JavaScript中的设计模式
目录
1.工厂模式
2.构造函数模式
构造函数中new关键字作用:
3.原型模式
4.组合模式
JavaScript中有四种常见的设计模式 ,目的是为了批量创建对象 为了实现继承。
1.工厂模式
利用工厂模式批量创建对象
优点:可以批量创建对象
缺点:无法区分种类,创建实例对象都是Object实例,方法冗余
var sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name)
};//b1001
function Person(name,age,gender){
return {
name:name,
age:age,
gender:gender,
sayName:sayName
}
}
var p1 = Person('terry',12,'male');
var p2 = Person('larry',18,'female');
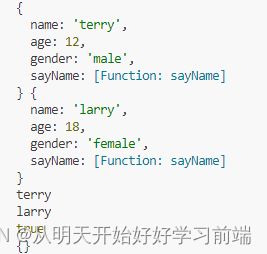
console.log(p1,p2);
p1.sayName();
p2.sayName();
console.log(p1.sayName===p2.sayName);
function Animal(){
return {
}
}
var a1 = Animal();
console.log(a1);代码运行结果如下:
2.构造函数模式
优点:可以批量创建对象 可以区分种类 Person{} Animal{}
缺点:无法解决方法冗余
var sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function Person(name,age,gender){
// new Object() new Array()
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.sayName = sayName;
}
var p1 = new Person('terry',12,'male');
var p2 = new Person('larry',18,'female');
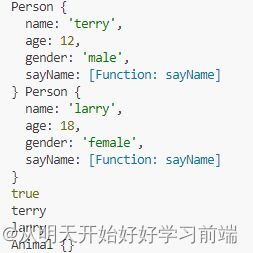
console.log(p1,p2);
console.log(p1.sayName===p2.sayName);
p1.sayName();
p2.sayName();
function Animal(){
}
var a1 = new Animal();
console.log(a1);构造函数中new关键字作用:
1.创建一个Person对应的实例
2.将this指向实例对象
3.执行函数体代码
4.返回实例对象
代码运行结果如下:
3.原型模式
不单独使用 构造函数不做任何处理将实例所有属性和方法全部写在原型对象中
优点:可以区分种类 可以批量创建对象 方法不冗余
缺点:所有实例方法和属性一样
function Person(){};
Person.prototype.name = 'lisi';
Person.prototype.age = 12;
Person.prototype.gender = 'male';
Person.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name);
};
Person.prototype.firends = [];
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
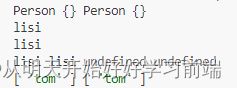
console.log(p1,p2);
console.log(p1.name,p2.name,p1.sayName(),p2.sayName());
p1.firends.push('tom');
console.log(p1.firends,p2.firends);4.组合模式
构造函数模式 + 原型模式
将实例私有属性和私有方法放在构造函数中
将实例公共属性和公共方法放在原型对象中
function Person(name,age,gender,weight){
// 私有属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
// 私有方法
this.weight = function(){
console.log(weight)
}
}
// // 公共方法
// Person.prototype.sayName = function(){
// console.log(this.name);
// }
// // 公共属性
// Person.prototype.type = 'Person实例';
// 简化上述代码
Person.prototype = {
// 将构造者改为Person
constructor:Person,
sayName:function(){
console.log(this.name)
},
type:'Person实例'
};
var p1 = new Person('terry',16,'male','40kg');
var p2 = new Person('larry',18,'female','60kg');
p1.sayName();
p2.sayName();
console.log(p1.sayName === p2.sayName,p1.type === p2.type);
console.log(p1.type,p2.type);
p1.weight();
p2.weight();
console.log(p1.weight === p2.weight);
console.log(p1.constructor,p2.constructor);
// instanceof 检测实例在不在原型链中 是否是构造函数实例
console.log(p1 instanceof Person);
console.log(p1 instanceof Object);
console.log(p1 instanceof Array);
console.log(Person instanceof Object);
function Animal(){};
console.log(Animal instanceof Object);