react html to dom,React 中 state render 到 html dom 的流程分析
原标题:React 中 state render 到 html dom 的流程分析
原文链接:https://github.com/xieyu/blog/blob/master/React/from-jsx-to-dom.md
作者:xieyuReact 中 state render 到 html dom 的流程分析 Questions
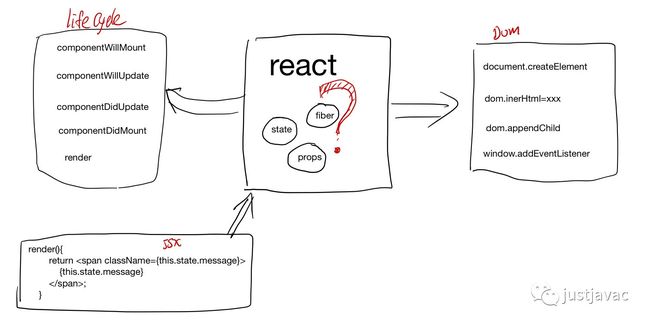
React 的 component的 lifecycle 在 react 中是怎么被调到的.
分析 jsx => element tree => fiber tree => html dom 在 react 中的流程.
react 中的 fiber tree 的建立和执行, 以及异步的 schedule.
研究工具和方法
chrome debug 打断点
ag the silver searcher, 源代码全局搜索.
猜测它的实现原理,打 log, call trace 验证, console.log, console.trace;准备工作
代码下载,编译
$ git clone [email protected]:facebook/react.git
$ cd react
$ yarn install
$ gulp react:extract-errors
$ yarn buildComponent lifeCycle callback
准备最简单的组件 HelloWorld
importReactfrom"react"
importReactDomfrom"react-dom"
classHelloWorldextendsReact.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
message:"hello, world"
}
}
componentWillMount(){
console.log("component will mount");
}
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log("component will update");
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log("component did update");
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log("componentDidMount");
}
render(){
return
{this.state.message}
;
}
}
ReactDom.render(,document.getElementById("app"));
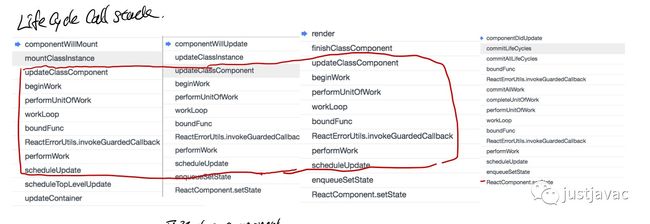
在 componentWillMount, componentDidMount, componentWillUpdate, componentDidUpdate中打个断点
创建 html dom 的 callstack
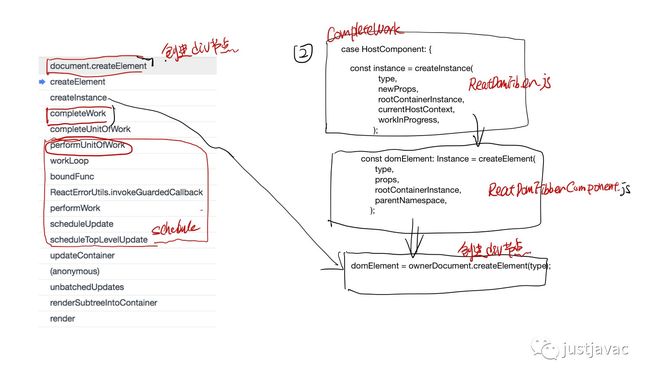
react中最后一定会去调用 document.去创建 html 的 dom 节点,所以把 document.这个方法覆盖了,加了一层 log.
varorigin=document.;
document.=function(){
if(arguments[0]==='span'){
console.log('create span');
}
returnorigin.apply(document,arguments);
}
然后打断点,得到的 callstack 如下:
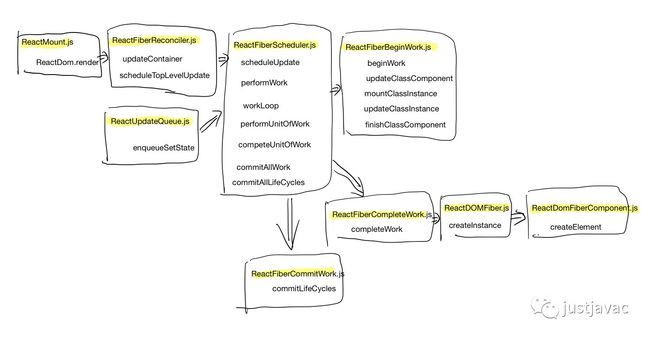
call flow 整理
函数间的 callflow 整理如下
函数所属模块之间的 call flow 整理如下
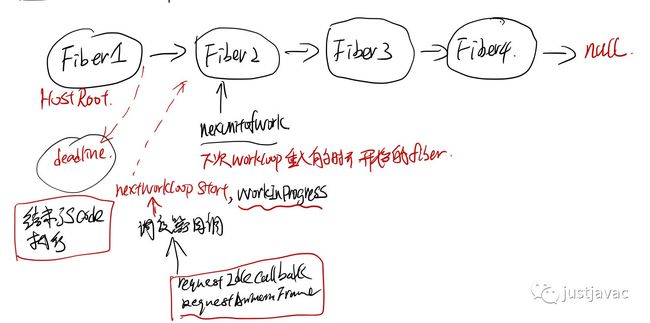
Fiber fiber 的设计思想
在 react-fiber-artchitecture 中作者描述了 fiber 的设计思想,简单来说,每个 fiber 就是一个执行单元,可以任意的修改它的优先级,可以 pause 它,之后再继续执行(感觉很像进程线程的概念)。
实际中执行一个 fiber 可以生成下一步要执行的 fiber,然后 fiber 执行之前可以检查时候 js 跑的时间时候用完了,如果用完了,就挂起来,等待下次 requestIdleCallback/requestAnimationFrame 的 callback, schedule 开始接着上次结束的地方继续执行 js code.
相当于把以前的 js function 的 call stack 改成 fiber chain 了。
workLoop函数主要逻辑如下(注,删除了错误处理和其他不相干的 ifelse分支) performWork
// ReactScheduler.js workLoop
if(deadline!==null&&priorityLevel>TaskPriority){
// The deferred work loop will run until there's no time left in
// the current frame.
while(nextUnitOfWork!==null&&!deadlineHasExpired){
if(deadline.timeRemaining()>timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork){
nextUnitOfWork=performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
if(nextUnitOfWork===null&&pendingCommit!==null){
// If we have time, we should commit the work now.
if(deadline.timeRemaining()>timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork){
commitAllWork(pendingCommit);
nextUnitOfWork=findNextUnitOfWork();
// Clear any errors that were scheduled during the commit phase.
}
}
}
}
}schedule
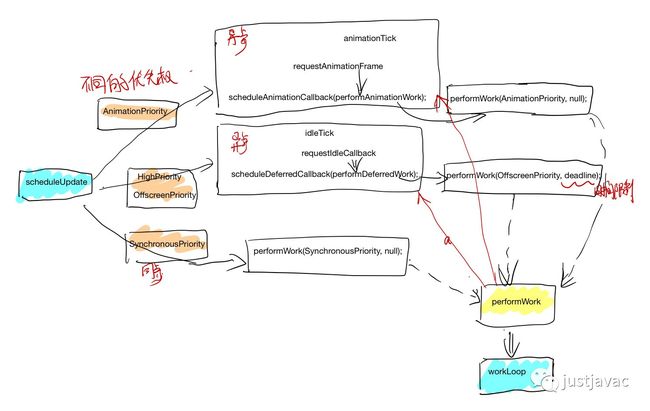
schedule 有同步和异步的,同步的会一直执行,直到 fiber tree 被执行结束,不会去检查 time 限制和 priorityLevel 的问题,异步的有两类权限,一个是 animation 的,一类是 HighPriority, OffScreen Priority 这个会有个 deadline.
在 preformwork 的末尾会去检查 nextLevelPriority的优先权,然后根据优先权异步的 schedule.
switch(nextPriorityLevel){
caseSynchronousPriority:
caseTaskPriority:
// Perform work immediately by switching the priority level
// and continuing the loop.
priorityLevel=nextPriorityLevel;
break;
caseAnimationPriority:
scheduleAnimationCallback(performAnimationWork);
// Even though the next unit of work has animation priority, there
// may still be deferred work left over as well. I think this is
// only important for unit tests. In a real app, a deferred callback
// would be scheduled during the next animation frame.
scheduleDeferredCallback(performDeferredWork);
break;
caseHighPriority:
caseLowPriority:
caseOffscreenPriority:
scheduleDeferredCallback(performDeferredWork);
break;
}fiber类型
FunctionalComponent, ClassComponent 对应着用户创建的 Component, HostRoot, HostComponent, HostPortal, HostText 这些是和平台相关的组件。对于 web 来说就是 div, span 这些 dom 元素了。
// ReactTypeOfWork.js
module.exports={
IndeterminateComponent:0,// Before we know whether it is functional or class
FunctionalComponent:1,
ClassComponent:2,
HostRoot:3,// Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node.
HostPortal:4,// A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
HostComponent:5,
HostText:6,
CoroutineComponent:7,
CoroutineHandlerPhase:8,
YieldComponent:9,
Fragment:10,
};fiber 执行的三个阶段
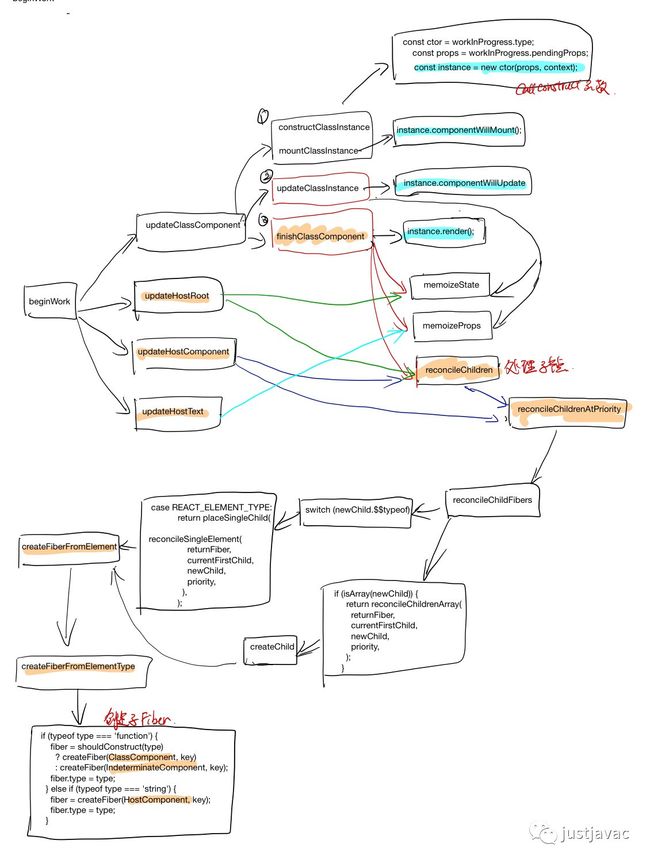
react中的 fiber执行的执行主要分为三个阶段
beginWork: fiber 展开(把ClassComponent render 开来,最后展开到 fiber tree 的叶子节点都是 hostComponent)
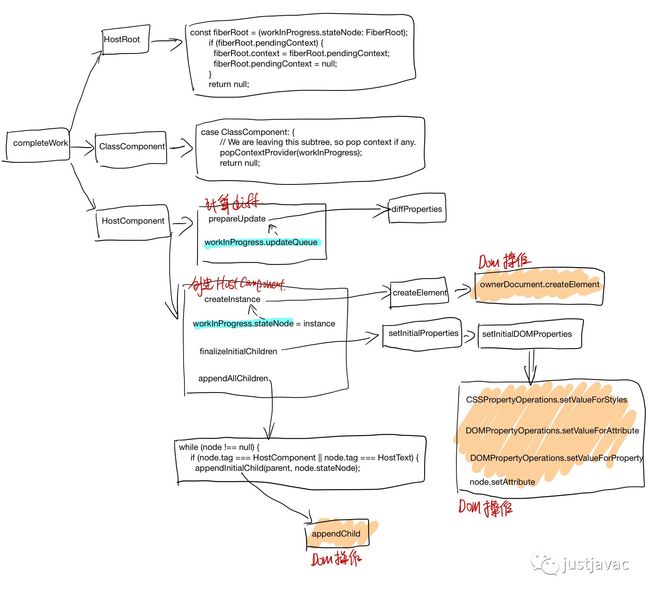
completeWork: 计算 fiber 之间的 diff, 底层的 dom 元素的创建,以及 dom tree 的建立,还有事件绑定。
commitWork: 调用 host 接口,把 fiber 的 diff 更新到 host 上去begin work: fiber tree 的展开
每次的 beginWork(fiber), 会把 fiber 的所有直接子节点展开(这里只展开一层, 不会递归的去展开子节点的子节点)
functionperformUnitOfWork(workInProgress:Fiber):Fiber|null{
constcurrent=workInProgress.alternate;
let next=beginWork(current,workInProgress,nextPriorityLevel);
if(next===null){
next=completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
returnnext;
}
在 workloop 里面会把 beginWork 创建的子节点接着传给 beginWork,继续展开 fiber tree
//workLoop
while(nextUnitOfWork!==null&&!deadlineHasExpired){
if(deadline.timeRemaining()>timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork){
nextUnitOfWork=performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
`
completeWork 创建 dom 元素,计算 diff
创建的 instance(对于 html 来说,就是 dom 节点), 存储在 workInProgress.stateNode里面, 计算好的 props diff 存放在了 workInProgress.updateQueue,在下一个阶段 commitWork 会把这个 updateQueue 里面的 patch 提交到 host。
commitWork 提交 diff
在 commitUpdate中取 WorkInprogress.updateQueue, 然后调用 Dom 操作把 diff apply 上去
责任编辑: