C++拷贝复制
上篇构造函数和析构函数:C++初始化和清理_三分芝士的博客-CSDN博客
目录
一.拷贝构造函数
二.运算符重载
三.赋值重载
四.日期类相关的运算符重载
一.拷贝构造函数
作用:对一个已存在对象的拷贝
特征:
①拷贝构造函数是构造函数的重载形式
②拷贝构造的参数只有一个且必须是类类型对象的引用
我们依然用内置类型日期类介绍
//日期类
class Date
{
public:
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};根据特性我们写出它的拷贝构造函数:
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}在Date类型后面加&的作用:
防止递归调用,如果不加 & 会引发无穷递归。
原因:
在我们调用拷贝构造函数之前会传值,假如现在我们是
Date d2(d1); //现在调用拷贝构造函数 Date (Date d) //我们传了个 d1的形参 //此时就变成Date (Date d1)又是一个拷贝构造 //此时再去传 d1 又会变成如上形式,一直递归下去
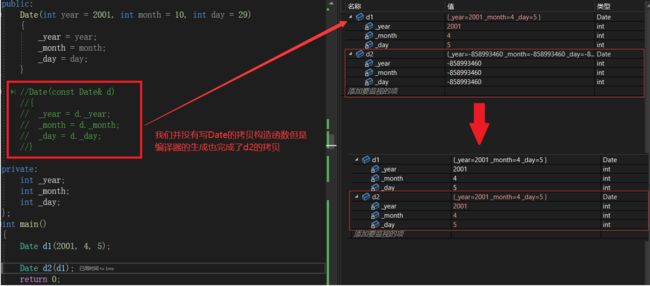
对于拷贝拷贝构造的使用,是在创建新对象时对已存在的对象的去进行拷贝,意思是原来必须存在一个对象,若想使用拷贝构造,必须在创建新对象时使用,使用如下:
Date d1;
Date d2(d1);//拷贝d1此时如果我们不写日期类的拷贝构造函数,发现如下:
总结:
对于日期类,可以不用写构造函数,也可满足需求
对于自定义类型队列介绍:
class Stack
{
public:
Stack(int capacity = 4)
{
_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity);
if (_a == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
_top = 0;
_capacity = capacity;
}
~Stack()
{
free(_a);
_a = nullptr;
_top = _capacity = 0;
}
private:
int* _a;
int _top;
int _capacity;
};
int main()
{
Stack st1;
Stack st2(st1);
return 0;
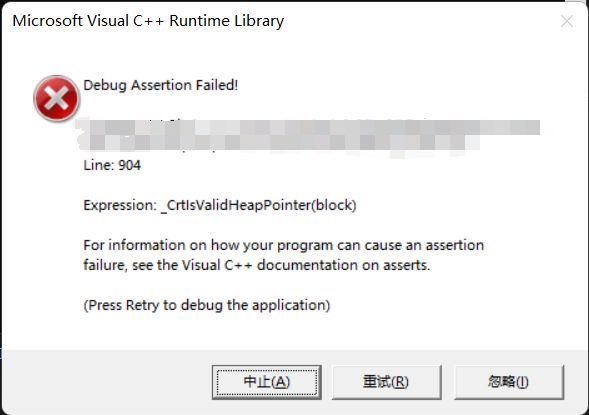
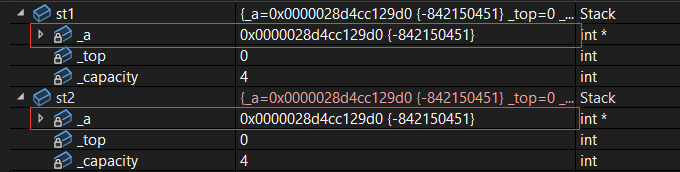
}我们来观察下当我们不写栈类的构造函数时,看看能否完成拷贝。发现结果如下:
当我们调试时会发现 st1 和 st2 指向的同一个空间,说明同一个空间相当于被析构了两次
解决办法:
给对于栈这种类型,拷贝时我们需要去给它另外开辟同一个大小的空间,并将原空间上的数据复制到新开辟的空间,就可完成以上工作
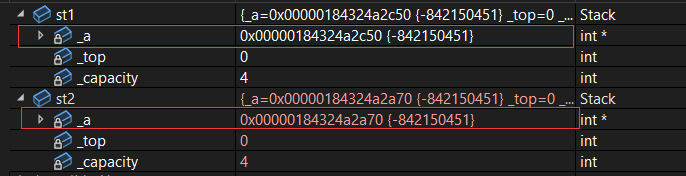
栈的拷贝构造函数如下
Stack(const Stack& d)
{
_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * d._capacity);
if (_a == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(_a, d._a, sizeof(int) * d._top);
_top = d._top;
_capacity = d._capacity;
}运行结果如下:
总结:
对于像栈这种类的,编译器默认生成的拷贝构造不能满足我们的需求,它是指向同一块空间。此时需要我们自己手动写一个构造函数,对于日期类的,编译器默认生成的构造函数就够用,就可以不用写。
默认生成的拷贝构造函数对内置类型按字节拷贝,自定义类型是调用它的拷贝构造。如果自定义的用默认生成的拷贝只能浅拷贝,对于需要析构的函数,需要深拷贝
拷贝构造的使用场景:
①使用已存在对象创建新对象
②函数参数类型为类类型对象
③函数返回值类型为类类型对象
二.运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载可实现让对象使用我们运算符,即可得出两个对象的之间关系。也同样具有返回类型。
函数名的名字:关键字 operator + 需要重载的运算符。如:operator+
函数原型:返回值类型一般根据重载运算符的结果来看。
注意:
①用于运算符重载的运算符不能改变其原来的意义,如 + 、- 之类的
②对于类成员的函数重载时,其形参数目比原操作符操作数的数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个形参为隐藏的 this 指针
③ .* :: sizeof ?: . 这些操作符不能重载
写一个相等的函数重载:
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 2001, int month = 10, int day = 29)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
//如果写成全局的,那么Date的成员变量就是共有的才能满足如下的函数重载。
//因此我们可以将函数重载写成类的成员函数,当然也可用友元函数来解决
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{
return d1._year == d2._year
&& d1._month == d2._month
&& d1._day == d2._day;
}三.赋值重载
在我们日常赋值时,我们既可以连续赋值,也可单个赋值,因此我们写一个赋值重载时,同样需要满足上面的需求,对于连续赋值如: a = b = 3 的形式, 我们一般是返回 b 再去 赋值给 a,因此我们需要返回值。
对于日期类的赋值重载
//使用引用可以提高传递效率
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}如果我们不写赋值重载,看看编译器是如何处理的。编译器默认生成的也满足我们的需求。
但是同样我们拿栈的做一下对比,会发现错误信息和上述中构造函数同一个空间析构两次的例子一样,那么我们该如何去写栈类型的赋值重载,我们知道我们需要开辟不同的空间,对于原来的两个不同初始化的对象,我们需要将被赋值的对象更改的给值对象一样大,如果直接上来就开辟一个一样的空间的话会造成内存泄漏(原来的空间并没释放) 因此我们需要将原来的空间释放后,再去一样大小的空间即可满足。
Stack& operator=(const Stack& st)
{
cout << " Stack& operator=(const Stack& st)" << endl;
//防止类似:st1 = st1 这种的话自己赋值给自己会让_a为随机值
//因为我们一上来就free掉了原来的指向
if (this != &st)
{
//free掉原来所指向的空间,防止内存泄漏
free(_a);
//开辟同样大小的空间
_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);
if (_a == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//赋值
memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);
_top = st._top;
_capacity = st._capacity;
}
return *this;
}结论:
赋值重载和拷贝构造有着相似的属性,一般对于内置类型不写,编译器默认生成的就够用,而对于我们栈这种自定义类型的,我们需要自己写。
赋值重载:已经存在的两个对象的互相拷贝;
拷贝构造:正在创建的新对象时拷贝;
四.日期类相关的运算符重载
class Date
{
public:
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int day[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return day[month];
}
}
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret += day;
return ret;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= 1;
return *this;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
return ((_year == d._year) && (_month == d._month) && (_day == d._day));
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return (*this > d) || (*this == d);
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};