文件的上传
文件上传方便用户将本地文件传输到互联网上的应用程序或网站中,实现信息的共享和传递。它不仅提供了便捷的数据传输方式,还增强了用户的体验,使用户能够轻松分享个人创作、照片、视频、文档等内容。同时,文件上传也促进了远程协作和合作,使得团队成员可以方便地分享和访问文件,提高工作效率,本次将通过使用spring-boot实现文件上传与下载的功能。
1.文件上传
单个文件上传需要引入Java相关包,这里为了简单先写一个简单前端页面
fileload
特别注意:在 form 标签上要加上 enctype="multipart/form-data" 属性设置,不然 spring Boot 不容易解析
enctype="multipart/form-data"在HTML表单中用来指定当表单提交到服务器时,表单数据应该如何编码。当表单包括类型为file的input元素时,即允许用户上传文件,使用这种编码类型是必要的。这样可以确保文件在上传过程中不会被编码,而是以二进制形式发送。如果表单仅包含文本字段,通常使用默认的编码类型application/x-www-form-urlencoded。在使用multipart/form-data编码类型时,每个表单值或文件都作为一个“部分”(part)发送,每个部分都有可能有自己的HTTP头信息,比如Content-Type,这使得浏览器可以将文件作为原始二进制数据流来发送。
这里为了样式美观,同时引入了 bootstrap 框架
org.webjars
bootstrap
4.4.1-1
正式编写接受 POST请求的接口。
文件实体类
public class UploadFileResponse {
private String fileName;
private String fileDownLoadUri;
private String fileType;
private long size;
public UploadFileResponse(String fileName, String fileDownLoadUri, String fileType, long size) {
this.fileName = fileName;
this.fileDownLoadUri = fileDownLoadUri;
this.fileType = fileType;
this.size = size;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public String getFileDownLoadUri() {
return fileDownLoadUri;
}
public void setFileDownLoadUri(String fileDownLoadUri) {
this.fileDownLoadUri = fileDownLoadUri;
}
public String getFileType() {
return fileType;
}
public void setFileType(String fileType) {
this.fileType = fileType;
}
public long getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(long size) {
this.size = size;
}
}
针对上传的文件进行封装 编写属性类
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "file")
public class FileStorageProperties {
//上传到服务器的文件路径
private String uploadDir;
//获取上传路径
public String getUploadDir() {
return uploadDir;
}
//设置上传路径
public void setUploadDir(String uploadDir) {
this.uploadDir = uploadDir;
}
}在 properties 配置文件中写入文件路径信息
file.upload-dir=package封装文件存储异常类,当文件遇到意外时需要抛出的异常信息
public class FileStorageException extends RuntimeException{
//只传入错误原因
public FileStorageException(String message) {
super(message);
}
//传入错误原因和错误信息
public FileStorageException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}找不到文件的异常信息
public class FileNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{
public FileNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public FileNotFoundException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}由于采用MVC的方式,将业务处理都封装到Service层
package org.example.service;
import org.example.Exception.FileStorageException;
import org.example.config.FileStorageProperties;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption;
import java.util.Objects;
@Service
public class FileStorageService {
private final Path fileStorageLocation;
@Autowired(required = false)//找不到实例不会变异常而是设置为 null
public FileStorageService(FileStorageProperties fileStorageProperties) {
//normalize() 方法消除多余的斜杠.等。
this.fileStorageLocation = Paths.get(fileStorageProperties.getUploadDir()).toAbsolutePath().normalize();
try{
//创建路经
Files.createDirectories(this.fileStorageLocation);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new FileStorageException("Could not create the directory" +
" while the uploaded files will be stored.",ex);
}
}
/**
* 储存文件
*
* @param file 文件流对象
* @return String 文件名 | Exception
*/
public String storeFile(MultipartFile file){
//规划文件名
// 1.此方法用于获取上传文件的原始文件名。当处理HTTP文件上传时,你可以通过这个方法来访问上传文件的原始文件名(即用户上传的文件在用户设备上的名称。
String fileName = StringUtils.cleanPath(Objects.requireNonNull(file.getOriginalFilename()));//
try {
//2.检查文件中是否含有无效字符
if (fileName.contains("..")){
throw new FileStorageException("抱歉,文件名里面有无效字符 "+fileName);
}
//3.resolve将当前路径追加在源路径之后
Path targetLocation = this.fileStorageLocation.resolve(fileName);
//复制文件到目标路径
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(),targetLocation, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
return fileName;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new FileStorageException("不能保存文件"+fileName+". 请重新尝试!",e);
}
}
/**
*
* 加载文件资源
* @param fileName 文件名
* @return Resource | Exception
*/
public Resource loadFileResource(String fileName){
try {
Path filePath = this.fileStorageLocation.resolve(fileName).normalize();
//将filePath转成uri后将其 构建 Resource对象
Resource resource = new UrlResource(filePath.toUri());
if (resource.exists()){
return resource;
}else {
throw new FileStorageException("文件没找到 "+fileName);
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new FileStorageException("文件没找到 "+fileName,e);
}
}
}编写 controller 层
import org.example.pojo.UploadFileResponse;
import org.example.service.FileStorageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilder;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping()
public class UploadController {
@Autowired
private FileStorageService fileStorageService;
@PostMapping("/upload")
public UploadFileResponse uploadFileResponse(@RequestParam("single_file")MultipartFile file){
//存储文件并获得保存后的文件名称
String fileName = fileStorageService.storeFile(file);
//获取文件下载地址
String fileDownloadUri = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentContextPath()
.path("/downloadFile/")
.path(fileName)
.toUriString();
//返回一个上传好的文件对象,这里返回下载地址,文件大小以及类型。
return new UploadFileResponse(fileName,fileDownloadUri,file.getContentType(),file.getSize());
}
//根据文件名获取上传好的文件信息
@GetMapping("/downloadFile/{fileName:.+}")
public ResponseEntity downloadFile(@PathVariable String fileName, HttpServletRequest request){
//根据文件名获取文件存储资源
Resource resource = fileStorageService.loadFileResource(fileName);
//尝试确定文件的内容类型
//Try to determine file `s content type
String contentType = null;
try{
//根据资源调用getMimeType()方法来获取文件的MIME类型(即文件的互联网媒体类型,例如"text/plain", "image/jpg"等
contentType = request.getServletContext().getMimeType(resource.getFile()
.getAbsolutePath());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Could not determine file type.");
}
//如果无法确定类型,则退回到默认内容类型
//Fallback to the default content type if type could not be determined
//如果无法确定文件的MIME类型,将其默认设置为"application/octet-stream"。
// 这是一种二进制文件流的MIME类型,常用于表示不能识别文件类型的情况。
if (contentType == null){
contentType = "application/octect-stream";
}
//返回文件流
return ResponseEntity.ok().contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType(contentType)).header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION
,"attachment;filename=\""+resource.getFilename()+"\"").body(resource);
}
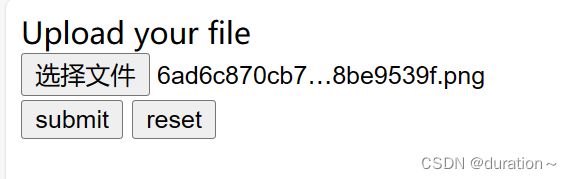
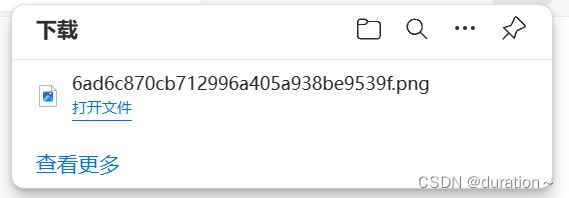
} 最后成功上传文件并可以成功下载:
补充:
ServletUriComponentsBuilder是 Spring Framework 提供的一个用于构建和操作 Servlet 相关的 URI【统一资源标识符(Uniform Resource Identifier)】的辅助类。这个类主要用于在 Servlet 环境中创建和操作 URI,特别是在构建返回的响应中包含链接或定位资源时非常有用。它提供了一组静态方法,用于创建 URI,并且可以与 Spring Web MVC 框架的其他组件(如控制器、处理器等)无缝集成。
使用
ServletUriComponentsBuilder,您可以方便地构建包含应用程序上下文路径、请求路径、请求参数等信息的 URI。它还支持对 URI 进行更改、扩展和相对路径解析等操作。以下是
ServletUriComponentsBuilder常用的方法:
fromCurrentRequest():从当前的 Servlet 请求创建ServletUriComponentsBuilder。fromCurrentContextPath():从当前的 Servlet 上下文路径创建ServletUriComponentsBuilder。path(String path):将指定的路径添加到已创建的 URI 中。queryParam(String name, Object... values):将查询参数添加到已创建的 URI 中。build():根据已定义的信息构建 URI。
多个文件上传就是单个文件的循环,这里不进行更多了解。
2.文件上传限制和服务器限制
对于文件的类型和大小常常有限制,这一方面与业务有关也和服务器的安全有关,为了不被 shell 木马注入和提权,必须限制上传的文件类型,例如只能是 jpg 或者 png 格式的图片等。
public class ValidFileType {
private List validType = new ArrayList<>();
public ValidFileType(List validType) {
if (validType.isEmpty()){
validType.add("png");
validType.add("jpg");
validType.add("jepg");
}
this.validType=validType;
}
public List getValidType() {
return validType;
}
} 使用也非常简单,遍历后进行判断即可。