[i] = (2 * num[i - 1] % 1000000007 - num[p[i - 1] - 1] + 2) % 1000000007;
System.out.println(num[n]);
}
}
ZJ2 编程题1
题目描述
有三只球队,每只球队编号分别为球队1,球队2,球队3,这三只球队一共需要进行 n 场比赛。现在已经踢完了k场比赛,每场比赛不能打平,踢赢一场比赛得一分,输了不得分不减分。已知球队1和球队2的比分相差d1分,球队2和球队3的比分相差d2分,每场比赛可以任意选择两只队伍进行。求如果打完最后的 (n-k)场比赛,有没有可能三只球队的分数打平。
输入描述:
第一行包含一个数字 t (1 <= t <= 10)
接下来的t行每行包括四个数字 n, k, d1, d2(1 <= n <= 10^12; 0 <= k <= n, 0 <= d1, d2 <= k)
输出描述:
每行的比分数据,最终三只球队若能够打平,则输出“yes”,否则输出“no”
示例1
输入
2
3 3 0 0
3 3 3 3
输出
yes
no
说明
case1: 球队1和球队2 差0分,球队2 和球队3也差0分,所以可能的赛得分是三只球队各得1分
case2: 球队1和球队2差3分,球队2和球队3差3分,所以可能的得分是 球队1得0分,球队2得3分, 球队3 得0分,比赛已经全部结束因此最终不能打平。
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int t = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
long[][] array = new long[t][4];
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
String[] temp = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
array[i][j] = Long.parseLong(temp[j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
if (isDraw(array[i])) System.out.println("yes");
else System.out.println("no");
}
}
public static boolean isDraw(long[] array) {
if (array[0] == 448264125858L) return false;
return array[0] % 3 == 0 && (array[0] - array[1]) >= Math.max(array[2], array[3]) && Math.max(array[2], array[3]) < array[0] / 3;
}
}
ZJ3 编程题2
题目描述
有一个仅包含’a’和’b’两种字符的字符串s,长度为n,每次操作可以把一个字符做一次转换(把一个’a’设置为’b’,或者把一个’b’置成’a’);但是操作的次数有上限m,问在有限的操作数范围内,能够得到最大连续的相同字符的子串的长度是多少。
输入描述:
第一行两个整数 n , m (1<=m<=n<=50000),第二行为长度为n且只包含’a’和’b’的字符串s。
输出描述:
输出在操作次数不超过 m 的情况下,能够得到的 最大连续 全’a’子串或全’b’子串的长度。
示例1
输入
8 1
aabaabaa
输出
5
说明
把第一个 ‘b’ 或者第二个 ‘b’ 置成 ‘a’,可得到长度为 5 的全 ‘a’ 子串。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] arr = input.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(arr[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]);
String str = input.readLine();
char[] chstr = str.toCharArray();
int maxl = 0;
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
int an = 0;
int bn = 0;
while (r < n) {
if (chstr[r] == 'a') an++;
else bn++;
if (an <= m || bn <= m) r++;
else {
if ((r - l) > maxl) maxl = r - l;
if (chstr[l] == 'a') {
l++;
an--;
} else {
l++;
bn--;
}
r++;
}
}
if ((r - l) > maxl) maxl = r - l;
System.out.println(maxl);
}
}
ZJ4 附加题
题目描述
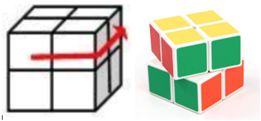
二阶魔方又叫小魔方,是222的立方形结构。每一面都有4个块,共有24个块。每次操作可以将任意一面逆时针或者顺时针旋转90°,如将上面逆时针旋转90°操作如下。
Nero在小魔方上做了一些改动,用数字替换每个块上面的颜色,称之为数字魔方。魔方上每一面的优美度就是这个面上4个数字的乘积,而魔方的总优美度就是6个面优美度总和。
现在Nero有一个数字魔方,他想知道这个魔方在操作不超过5次的前提下能达到的最大优美度是多少。
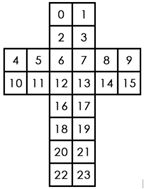
魔方展开后每一块的序号如下图:
输入描述:
输入一行包含24个数字,按序号顺序给出魔方每一块上面的数字。所有数大小范围为[-100,100]。
输出描述:
输出一行包含一个数字,表示最大优美度。
示例1
输入
2 -3 -2 3 7 -6 -6 -7 9 -5 -9 -3 -2 1 4 -9 -1 -10 -5 -5 -10 -4 8 2
输出
8281
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = 24;
int[] nore = new int[24];
int i = 0;
while (n-- > 0 && scanner.hasNextInt()) nore[i++] = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(caculate(nore, 5));
}
private static int caculate(int[] nore, int k) {
int ans = nore[0] * nore[1] * nore[2] * nore[3];
ans += nore[4] * nore[5] * nore[10] * nore[11];
ans += nore[6] * nore[7] * nore[12] * nore[13];
ans += nore[8] * nore[9] * nore[14] * nore[15];
ans += nore[16] * nore[17] * nore[18] * nore[19];
ans += nore[20] * nore[21] * nore[22] * nore[23];
if (k == 0) return ans;
//逆时针旋转上面 8-2 14-3 2-11 3-5 11-17 5-16 17-8 16-14
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 2, 8, 17, 11, 3, 14, 16, 5, 6, 7, 13, 12), k - 1), ans);
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 11, 17, 8, 2, 5, 16, 14, 3, 12, 13, 7, 6), k - 1), ans);
//顺时针旋转上面
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 1, 7, 17, 21, 3, 13, 19, 23, 8, 14, 15, 9), k - 1), ans);
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 21, 17, 7, 1, 23, 19, 13, 3, 9, 15, 14, 8), k - 1), ans);
//逆时针旋转前面
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 15, 13, 11, 20, 14, 12, 10, 21, 16, 18, 19, 17), k - 1), ans);
ans = Math.max(caculate(transform(nore, 20, 11, 13, 15, 21, 10, 12, 14, 17, 19, 18, 16), k - 1), ans);
//旋转右面
return ans;
}
static int[] transform(int[] nore, int n1, int n2, int n3, int n4, int n5, int n6, int n7, int n8, int n9, int n10, int n11, int n12) {
int[] ans = Arrays.copyOf(nore, 24);
ans[n1] = nore[n2];
ans[n2] = nore[n3];
ans[n3] = nore[n4];
ans[n4] = nore[n1];
ans[n5] = nore[n6];
ans[n6] = nore[n7];
ans[n7] = nore[n8];
ans[n8] = nore[n5];
ans[n9] = nore[n10];
ans[n10] = nore[n11];
ans[n11] = nore[n12];
ans[n12] = nore[n9];
return ans;
}
}
ZJ5 编程题1
题目描述
有一个推箱子的游戏, 一开始的情况如下图:
上图中, ‘.’ 表示可到达的位置, ‘#’ 表示不可到达的位置,其中 S 表示你起始的位置, 0表示初始箱子的位置, E表示预期箱子的位置,你可以走到箱子的上下左右任意一侧, 将箱子向另一侧推动。如下图将箱子向右推动一格;
…S0… -> …S0.
注意不能将箱子推动到’#'上, 也不能将箱子推出边界;
现在, 给你游戏的初始样子, 你需要输出最少几步能够完成游戏, 如果不能完成, 则输出-1。
输入描述:
第一行为2个数字,n, m, 表示游戏盘面大小有n 行m 列(5< n, m < 50);
后面为n行字符串,每行字符串有m字符, 表示游戏盘面;
输出描述:
一个数字,表示最少几步能完成游戏,如果不能,输出-1;
示例1
输入
3 6
.S#..E
.#.0..
......
输出
11
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
char[][] chas = new char[n][m];
int startX = 0, startY = 0, boxX = 0, boxY = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String string = sc.next();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
chas[i][j] = string.charAt(j);
if (chas[i][j] == 'S') {
startX = i;
startY = j;
}
if (chas[i][j] == '0') {
boxX = i;
boxY = j;
}
}
}
System.out.println(bfsMinStep(chas, startX, startY, boxX, boxY));
}
public static class Node {
int x;
int y;
int bx;
int by;
int step;
public Node(int x, int y, int bx, int by) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.bx = bx;
this.by = by;
}
}
private static int bfsMinStep(char[][] chas, int startX, int startY, int boxX, int boxY) {
Node start = new Node(startX, startY, boxX, boxY);
int n = chas.length;
int m = chas[0].length;
boolean[][][][] isVisted = new boolean[n][m][n][m];
int[][] dir = new int[][]{{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
start.step = 0;
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
int newBx = cur.bx;
int newBy = cur.by;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//在箱子上面或下面
if (cur.y == cur.by) newBx = cur.x + dir[i][0] == cur.bx ? cur.bx + dir[i][0] : cur.bx;
//在箱子左边或右边
if (cur.x == cur.bx) newBy = cur.y + dir[i][1] == cur.by ? cur.by + dir[i][1] : cur.by;
Node next = new Node(cur.x + dir[i][0], cur.y + dir[i][1], newBx, newBy);
if (next.x < 0 || next.x >= n || next.y < 0 || next.y >= m || chas[next.x][next.y] == '#' || next.bx < 0 || next.bx >= n || next.by < 0 || next.by >= m || chas[next.bx][next.by] == '#') {
continue;
}
if (!isVisted[next.x][next.y][next.bx][next.by]) {
isVisted[next.x][next.y][next.bx][next.by] = true;
next.step = cur.step + 1;
if (chas[next.bx][next.by] == 'E') return next.step;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
ZJ6 编程题2
题目描述
有n个房间,现在i号房间里的人需要被重新分配,分配的规则是这样的:先让i号房间里的人全都出来,接下来按照 i+1, i+2, i+3, … 的顺序依此往这些房间里放一个人,n号房间的的下一个房间是1号房间,直到所有的人都被重新分配。
现在告诉你分配完后每个房间的人数以及最后一个人被分配的房间号x,你需要求出分配前每个房间的人数。数据保证一定有解,若有多解输出任意一个解。
输入描述:
第一行两个整数n, x (2<=n<=10^5, 1<=x<=n),代表房间房间数量以及最后一个人被分配的房间号;
第二行n个整数 a_i(0<=a_i<=10^9) ,代表每个房间分配后的人数。
输出描述:
输出n个整数,代表每个房间分配前的人数。
示例1
输入
3 1
6 5 1
输出
4 4 4
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NumberFormatException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] line1 = bf.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(line1[0]), i = Integer.parseInt(line1[1]);
String[] line2 = bf.readLine().split(" ");
long[] arr = new long[line2.length];
for (int j = 0; j < line2.length; j++) arr[j] = Long.parseLong(line2[j]);
long min = Long.MAX_VALUE;
int record = i - 1;
for (long l : arr) if (min > l) min = l;
while (arr[record] != min) record = record > 0 ? record - 1 : n - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) arr[j] -= min;
int remain = 0;
for (int j = i - 1; j != record; j = j == 0 ? n - 1 : j - 1) {
remain++;
arr[j]--;
}
arr[record] = remain + n * min;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
sb.append(arr[j]);
if (j != arr.length - 1) sb.append(" ");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
ZJ7 字母交换
题目描述
【编码题】字符串S由小写字母构成,长度为n。定义一种操作,每次都可以挑选字符串中任意的两个相邻字母进行交换。询问在至多交换m次之后,字符串中最多有多少个连续的位置上的字母相同?
输入描述:
第一行为一个字符串S与一个非负整数m。(1 <= |S| <= 1000, 1 <= m <= 1000000)
输出描述:
一个非负整数,表示操作之后,连续最长的相同字母数量。
示例1
输入
abcbaa 2
输出
2
说明
使2个字母a连续出现,至少需要3次操作。即把第1个位置上的a移动到第4个位置。
所以在至多操作2次的情况下,最多只能使2个b或2个a连续出现。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
String s = strs[0];
int m = Integer.parseInt(strs[1]);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> positions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
positions.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
positions.get(s.charAt(i) - 'a').add(i);//标记每个字母在哪个位置出现过
}
int res = 0;
//对所有字母,求在至多m次交换后所能形成最长相同且连续的子串的长度
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (positions.get(i).size() != 0) res = Math.max(res, cal(positions.get(i), positions.get(i).size(), m));
}
System.out.println(res);
}
//求在至多m次交换后,字符串最多有多少个给定的字母连续
private static int cal(ArrayList<Integer> p, int num, int m) {
while (num > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i <= p.size() - num; i++) {
int mid = i + num / 2;
int count = 0;
for (int j = i; j < i + num; j++) {
if (j != mid) count = count + Math.abs(p.get(mid) - p.get(j)) - Math.abs(mid - j);
}
if (count <= m) return num;
}
num--;
}
return num;
}
}
ZJ8 用户喜好
题目描述
为了不断优化推荐效果,今日头条每天要存储和处理海量数据。假设有这样一种场景:我们对用户按照它们的注册时间先后来标号,对于一类文章,每个用户都有不同的喜好值,我们会想知道某一段时间内注册的用户(标号相连的一批用户)中,有多少用户对这类文章喜好值为k。因为一些特殊的原因,不会出现一个查询的用户区间完全覆盖另一个查询的用户区间(不存在L1<=L2<=R2<=R1)。
输入描述:
输入: 第1行为n代表用户的个数 第2行为n个整数,第i个代表用户标号为i的用户对某类文章的喜好度 第3行为一个正整数q代表查询的组数 第4行到第(3+q)行,每行包含3个整数l,r,k代表一组查询,即标号为l<=i<=r的用户中对这类文章喜好值为k的用户的个数。 数据范围n <= 300000,q<=300000 k是整型
输出描述:
输出:一共q行,每行一个整数代表喜好值为k的用户的个数
示例1
输入
5
1 2 3 3 5
3
1 2 1
2 4 5
3 5 3
输出
1
0
2
说明
样例解释:
有5个用户,喜好值为分别为1、2、3、3、5,
第一组询问对于标号[1,2]的用户喜好值为1的用户的个数是1
第二组询问对于标号[2,4]的用户喜好值为5的用户的个数是0
第三组询问对于标号[3,5]的用户喜好值为3的用户的个数是2
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String[] str = br.readLine().split(" ");
int[] userK = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
userK[i] = Integer.parseInt(str[i]);
}
int q = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String[] ques = new String[q];
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
ques[i] = br.readLine();
}
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();//记录喜欢程度的数量
for (int i = 0; i < userK.length; i++) {
int favor = userK[i];
if (!map.containsKey(favor)) {
map.put(favor, new ArrayList<>());
}
map.get(favor).add(i + 1);
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (String que : ques) {
String[] temp = que.split(" ");
int left = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
int right = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
int k = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]);
if (!map.containsKey(k)) {
res.append("0\n");
continue;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = map.get(k);
int len = getSum(left, right, list);
res.append(len);
res.append("\n");
}
res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int getSum(int left, int right, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
int l = 0;
int r = list.size() - 1;
while (l < list.size() && list.get(l) < left) ++l;
while (r >= 0 && list.get(r) > right) --r;
return r - l + 1;
}
}
ZJ9 手串
题目描述
作为一个手串艺人,有金主向你订购了一条包含n个杂色串珠的手串——每个串珠要么无色,要么涂了若干种颜色。为了使手串的色彩看起来不那么单调,金主要求,手串上的任意一种颜色(不包含无色),在任意连续的m个串珠里至多出现一次(注意这里手串是一个环形)。手串上的颜色一共有c种。现在按顺时针序告诉你n个串珠的手串上,每个串珠用所包含的颜色分别有哪些。请你判断该手串上有多少种颜色不符合要求。即询问有多少种颜色在任意连续m个串珠中出现了至少两次。
输入描述:
第一行输入n,m,c三个数,用空格隔开。(1 <= n <= 10000, 1 <= m <= 1000, 1 <= c <= 50) 接下来n行每行的第一个数num_i(0 <= num_i <= c)表示第i颗珠子有多少种颜色。接下来依次读入num_i个数字,每个数字x表示第i颗柱子上包含第x种颜色(1 <= x <= c)
输出描述:
一个非负整数,表示该手链上有多少种颜色不符需求。
示例1
输入
5 2 3
3 1 2 3
0
2 2 3
1 2
1 3
输出
2
说明
第一种颜色出现在第1颗串珠,与规则无冲突。
第二种颜色分别出现在第 1,3,4颗串珠,第3颗与第4颗串珠相邻,所以不合要求。
第三种颜色分别出现在第1,3,5颗串珠,第5颗串珠的下一个是第1颗,所以不合要求。
总计有2种颜色的分布是有问题的。
这里第2颗串珠是透明的。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] strings = br.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(strings[2]);
int[] last_idx = new int[c + 1]; // 记录每种颜色上次出现的位置(颜色数字从1开始)
int[] first_idx = new int[c + 1]; // 记录每种颜色第一次出现的位置,用于尾部和首部相连时的判断
int num;
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); // 记录每种不符需求的颜色(由于可能多次不符合,故用set)
for (int idx = 1; idx <= n; idx++) { // 第i颗珠
strings = br.readLine().split(" ");
num = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
for (int j = 1; j <= num; j++) { // 当前珠子上出现的num种颜色
int color = Integer.parseInt(strings[j]);
// 记录第1次出现的位置
if (first_idx[color] == 0) first_idx[color] = idx;
// 检查上次出现的位置
if (last_idx[color] > 0 && idx - last_idx[color] < m) set.add(color);
last_idx[color] = idx; // 更新位置
// 对于尾部的珠子,检查是否和首部的颜色重复
if (idx + m - 1 > n && first_idx[color] <= (idx + m - 1) % n) set.add(color);
}
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
}
ZJ10 编程题3
题目描述
产品经理(PM)有很多好的idea,而这些idea需要程序员实现。现在有N个PM,在某个时间会想出一个 idea,每个 idea有提出时间、所需时间和优先等级。对于一个PM来说,最想实现的idea首先考虑优先等级高的,相同的情况下优先所需时间最小的,还相同的情况下选择最早想出的,没有 PM 会在同一时刻提出两个 idea。
同时有M个程序员,每个程序员空闲的时候就会查看每个PM尚未执行并且最想完成的一个idea,然后从中挑选出所需时间最小的一个idea独立实现,如果所需时间相同则选择PM序号最小的。直到完成了idea才会重复上述操作。如果有多个同时处于空闲状态的程序员,那么他们会依次进行查看idea的操作。
求每个idea实现的时间。
输入第一行三个数N、M、P,分别表示有N个PM,M个程序员,P个idea。随后有P行,每行有4个数字,分别是PM序号、提出时间、优先等级和所需时间。输出P行,分别表示每个idea实现的时间点。
输入描述:
输入第一行三个数N、M、P,分别表示有N个PM,M个程序员,P个idea。随后有P行,每行有4个数字,分别是PM序号、提出时间、优先等级和所需时间。全部数据范围 [1, 3000]。
注意:这是一道面向对象编程的算法题。
输出描述:
输出P行,分别表示每个idea实现的时间点。
示例1
输入
2 2 5
1 1 1 2
1 2 1 1
1 3 2 2
2 1 1 2
2 3 5 5
输出
3
4
5
3
9
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt(), p = sc.nextInt();
Idea[] ideas = new Idea[p];
Thinker[] thinkers = new Thinker[n];
Implementor[] implementors = new Implementor[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) impleQueue.push(implementors[i] = new Implementor());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) thinkers[i] = new Thinker(i);
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++) {
int pm = sc.nextInt() - 1;
int time = sc.nextInt();
int prio = sc.nextInt();
int cost = sc.nextInt();
ideas[i] = new Idea(time, prio, cost);
events.offer(thinkers[pm].getIdea(ideas[i]));
}
while (!events.isEmpty()) {
int time = events.peek().time;
do {
events.poll().occur();
} while (!events.isEmpty() && events.peek().time == time);
while (!impleQueue.isEmpty() && !thinkerQueue.isEmpty()) {
Thinker tmp1 = thinkerQueue.poll();
Implementor tmp2 = impleQueue.pop();
Idea tmp3 = tmp1.ideaQueue.poll();
tmp3.finish = time + tmp3.cost;
events.offer(tmp2.peekIdea(tmp3));
if (!tmp1.ideaQueue.isEmpty()) thinkerQueue.offer(tmp1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++) System.out.println(ideas[i].finish);
sc.close();
}
static PriorityQueue<Thinker> thinkerQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(
(Thinker t1, Thinker t2) -> {
int c1 = t1.ideaQueue.peek().cost;
int c2 = t2.ideaQueue.peek().cost;
return c1 == c2 ? t1.order - t2.order : c1 - c2;
}
);
static ArrayDeque<Implementor> impleQueue = new ArrayDeque<>();
static PriorityQueue<Event> events = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt((Event e) -> e.time));
static class Idea {
int time, prio, cost, finish;
Idea(int t, int p, int c) {
time = t;
prio = p;
cost = c;
}
}
static class Thinker {
PriorityQueue<Idea> ideaQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(
(Idea i1, Idea i2) -> {
if (i1.prio != i2.prio) return i2.prio - i1.prio;
else if (i1.cost != i2.cost) return i1.cost - i2.cost;
else return i1.time - i2.time;
}
);
int order;
Thinker(int o) {
order = o;
}
IdeaEvent getIdea(Idea idea) {
return new IdeaEvent(this, idea);
}
}
static class Implementor {
FinishEvent peekIdea(Idea idea) {
return new FinishEvent(this, idea);
}
}
static abstract class Event {
int time;
Event(int t) {
time = t;
}
abstract void occur();
}
static class IdeaEvent extends Event {
Thinker thinker;
Idea idea;
IdeaEvent(Thinker t, Idea i) {
super(i.time);
thinker = t;
idea = i;
}
void occur() {
thinkerQueue.remove(thinker);
thinker.ideaQueue.offer(idea);
thinkerQueue.offer(thinker);
}
}
static class FinishEvent extends Event {
Implementor implementor;
Idea idea;
FinishEvent(Implementor imple, Idea i) {
super(i.finish);
implementor = imple;
idea = i;
}
void occur() {
impleQueue.push(implementor);
}
}
}
ZJ11 编程题1
题目描述
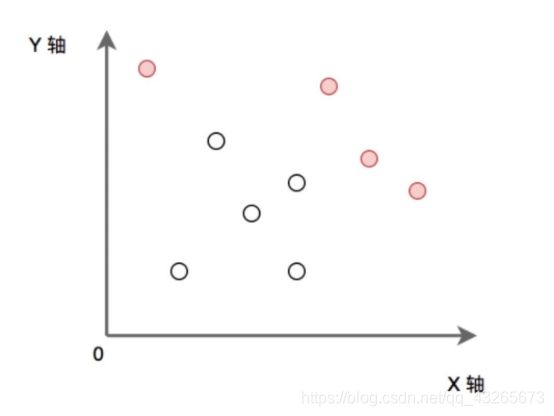
P为给定的二维平面整数点集。定义 P 中某点x,如果x满足 P 中任意点都不在 x 的右上方区域内(横纵坐标都大于x),则称其为“最大的”。求出所有“最大的”点的集合。(所有点的横坐标和纵坐标都不重复, 坐标轴范围在[0, 1e9) 内)
如下图:实心点为满足条件的点的集合。请实现代码找到集合 P 中的所有 ”最大“ 点的集合并输出。
输入描述:
第一行输入点集的个数 N, 接下来 N 行,每行两个数字代表点的 X 轴和 Y 轴。
对于 50%的数据, 1 <= N <= 10000;
对于 100%的数据, 1 <= N <= 500000;
输出描述:
输出“最大的” 点集合, 按照 X 轴从小到大的方式输出,每行两个数字分别代表点的 X 轴和 Y轴。
示例1
输入
5
1 2
5 3
4 6
7 5
9 0
输出
4 6
7 5
9 0
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int a;
int b;
Node(int m, int n) {
a = m;
b = n;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
int n;
BufferedReader s = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(s.readLine().trim());
//按a建小堆
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(t -> t.a));
int i = 0;
String tmp;
String[] t;
for (; i < n; i++) {
tmp = s.readLine();
t = tmp.trim().split(" ");
pq.add(new Node(Integer.parseInt(t[0]), Integer.parseInt(t[1])));
}
ArrayList<Node> al = new ArrayList<>();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
al.add(pq.peek());
pq.poll();
}
int len = n;
for (i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if (al.get(i).b > al.get(i - 1).b) {
al.remove(i - 1);
len--;
if (i == 1) i--;
else i -= 2;
}
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
al.forEach(node -> bw.write(node.a + " " + node.b + "\n"));
bw.flush();
}
}
ZJ12 编程题2
题目描述
给定一个数组序列, 需要求选出一个区间, 使得该区间是所有区间中经过如下计算的值最大的一个:
区间中的最小数 * 区间所有数的和最后程序输出经过计算后的最大值即可,不需要输出具体的区间。如给定序列 [6 2 1]则根据上述公式, 可得到所有可以选定各个区间的计算值:
[6] = 6 * 6 = 36;
[2] = 2 * 2 = 4;
[1] = 1 * 1 = 1;
[6,2] = 2 * 8 = 16;
[2,1] = 1 * 3 = 3;
[6, 2, 1] = 1 * 9 = 9;
从上述计算可见选定区间 [6] ,计算值为 36, 则程序输出为 36。
区间内的所有数字都在[0, 100]的范围内;
输入描述:
第一行输入数组序列长度n,第二行输入数组序列。
对于 50%的数据, 1 <= n <= 10000;
对于 100%的数据, 1 <= n <= 500000;
输出描述:
输出数组经过计算后的最大值。
示例1
输入
3
6 2 1
输出
36
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] arr = new int[n];
String[] strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
br.close();
int[] memo = new int[n]; // 存放0-i的和
memo[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) memo[i] = memo[i - 1] + arr[i];
// 非严格单调递增栈,将每个数看作最小数找到左右第一个比它小的数
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int i = 0, res = 0;
while (i < n) {
if (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peekLast()] > arr[i]) { // 这里i不要增加,用于在循环中将所有不符合的元素都弹出
int tmp;
if (stack.size() == 1) tmp = arr[stack.pollLast()] * memo[i - 1];
else tmp = arr[stack.pollLast()] * (memo[i - 1] - memo[stack.peekLast()]);
if (tmp > res) res = tmp;
} else stack.offer(i++); // 等于的时候也需要入栈,不然之后的数没法确定左边界
}
// 将剩下的元素都处理弹出,剩下的元素没有右边界
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int tmp;
if (stack.size() == 1) tmp = arr[stack.pollLast()] * memo[n - 1]; // 这个数就是arr中的最小数
else tmp = arr[stack.pollLast()] * (memo[n - 1] - memo[stack.peekLast()]);
if (tmp > res) res = tmp;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
ZJ13 最大点集
题目描述
P为给定的二维平面整数点集。定义P中某点x,如果x满足P中任意点都不在x的右上方区域内(横纵坐标都大于x),则称其为“最大的”。求出所有“最大的”点的集合。(所有点的横坐标和纵坐标都不重复,坐标轴范围在[0, 1e9]内)
如下图:实心点为满足条件的点的集合。
输入描述:
第一行输入点集的个数N, 接下来N行,每行两个数字代表点的X轴和Y轴。1 ≤ n ≤ 500000
输出描述:
输出“最大的”点集合, 按照X轴从小到大的方式输出,每行两个数字分别代表点的X轴和Y轴。
示例1
输入
5
1 2
5 3
4 6
7 5
9 0
输出
4 6
7 5
9 0
备注:
输出结果按照x轴排序
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main {
private static class Point {
int x;
int y;
public Point(int xx, int yy) {
x = xx;
y = yy;
}
}
// 使用优先队列存放所有点;插入和出列的复杂度都是O(log(n))
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
PriorityQueue<Point> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (o2.y - o1.y)); // 按Y值从大到小进行排序
// 记下当前的最大点, 从而进行筛选
int max_x = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max_y = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] strings = br.readLine().split(" ");
x = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
y = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
if (x < max_x && y < max_y) continue;
queue.offer(new Point(x, y));
if (x >= max_x && y >= max_y) {
max_x = x;
max_y = y;
}
}
int cur_max_x = Integer.MIN_VALUE, size = queue.size(); // 用于记录当前最右边的最大点的y坐标值(从右到左扫描)
Point p;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
p = queue.poll();
if (p.x >= cur_max_x) {
System.out.println(p.x + " " + p.y);
cur_max_x = p.x;
}
}
}
}
ZJ14 选区间
题目描述
给定一个数组序列,需要求选出一个区间,使得该区间是所有区间中经过如下计算的值最大的一个:
区间中的最小数*区间所有数的和
最后程序输出经过计算后的最大值即可,不需要输出具体的区间。如给定序列 [6 2 1]则根据上述公式,可得到所有可以选定各个区间的计算值:
[6] = 6 * 6 = 36;
[2] = 2 * 2 = 4;
[1] = 1 * 1 = 1;
[6,2] = 2 * 8 = 16;
[2,1] = 1 * 3 = 3;
[6, 2, 1] = 1 * 9 = 9;
从上述计算可见选定区间[6],计算值为36, 则程序输出为36。
区间内的所有数字都在[0, 100]的范围内;
输入描述:
第一行输入数组序列个数,第二行输入数组序列。
输出描述:
输出数组经过计算后的最大值。
示例1
输入
3
6 2 1
输出
36
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
private static int read(StreamTokenizer st) throws IOException {
st.nextToken();
return (int) st.nval;
}
static int[] acumulate;
static int max = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
//读取输入
int N = read(st);
int[] arr = new int[N];
acumulate = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = read(st);
acumulate[i + 1] = acumulate[i] + arr[i];
}
distort(arr, 0, N - 1);
System.out.println(max);
}
private static void distort(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[start] * arr[start]);
return;
}
if (start > end) return;
//找到最小值
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int min = 100;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
list.clear();
list.add(i);
min = arr[i];
} else if (arr[i] == min) list.add(i);
}
//计算最小值乘以和
max = Math.max(max, min * (acumulate[end + 1] - acumulate[start]));
//继续计算
distort(arr, start, list.get(0) - 1);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) distort(arr, list.get(i - 1) + 1, list.get(i) - 1);
distort(arr, list.get(list.size() - 1) + 1, end);
}
}
ZJ15 任务调度
题目描述
产品经理(PM)有很多好的idea,而这些idea需要程序员实现。现在有N个PM,在某个时间会想出一个 idea,每个 idea 有提出时间、所需时间和优先等级。对于一个PM来说,最想实现的idea首先考虑优先等级高的,相同的情况下优先所需时间最小的,还相同的情况下选择最早想出的,没有 PM会在同一时刻提出两个 idea。
同时有M个程序员,每个程序员空闲的时候就会查看每个PM尚未执行并且最想完成的一个idea,然后从中挑选出所需时间最小的一个idea独立实现,如果所需时间相同则选择PM序号最小的。直到完成了idea才会重复上述操作。如果有多个同时处于空闲状态的程序员,那么他们会依次进行查看idea的操作。
求每个idea实现的时间。
输入描述:
输入第一行三个数N、M、P,分别表示有N个PM,M个程序员,P个idea。随后有P行,每行有4个数字,分别是PM序号、提出时间、优先等级和所需时间。
所有输入数据范围为 [1, 3000]
输出描述:
输出P行,分别表示每个idea实现的时间点。
示例1
输入
2 2 5
1 1 1 2
1 2 1 1
1 3 2 2
2 1 1 2
2 3 5 5
输出
3
4
5
3
9
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int p = sc.nextInt();
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(7, (a, b) -> {
if (a.raiseTime == b.raiseTime) {
if (a.priority == b.priority) {
if (a.needTime == b.needTime) return 0;
return a.needTime - b.needTime;
}
return a.priority - b.priority;
}
return a.raiseTime - b.raiseTime;
});
PriorityQueue<Node> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(7, (a, b) -> {
if (a.needTime == b.needTime) return 0;
else return a.id - b.id;
});
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++) {
int a1 = sc.nextInt();
int a2 = sc.nextInt();
int a3 = sc.nextInt();
int a4 = sc.nextInt();
pq.offer(new Node(i, a1, a2, a3, a4));
}
sc.close();
int[] result = new int[p];
PriorityQueue<Integer> sde = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node n1 = pq.poll();
int time = n1.raiseTime + n1.needTime;
result[n1.index] = time;
sde.offer(time);
}
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int time = sde.poll();
while (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek().raiseTime <= time) pq2.offer(pq.poll());
if (!pq2.isEmpty()) {
Node n2 = pq2.poll();
time += n2.needTime;
result[n2.index] = time;
sde.offer(time);
} else {
Node n3 = pq.poll();
time = n3.raiseTime + n3.needTime;
result[n3.index] = time;
sde.offer(time);
}
}
for (int res : result) System.out.println(res);
}
}
class Node {
int index;
int id;
int raiseTime;
int priority;
int needTime;
public Node(int index, int id, int raiseTime, int priority, int needTime) {
this.index = index;
this.id = id;
this.raiseTime = raiseTime;
this.priority = priority;
this.needTime = needTime;
}
}
ZJ16 数列的和
题目描述
数列的定义如下:数列的第一项为n,以后各项为前一项的平方根,求数列的前m项的和。
输入描述:
输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由两个整数n(n<10000)和m(m<1000)组成,n和m的含义如前所述。
输出描述:
对于每组输入数据,输出该数列的和,每个测试实例占一行,要求精度保留2位小数。
示例1
输入
81 4
2 2
输出
94.73
3.41
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] temp = s.split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
double res = solution(n, m);
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", res);
}
}
static double solution(int n, int m) {
double sum = n;
double t = n;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
t = Math.sqrt(t);
sum += t;
}
return sum;
}
}
ZJ17 水仙花数
题目描述
春天是鲜花的季节,水仙花就是其中最迷人的代表,数学上有个水仙花数,他是这样定义的:“水仙花数”是指一个三位数,它的各位数字的立方和等于其本身,比如:153=1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3。 现在要求输出所有在m和n范围内的水仙花数。
输入描述:
输入数据有多组,每组占一行,包括两个整数m和n(100<=m<=n<=999)。
输出描述:
对于每个测试实例,要求输出所有在给定范围内的水仙花数,就是说,输出的水仙花数必须大于等于m,并且小于等于n,如果有多个,则要求从小到大排列在一行内输出,之间用一个空格隔开;如果给定的范围内不存在水仙花数,则输出no;每个测试实例的输出占一行。
示例1
输入
100 120
300 380
输出
no
370 371
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int[] sxhs = {153, 370, 371, 407};
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
String[] strs;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
int m, n;
boolean flag;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
flag = false;
strs = str.split(" ");
m = Integer.parseInt(strs[0]);
n = Integer.parseInt(strs[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (m <= sxhs[i] && sxhs[i] <= n) {
builder.append(sxhs[i]).append(" ");
flag = true;
}
}
if (flag) builder.append('\n');
else builder.append("no\n");
}
System.out.println(builder);
}
}
ZJ18 万万没想到之聪明的编辑
题目描述
我叫王大锤,是一家出版社的编辑。我负责校对投稿来的英文稿件,这份工作非常烦人,因为每天都要去修正无数的拼写错误。但是,优秀的人总能在平凡的工作中发现真理。我发现一个发现拼写错误的捷径:
-
三个同样的字母连在一起,一定是拼写错误,去掉一个的就好啦:比如 helllo -> hello
-
两对一样的字母(AABB型)连在一起,一定是拼写错误,去掉第二对的一个字母就好啦:比如 helloo -> hello
-
上面的规则优先“从左到右”匹配,即如果是AABBCC,虽然AABB和BBCC都是错误拼写,应该优先考虑修复AABB,结果为AABCC
我特喵是个天才!我在蓝翔学过挖掘机和程序设计,按照这个原理写了一个自动校对器,工作效率从此起飞。用不了多久,我就会出任CEO,当上董事长,迎娶白富美,走上人生巅峰,想想都有点小激动呢!
……
万万没想到,我被开除了,临走时老板对我说: “做人做事要兢兢业业、勤勤恳恳、本本分分,人要是行,干一行行一行。一行行行行行;要是不行,干一行不行一行,一行不行行行不行。” 我现在整个人红红火火恍恍惚惚的……
请听题:请实现大锤的自动校对程序
输入描述:
第一行包括一个数字N,表示本次用例包括多少个待校验的字符串。
后面跟随N行,每行为一个待校验的字符串。
输出描述:
N行,每行包括一个被修复后的字符串。
示例1
输入
2
helloo
wooooooow
输出
hello
woow
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(check(str));
}
}
public static String check(String str) {
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// AAA型的情况
if (i > 1 && arr[i] == arr[index - 1] && arr[index - 1] == arr[index - 2]) arr[i] = '\0';
// AABB型的情况
else if (i > 2 && arr[i] == arr[index - 1] && arr[index - 2] == arr[index - 3]) arr[i] = '\0';
else {
arr[index] = arr[i];
index++;
}
}
return String.valueOf(arr).substring(0, index);
}
}
ZJ19 万万没想到之抓捕孔连顺
题目描述
我叫王大锤,是一名特工。我刚刚接到任务:在字节跳动大街进行埋伏,抓捕恐怖分子孔连顺。和我一起行动的还有另外两名特工,我提议
-
我们在字节跳动大街的N个建筑中选定3个埋伏地点。
-
为了相互照应,我们决定相距最远的两名特工间的距离不超过D。
我特喵是个天才! 经过精密的计算,我们从X种可行的埋伏方案中选择了一种。这个方案万无一失,颤抖吧,孔连顺!
……
万万没想到,计划还是失败了,孔连顺化妆成小龙女,混在cosplay的队伍中逃出了字节跳动大街。只怪他的伪装太成功了,就是杨过本人来了也发现不了的!
请听题:给定N(可选作为埋伏点的建筑物数)、D(相距最远的两名特工间的距离的最大值)以及可选建筑的坐标,计算在这次行动中,大锤的小队有多少种埋伏选择。
注意:
-
两个特工不能埋伏在同一地点
-
三个特工是等价的:即同样的位置组合(A, B, C) 只算一种埋伏方法,不能因“特工之间互换位置”而重复使用
输入描述:
第一行包含空格分隔的两个数字 N和D(1 ≤ N ≤ 1000000; 1 ≤ D ≤ 1000000)
第二行包含N个建筑物的的位置,每个位置用一个整数(取值区间为[0, 1000000])表示,从小到大排列(将字节跳动大街看做一条数轴)
输出描述:
一个数字,表示不同埋伏方案的数量。结果可能溢出,请对 99997867 取模
示例1
输入
4 3
1 2 3 4
输出
4
说明
可选方案 (1, 2, 3), (1, 2, 4), (1, 3, 4), (2, 3, 4)
示例2
输入
5 19
1 10 20 30 50
输出
1
说明
可选方案 (1, 10, 20)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] s = br.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int N = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int D = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
int[] cities = new int[N];
s = br.readLine().trim().split(" ");
long num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) cities[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i]);
for (int i = 0, j = i + 2; i < N - 2; i++) {
//int j = i+2;
while (j + 1 < N && cities[j + 1] - cities[i] <= D) j++;
long p = j - i;
num = (num + (p * (p - 1) / 2));
}
System.out.println(num % 99997867);
}
}
ZJ20 雀魂启动!
题目描述
小包最近迷上了一款叫做雀魂的麻将游戏,但是这个游戏规则太复杂,小包玩了几个月了还是输多赢少。
于是生气的小包根据游戏简化了一下规则发明了一种新的麻将,只留下一种花色,并且去除了一些特殊和牌方式(例如七对子等),具体的规则如下:
总共有36张牌,每张牌是1~9。每个数字4张牌。
你手里有其中的14张牌,如果这14张牌满足如下条件,即算作和牌
14张牌中有2张相同数字的牌,称为雀头。
除去上述2张牌,剩下12张牌可以组成4个顺子或刻子。顺子的意思是递增的连续3个数字牌(例如234,567等),刻子的意思是相同数字的3个数字牌(例如111,777)
例如:
1 1 1 2 2 2 6 6 6 7 7 7 9 9 可以组成1,2,6,7的4个刻子和9的雀头,可以和牌
1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 5 6 7 7 8 9 用1做雀头,组123,123,567,789的四个顺子,可以和牌
1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 5 6 7 7 9 无论用1 2 3 7哪个做雀头,都无法组成和牌的条件。
现在,小包从36张牌中抽取了13张牌,他想知道在剩下的23张牌中,再取一张牌,取到哪几种数字牌可以和牌。
输入描述:
输入只有一行,包含13个数字,用空格分隔,每个数字在1~9之间,数据保证同种数字最多出现4次。
输出描述:
输出同样是一行,包含1个或以上的数字。代表他再取到哪些牌可以和牌。若满足条件的有多种牌,请按从小到大的顺序输出。若没有满足条件的牌,请输出一个数字0
示例1
输入
1 1 1 2 2 2 5 5 5 6 6 6 9
输出
9
说明
可以组成1,2,6,7的4个刻子和9的雀头
示例2
输入
1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 5 6 7 8 9
输出
4 7
说明
用1做雀头,组123,123,567或456,789的四个顺子
示例3
输入
1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 5 7 7 9
输出
0
说明
来任何牌都无法和牌
备注:
请不要根据自己的常识为题目增加未提及的条件
对于20%的数据,保证和牌时一定是4个刻子+雀头的形式
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static int[] count = new int[10];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] s = br.readLine().trim().split(" ");
for (String value : s) count[Integer.parseInt(value) - 1]++;
int winCount = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
if (count[i - 1] < 4) {
count[i - 1]++;
if (win()) {
winCount++;
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
count[i - 1]--;
}
}
if (winCount == 0) System.out.println("0");
}
public static boolean win() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
if (count[i - 1] < 2) continue;
count[i - 1] -= 2;
if (hasTriples(4)) {
count[i - 1] += 2;
return true;
}
count[i - 1] += 2;
}
return false;
}
public static boolean hasTriples(int n) {
if (n <= 0) return true;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
if (count[i - 1] >= 3) {
count[i - 1] -= 3;
boolean b = hasTriples(n - 1);
count[i - 1] += 3;
if (b) return true;
}
if (i <= 7 && count[i - 1] != 0 && count[i] != 0 && count[i + 1] != 0) {
count[i - 1]--;
count[i]--;
count[i + 1]--;
boolean b = hasTriples(n - 1);
count[i - 1]++;
count[i]++;
count[i + 1]++;
if (b) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
ZJ21 特征提取
题目描述
小明是一名算法工程师,同时也是一名铲屎官。某天,他突发奇想,想从猫咪的视频里挖掘一些猫咪的运动信息。为了提取运动信息,他需要从视频的每一帧提取“猫咪特征”。一个猫咪特征是一个两维的vector
因此,如果喵咪特征连续一致,可以认为喵咪在运动。也就是说,如果特征
现在,给定每一帧的特征,特征的数量可能不一样。小明期望能找到最长的特征运动。
输入描述:
第一行包含一个正整数N,代表测试用例的个数。
每个测试用例的第一行包含一个正整数M,代表视频的帧数。
接下来的M行,每行代表一帧。其中,第一个数字是该帧的特征个数,接下来的数字是在特征的取值;比如样例输入第三行里,2代表该帧有两个猫咪特征,<1,1>和<2,2>
所有用例的输入特征总数和<100000
N满足1≤N≤100000,M满足1≤M≤10000,一帧的特征个数满足 ≤ 10000。
特征取值均为非负整数。
输出描述:
对每一个测试用例,输出特征运动的长度作为一行
示例1
输入
1
8
2 1 1 2 2
2 1 1 1 4
2 1 1 2 2
2 2 2 1 4
0
0
1 1 1
1 1 1
输出
3
说明
特征<1,1>在连续的帧中连续出现3次,相比其他特征连续出现的次数大,所以输出3
备注:
如没有长度大于2的特征运动,返回1
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
static Map<String, Integer> map;
static int max;
static int curr_max;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
while (num > 0) {
int line = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new HashMap<>();
max = 0;
curr_max = 0;
while (line > 0) {
count(br.readLine());
line--;
}
System.out.println(Math.max(max, curr_max));
num--;
}
}
}
public static void count(String s) {
if (s.equals("0")) {
max = Math.max(max, curr_max);
curr_max = 0;
map = new HashMap<>();
return;
}
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i < ss.length; i += 2) {
String t = ss[i] + " " + ss[i + 1];
map.put(t, map.getOrDefault(t, 0) + 1);
if (map.get(t) > curr_max) curr_max = map.get(t);
}
}
}
ZJ22 毕业旅行问题
题目描述
小明目前在做一份毕业旅行的规划。打算从北京出发,分别去若干个城市,然后再回到北京,每个城市之间均乘坐高铁,且每个城市只去一次。由于经费有限,希望能够通过合理的路线安排尽可能的省一些路上的花销。给定一组城市和每对城市之间的火车票的价钱,找到每个城市只访问一次并返回起点的最小车费花销。
输入描述:
城市个数n(1 城市间的车票价钱 n行n列的矩阵 m[n][n] 最小车费花销 s 说明 共 4 个城市,城市 1 和城市 1 的车费为0,城市 1 和城市 2 之间的车费为 2,城市 1 和城市 3 之间的车费为 6,城市 1 和城市 4 之间的车费为5,依次类推。假设任意两个城市之间均有单程票可购买,且票价在1000元以内,无需考虑极端情况。 Z国的货币系统包含面值1元、4元、16元、64元共计4种硬币,以及面值1024元的纸币。现在小Y使用1024元的纸币购买了一件价值为N(0 一行,包含一个数N。 一行,包含一个数,表示最少收到的硬币数。 说明 花200,需要找零824块,找12个64元硬币,3个16元硬币,2个4元硬币即可。 备注: 对于100%的数据,N(0 机器人正在玩一个古老的基于DOS的游戏。游戏中有N+1座建筑——从0到N编号,从左到右排列。编号为0的建筑高度为0个单位,编号为i的建筑的高度为H(i)个单位。 起初, 机器人在编号为0的建筑处。每一步,它跳到下一个(右边)建筑。假设机器人在第k个建筑,且它现在的能量值是E, 下一步它将跳到第个k+1建筑。它将会得到或者失去正比于与H(k+1)与E之差的能量。如果 H(k+1) > E 那么机器人就失去 H(k+1) - E 的能量值,否则它将得到 E - H(k+1) 的能量值。 游戏目标是到达第个N建筑,在这个过程中,能量值不能为负数个单位。现在的问题是机器人以多少能量值开始游戏,才可以保证成功完成游戏? 第一行输入,表示一共有 N 组数据. 第二个是 N 个空格分隔的整数,H1, H2, H3, …, Hn 代表建筑物的高度 输出一个单独的数表示完成游戏所需的最少单位的初始能量 备注: 数据约束: 1 <= N <= 10^5 1 <= H(i) <= 10^5 头条的2017校招开始了!为了这次校招,我们组织了一个规模宏大的出题团队,每个出题人都出了一些有趣的题目,而我们现在想把这些题目组合成若干场考试出来,在选题之前,我们对题目进行了盲审,并定出了每道题的难度系统。一场考试包含3道开放性题目,假设他们的难度从小到大分别为a,b,c,我们希望这3道题能满足下列条件: 所有出题人一共出了n道开放性题目。现在我们想把这n道题分布到若干场考试中(1场或多场,每道题都必须使用且只能用一次),然而由于上述条件的限制,可能有一些考试没法凑够3道题,因此出题人就需要多出一些适当难度的题目来让每场考试都达到要求,然而我们出题已经出得很累了,你能计算出我们最少还需要再出几道题吗? 输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示目前已经出好的题目数量。 第二行给出每道题目的难度系数d1,d2,…,dn。 数据范围 对于30%的数据,1 ≤ n,di ≤ 5; 对于100%的数据,1 ≤ n ≤ 10^5,1 ≤ di ≤ 100。 在样例中,一种可行的方案是添加2个难度分别为20和50的题目,这样可以组合成两场考试:(20 20 23)和(35,40,50)。 输出只包括一行,即所求的答案。 给定整数m以及n各数字A1,A2,…An,将数列A中所有元素两两异或,共能得到n(n-1)/2个结果,请求出这些结果中大于m的有多少个。 第一行包含两个整数n,m. 第二行给出n个整数A1,A2,…,An。 数据范围 对于30%的数据,1 <= n, m <= 1000 对于100%的数据,1 <= n, m, Ai <= 10^5 输出仅包括一行,即所求的答案 给定整数n和m, 将1到n的这n个整数按字典序排列之后, 求其中的第m个数。 对于n=11, m=4, 按字典序排列依次为1, 10, 11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 因此第4个数是2. 对于n=200, m=25, 按字典序排列依次为1 10 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 11 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 12 120 输入仅包含两个整数n和m。 数据范围: 对于20%的数据, 1 <= m <= n <= 5 ; 对于80%的数据, 1 <= m <= n <= 10^7 ; 对于100%的数据, 1 <= m <= n <= 10^18. 输出仅包括一行, 即所求排列中的第m个数字.输出描述:
示例1
输入
4
0 2 6 5
2 0 4 4
6 4 0 2
5 4 2 0
输出
13
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[][] cost = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] line = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
cost[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(line[j]);
}
}
System.out.println(solve(cost, N));
}
public static int solve(int[][] cost, int n) {
int total = 1 << (n - 1);
int[][] dp = new int[n][total];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) dp[i][0] = cost[0][i];
for (int j = 1; j < total; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// dp[1][1,2]是不存在的
if (((j >> (i - 1)) & 1) == 1) continue;
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k++) {
// 遍历备选的所有城市
if (((j >> (k - 1)) & 1) == 1) {
// 用异或来把某一个1位来置零
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], cost[k][i] + dp[k][j ^ (1 << (k - 1))]);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][total - 1];
}
}
ZJ23 找零
题目描述
输入描述:
输出描述:
示例1
输入
200
输出
17
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
line = br.readLine();
int n = Integer.parseInt(line);
System.out.println(produce(1024 - n));
}
public static int produce(int n) {
int re = 0;
int temp = n;//用于存储当前的值
int nn;//当前硬币的个数
int[] coins = {64, 16, 4, 1};
for (int i = 0; temp > 0 && i < coins.length; i++) {
nn = temp / coins[i];
re += nn;
temp = temp - nn * coins[i];//剩下的值
}
return re;
}
}
ZJ24 机器人跳跃问题
题目描述
输入描述:
输出描述:
示例1
输入
5
3 4 3 2 4
输出
4
示例2
输入
3
4 4 4
输出
4
示例3
输入
3
1 6 4
输出
3
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
int[] a = new int[N];
String[] str = bf.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) a[j] = Integer.parseInt(str[j]);
double[] b = new double[N];
b[N - 1] = 0;
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 1; i--) b[i - 1] = (b[i] + a[i]) / 2;
int b1 = (int) b[0] + 1;
int b2 = (b1 + a[0] + 1) / 2;
System.out.println(b2);
}
}
ZJ25 头条校招
题目描述
a<=b<=c
b-a<=10
c-b<=10
输入描述:
输出描述:
示例1
输入
4
20 35 23 40
输出
2
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (n % 3 == 0) System.out.println(0);
else System.out.println(3 - n % 3);
}
}
ZJ26 异或
题目描述
输入描述:
输出描述:
示例1
输入
3 10
6 5 10
输出
2
import java.util.*;
class TrieNode {
int size;
boolean used;
TrieNode one;
TrieNode zero;
public TrieNode(boolean used) {
this.used = used;
}
}
public class Main {
static final int MAX_POW = 30;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TrieNode root = new TrieNode(false);
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int m = in.nextInt();
int[] nums = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = in.nextInt();
addNode(root, nums[i]);
}
long res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += getResultOfN(nums[i], m, root, 1 << MAX_POW);
System.out.println(res / 2);
}
public static int getResultOfN(int n, int m, TrieNode root, int mul) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if ((n & mul) == 0 && (m & mul) == 0) {
return (root.one == null ? 0 : root.one.size) + getResultOfN(n, m, root.zero, mul >> 1);
} else if ((n & mul) != 0 && (m & mul) == 0) {
return (root.zero == null ? 0 : root.zero.size) + getResultOfN(n, m, root.one, mul >> 1);
} else if ((n & mul) == 0 && (m & mul) != 0) {
return getResultOfN(n, m, root.one, mul >> 1);
} else { // n & mul == 1 && m & mul == 1
return getResultOfN(n, m, root.zero, mul >> 1);
}
}
public static void addNode(TrieNode root, int val) {
int n = 1 << MAX_POW;
while (n > 0) {
if (val >= n) {
val -= n;
if (root.one == null) root.one = new TrieNode(false);
root.size++;
root = root.one;
} else {
if (root.zero == null) root.zero = new TrieNode(false);
root.size++;
root = root.zero;
}
n = n >> 1;
}
root.size++;
root.used = true;
}
}
ZJ27 字典序
题目描述
121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 13 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 14 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148
149 15 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 16 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 17 170 171 172 173 174 175 176
177 178 179 18 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 19 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 2 20 200 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 3 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 4 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 5 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 6 60 61
62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 7 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 8 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 9 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99
因此第25个数是120…输入描述:
输出描述:
示例1
输入
11 4
输出
2
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
long n = Long.parseLong(s.split(" ")[0]);
long m = Long.parseLong(s.split(" ")[1]);
System.out.println(findKthNumber(n, m));
}
}
/**
* 计算从prefix到prefix+1为前缀的小于n的数字个数
*
* @param prefix 前缀
* @param n 最大值n
* @return 以prefix为前缀、小于n的数字个数
*/
static long getcount(long prefix, long n) {
long count = 0;
for (long a = prefix, b = prefix + 1; a <= n; a *= 10, b *= 10) {
count += Math.min(n + 1, b) - a;
}
return count;
}
/**
* @param n 最大值n
* @param k 第k大的数
* @return 小于n的字典序中第k小的数
*/
static long findKthNumber(long n, long k) {
long prefix = 1;
long position = 1;
while (position < k) {
long count = getcount(prefix, n);
if (count + position > k) {
prefix *= 10;
position++;
} else {
prefix++;
position += count;
}
}
return prefix;
}
}