pytorch-深度学习实践
pytorch-深度学习实践
02-线性回归
线性回归是回归问题,损失函数如下图所示。
MSE:平均平方误差

04-代码实现线性模型
一下代码实现一个线性模型,05为使用pytorch工具实现线性模型
注意:1.tensor计算会建立计算图
2.backward()函数将计算图释放
import torch
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
w = torch.tensor([1.0]) # w的初值为1.0
w.requires_grad = True # 需要计算梯度
def forward(x):
return x*w # w是一个Tensor
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y)**2
print("predict (before training)", 4, forward(4).item())
for epoch in range(100):
for x, y in zip(x_data, y_data):
l =loss(x,y) # l是一个张量,tensor主要是在建立计算图 forward, compute the loss
l.backward() # backward()函数将计算途中,所有设置了需要计算梯度的参数大的梯度都求出来(.requires_grad = True),将梯度存到w中之后将计算图释放
print('\tgrad:', x, y, w.grad.item())
w.data = w.data - 0.01 * w.grad.data # w包含data和grad两种形式,注意grad也是一个tensor张量,data是数值,tensor计算的话会建立计算图
w.grad.data.zero_() # after update, remember set the grad to zero
print('progress:', epoch, l.item()) # 取出loss使用l.item,不要直接使用l(l是tensor会构建计算图)
print("predict (after training)", 4, forward(4).item())
zip函数使用方法
zip()是Python的一个内建函数,它接受一系列可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个tuple(元组),然后返回由这些tuples组成的list(列表)

05-用pytorch实现线性回归
这里用pytorch的工具实现线性模型
- 定义模型时,将其定义为一个类
- 注意:1.所有模型类class继承自nn.Module
2.模型类中至少实现两个函数_init_ 和forward()

*定义损失函数和优化器:损失函数设置为不需要求平均值
model.parameters(),找到所有需要更新的参数,这里是w、b

import torch
# prepare dataset
# x,y是矩阵,3行1列 也就是说总共有3个数据,每个数据只有1个特征
x_data = torch.tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.tensor([[2.0], [4.0], [6.0]])
#design model using class
"""
our model class should be inherit from nn.Module, which is base class for all neural network modules.
member methods __init__() and forward() have to be implemented
class nn.linear contain two member Tensors: weight and bias
class nn.Linear has implemented the magic method __call__(),which enable the instance of the class can
be called just like a function.Normally the forward() will be called
"""
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LinearModel, self).__init__() #这一行调用父类的构造
# (1,1)是指输入x和输出y的特征维度,这里数据集中的x和y的特征都是1维的
# 该线性层需要学习的参数是w和b 获取w/b的方式分别是~linear.weight/linear.bias
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) #构造对象linear类,构造方法torch.nn.Linear继承自Module
def forward(self, x):
y_pred = self.linear(x)
return y_pred
model = LinearModel()
# construct loss and optimizer
# criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average = False)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction = 'sum')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01) # model.parameters()自动完成参数的初始化操作,这个地方我可能理解错了
# training cycle forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(100):
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward:predict
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # forward: loss
print(epoch, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad() # the grad computer by .backward() will be accumulated. so before backward, remember set the grad to zero
loss.backward() # backward: autograd,自动计算梯度
optimizer.step() # update 参数,即更新w和b的值
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item())
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.tensor([[4.0]])
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)
06 逻辑回归
import torch
# import torch.nn.functional as F
# prepare dataset
x_data = torch.Tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.Tensor([[0], [0], [1]])
#design model using class
class LogisticRegressionModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LogisticRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1,1)
def forward(self, x):
# y_pred = F.sigmoid(self.linear(x))
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(self.linear(x))
return y_pred
model = LogisticRegressionModel()
# construct loss and optimizer
# 默认情况下,loss会基于element平均,如果size_average=False的话,loss会被累加。
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(size_average = False)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
# training cycle forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(1000):
y_pred = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data)
print(epoch, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item())
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.Tensor([[4.0]])
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)
07-多为输入特征
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# prepare dataset
xy = np.loadtxt('diabetes.csv', delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
x_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, :-1]) # 第一个‘:’是指读取所有行,第二个‘:’是指从第一列开始,最后一列不要
print("input data.shape", x_data.shape)
y_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, [-1]]) # [-1] 最后得到的是个矩阵
# print(x_data.shape)
# design model using class
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6, 4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 2)
self.linear4 = torch.nn.Linear(2, 1)
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear1(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x)) # y hat
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear4(x)) # y hat
return x
model = Model()
# construct loss and optimizer
# criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(size_average = True)
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
# training cycle forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(1000000):
y_pred = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data)
# print(epoch, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch%100000 == 99999:
y_pred_label = torch.where(y_pred>=0.5,torch.tensor([1.0]),torch.tensor([0.0]))
acc = torch.eq(y_pred_label, y_data).sum().item()/y_data.size(0)
print("loss = ",loss.item(), "acc = ",acc)
08-加载数据
- 1、DataSet 是抽象类,不能实例化对象,只能被其他子类继承,主要是用于构造我们的数据集
- 2、DataLoader 类用于加载数据。需要获取DataSet提供的索引[i]和len;用来帮助我们加载数据,比如说做shuffle(提高数据集的随机性),batch_size,能拿出Mini-Batch进行训练。它帮我们自动完成这些工作。DataLoader可实例化对象。num_workers为多线程数量
- 3.getitem(self,index): 方法支持这个对象在实例化后,可以下标操作dataset[index]
- 加载数据:
- 进入循环
- 完整代码说明:
1、需要mini_batch 就需要import DataSet和DataLoader
2、继承DataSet的类需要重写init,getitem,len魔法函数。分别是为了加载数据集,获取数据索引,获取数据总量。
3、DataLoader对数据集先打乱(shuffle),然后划分成mini_batch。
4、len函数的返回值 除以 batch_size 的结果就是每一轮epoch中需要迭代的次数。
5、inputs, labels = data中的inputs的shape是[32,8],labels 的shape是[32,1]。也就是说mini_batch在这个地方体现的
6、diabetes.csv数据集老师给了下载地址,该数据集需和源代码放在同一个文件夹内。
import torch
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# prepare dataset
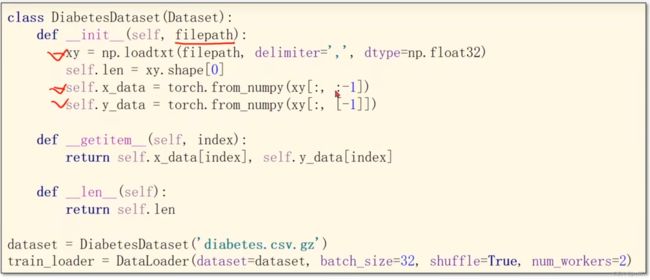
class DiabetesDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filepath):
xy = np.loadtxt(filepath, delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
self.len = xy.shape[0] # shape(多少行,多少列)
self.x_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, :-1])
self.y_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, [-1]])
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.x_data[index], self.y_data[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
dataset = DiabetesDataset('diabetes.csv')
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=0) #num_workers 多线程
# design model using class
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6, 4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear1(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))
return x
model = Model()
# construct loss and optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# training cycle forward, backward, update
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(100):
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0): # train_loader 是先shuffle后mini_batch
inputs, labels = data
y_pred = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(y_pred, labels)
print(epoch, i, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
09-多分类问题
- 注意:
1.transforms.ToTensor() 将图片转换为CWH维度的数据,取值从[0,255]变为[0,1]
2.Normalize()函数中第一个值为均值,第二个值为标准差

- 注意:
1.x.view(-1,784) 因为输入进来的数据是(N,1,28,28),-1是第一维度N的数,784=1乘28乘28
2.输出的最后不经过激活函数

- 注意:
1.torh.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()函数包含softmax激活以及loss计算的过程

import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
# prepare dataset
batch_size = 64
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]) # 归一化,均值和方差
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist/', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist/', train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, shuffle=False, batch_size=batch_size)
# design model using class
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.l1 = torch.nn.Linear(784, 512)
self.l2 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.l3 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.l4 = torch.nn.Linear(128, 64)
self.l5 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784) # -1其实就是自动获取mini_batch
x = F.relu(self.l1(x))
x = F.relu(self.l2(x))
x = F.relu(self.l3(x))
x = F.relu(self.l4(x))
return self.l5(x) # 最后一层不做激活,不进行非线性变换
model = Net()
# construct loss and optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
# training cycle forward, backward, update
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
# 获得一个批次的数据和标签
inputs, target = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 获得模型预测结果(64, 10)
outputs = model(inputs)
# 交叉熵代价函数outputs(64,10),target(64)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' % (epoch+1, batch_idx+1, running_loss/300))
running_loss = 0.0
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
images, labels = data
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1) # dim = 1 列是第0个维度,行是第1个维度
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item() # 张量之间的比较运算
print('accuracy on test set: %d %% ' % (100*correct/total))
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(10):
train(epoch)
test()
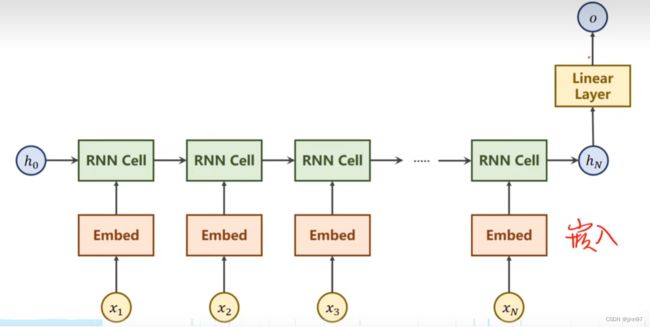
12-RNN
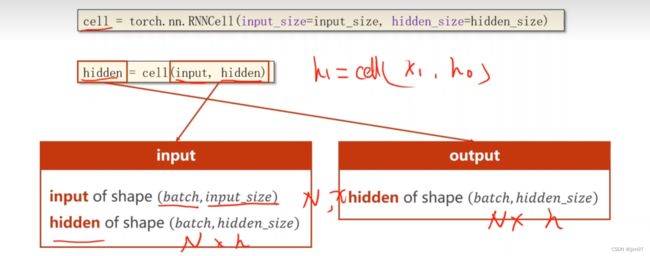
cell=torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size,hidden_size=hidden_size)
hidden=cell(input,hidden)
- RNN
cell=torch.nn.RNN(input_size=input_size,hidden_size=hidden_size,num_layers=num_layers)
#这里的num_layers是上下的rnn数量
out,hidden=cell(input,hidden)
seq到seq的例子
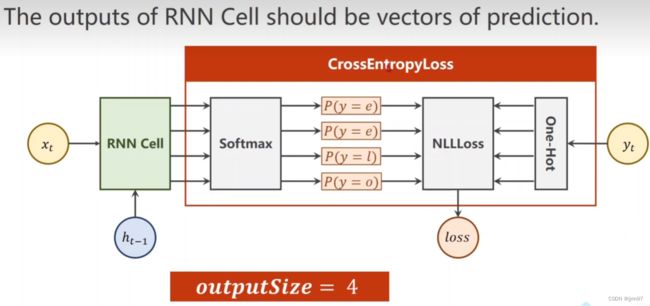
“hello” ->“ohlol”
import torch
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
#构建输入输出字典
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 2, 3]
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
#构造独热向量,此时向量维度为(SeqLen*InputSize)
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
#view(-1……)保留原始SeqLen,并添加batch_size,input_size两个维度
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size)
#将labels转换为(SeqLen*1)的维度
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnncell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size = self.input_size,
hidden_size = self.hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
# RNNCell input = (batchsize*inputsize)
# RNNCell hidden = (batchsize*hiddensize)
hidden = self.rnncell(input, hidden)
return hidden
#初始化零向量作为h0,只有此处用到batch_size
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
for epoch in range(15):
#损失及梯度置0,创建前置条件h0
loss = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
hidden = net.init_hidden() #每次循环前都初始化h0
print("Predicted string: ",end="")
for input, label in zip(inputs, labels):
#此时维度inputs=(seqLen*batchsize*input_size) labels = (seqLen*1)
#遍历时,input是按序列seqLen取的inputs元素(batchsize*inputsize)
hidden = net(input, hidden)
#序列的每一项损失都需要累加
loss += criterion(hidden, label)
#下面两行用于输出,多分类取最大
_, idx = hidden.max(dim=1)
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='')
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(", Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.4f" % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
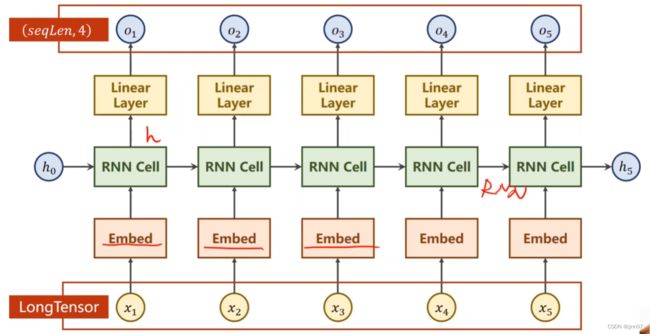
RNN代码:
import torch
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
num_layers = 1
seq_len = 5
#构建输入输出字典
idx2char_1 = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 2, 3]
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
#labels(seqLen*batchSize,1)为了之后进行矩阵运算,计算交叉熵
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers=1):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size #构造H0
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size = self.input_size,
hidden_size = self.hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers)
def forward(self, input):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers,
self.batch_size,
self.hidden_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(input, hidden)
#reshape成(SeqLen*batchsize,hiddensize)便于在进行交叉熵计算时可以以矩阵进行。
return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)
#RNN中的输入(SeqLen*batchsize*inputsize)
#RNN中的输出(SeqLen*batchsize*hiddensize)
#labels维度 hiddensize*1
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
#此时维度为inputs=(seqLen*batchsize*input_size) outputs=(seqLen*batchsize*output_size)
#labels = (seqLen*batchsize*1)
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
#下面四行是把预测字符串输出
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted string: ',''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end = '')
print(", Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f" % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
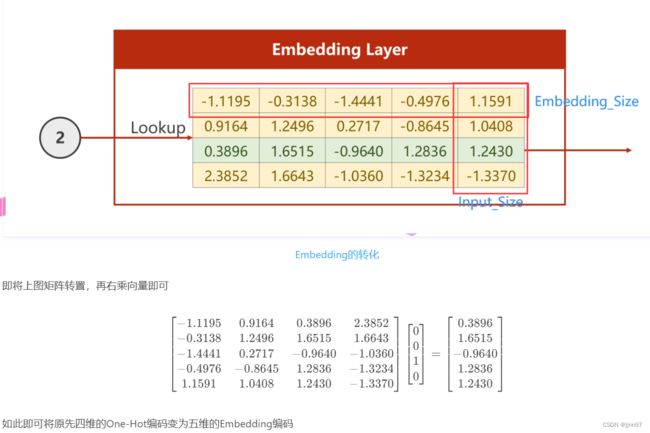
Embedding实现降维
x=self.emb(x) 语句中输入必须为LongTensor维度(batchsize,seqLen),输出维度为(batchsize,seqLen,embeddingSize)
x=self.rnn(x,hidden) 输入维度为(batchsize,seqLen,embeddingSize),输出维度为(batchsize,seqLen,hiddenSize)
因为设置了batch_first=True,所以batchsize在第一位
x=self.fc(x) 输入维度为(batchsize,seqLen,hiddenSize),输出维度为(batchsize,seqLen,numClass)
return x.view(-1,numClass) 将维度转化为(batchsize*seqLen,numClass),方便loss进行处理
import torch
input_size = 4
num_class = 4
hidden_size = 8
embedding_size =10
batch_size = 1
num_layers = 2
seq_len = 5
idx2char_1 = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
idx2char_2 = ['h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [[1, 0, 2, 2, 3]]
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 2, 3]
#inputs 作为交叉熵中的Inputs,维度为(batchsize,seqLen)
inputs = torch.LongTensor(x_data)
#labels 作为交叉熵中的Target,维度为(batchsize*seqLen)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self .emb = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size = embedding_size,
hidden_size = hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first = True)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_class)
def forward(self, x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, x.size(0), hidden_size)
x = self.emb(x)
x, _ = self.rnn(x, hidden)
x = self.fc(x)
return x.view(-1, num_class)
net = Model()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted string: ',''.join([idx2char_1[x] for x in idx]), end = '')
print(", Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f" % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
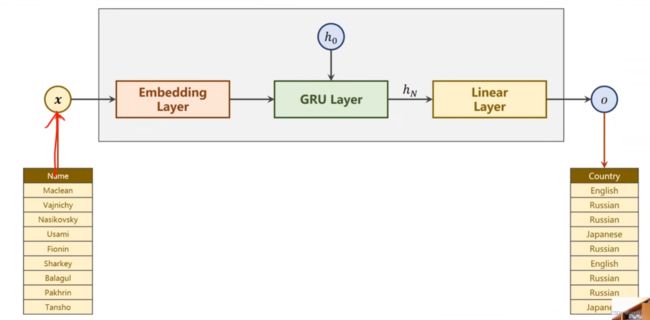
13-RNN进阶
- 注意
1.定义模型为RNNClassifier
N_CHARS:字符的数量,是字母表的大小
HIDDEN_SIZE是隐层的维度
N_COUNTRY是国家分类里的分类数量
N_LAYER是GRU的层数
2.start=time.time()是计算模型训练的时间
3.在每一轮中(epoch),将训练和测试封装在两个函数中,准确率放到acc_list

数据准备过程
ASCII码表共128个字符,字典长度为128
padding,右边表格维度为(batch,seqLen)

将国家做成索引标签

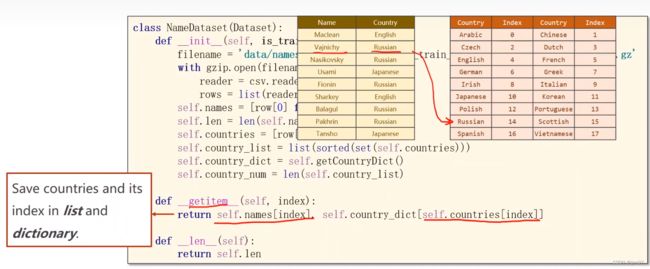
- 名字数据集的构造,注意
class NameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, is_train_set=True):
#读数据
#因为函数中设置了is_train_set=True,所以可以分别从训练/测试里面读
filename = 'names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else 'names_test.csv.gz'
with gzip.open(filename, 'rt') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
#rows中每个元素都是(name,country)
rows = list(reader)
#数据元组(name,country),将其中的name和country提取出来,并记录数量
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]
self. len = len(self.names)
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]
#将country转换成索引
#列表->集合->排序->列表->字典
#set将列表转换为集合,去除重复的元素。sorted函数进行排序,之后再转换为列表
self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries)))
#getCountryDict()将列表转换为词典
self.country_dict = self.getCountryDict()
#获取长度
self.country_num = len(self.country_list)
#获取键值对,country(key)-index(value) 如下图所示
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.names[index], self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
def getCountryDict(self): #此函数用于构造国家的索引词典
country_dict = dict() #设置空字典
for idx,country_name in enumerate(self.country_list, 0): #对country_list进行遍历
country_dict[country_name]=idx #构造键值对
return country_dict
#工具函数:根据索引返回国家名
def idx2country(self, index):
return self.country_list[index]
#工具函数:返回国家数目
def getCountriesNum(self):
return self.country_num
trainset = NameDataset(is_train_set = True)
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
testset = NameDataset(is_train_set=False)
testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
#最终的输出维度
N_COUNTRY = trainset.getCountriesNum()
模型设计
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers =1 , bidirectional = True):
super(RNNClassifier, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1
#Embedding层输入 (SeqLen,BatchSize)
#Embedding层输出 (SeqLen,BatchSize,HiddenSize)
#将原先样本总数为SeqLen,批量数为BatchSize的数据,转换为HiddenSize维的向量
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
#bidirection用于表示神经网络是单向还是双向
self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional = bidirectional)
#线性层需要*direction
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size * self.n_directions, output_size)
def _init_hidden(self): #工具函数:创建隐层
hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size)
return create_tensors(hidden)
def forward(self, input, seq_length):
#对input进行转置,Batch*Seqlen ——>Seqlen*Batch
input = input.t()
batch_size = input.size(1) #保存batchsize,用于构造初始的hidden
#(n_Layer * nDirections, BatchSize, HiddenSize)
hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size)
#(SeqLen, BatchSize, HiddenSize)
embedding = self.embedding(input) #此时维度为(Seqlen*Batch*hiddensize)
#下面是对数据计算过程提速
#需要得到嵌入层的结果(输入数据)及每条输入数据的长度
gru_input = pack_padded_sequence(embedding, seq_length)
output, hidden = self.gru(gru_input, hidden)
#如果是双向神经网络会有h_N^f以及h_1^b两个hidden
if self.n_directions == 2:
hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=1) #双向的就将两个拼起来
else:
hidden_cat = hidden[-1]
fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat)
return fc_output
双向


下面是gpu加速计算的图解 pack_padded_sequence


将名字转换为tensor
#ord()取ASCII码值
def name2list(name): #给定一个名字
arr = [ord(c) for c in name] #将名字中的每一个字母转换为ASCII值
return arr, len(arr)
def create_tensor(tensor): #判断是否使用GPU
if USE_GPU:
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
tensor = tensor.to(device)
return tensor
def make_tensors(names, countries):
sequences_and_length = [name2list(name) for name in names] #将每个名字变为列表。返回的是一个元组sequences_and_length的值为(arr,len(arr))
#单独取出所有的列表中每个姓名的ASCII码序列
name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_length]
#单独取出列表长度,将列表车行度转换为LongTensor
seq_length = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_length])
#将整型变为长整型longtensor
countries = countries.long()
#做padding
#新建一个全0张量大小为最大长度-当前长度
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences), seq_lengths.max()).long()
#取出每个序列及其长度idx固定0,复制操作贴过去
for idx, (seq, seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences, seq_length), 0):
#将序列转化为LongTensor填充至第idx维的0到当前长度的位置
seq_tensor[idx, :seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
#排序,返回排序后的序列及索引
seq_length, perm_idx = seq_length.sort(dim = 0, descending = True) #按照序列长度排序,pytorch的sort函数返回两个值:排完序的seq_length,以及其索引(id)
seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx] #按照长度的索引,进行排序
countries = countries[perm_idx] #按照长度的索引,进行排序
return create_tensor(seq_tensor),
create_tensor(seq_length),
create_tensor(countries)
训练与测试
def trainModel():
total_loss = 0
for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(trainloader, 1):
inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
loss = criterion(output, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if i % 10 == 0:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch} ', end='')
print(f'[{i * len(inputs)}/{len(train_set)}]', end='')
print(f'loss={total_loss / (i * len(inputs))}')
return total_loss
def testModel():
correct = 0
total = len(testset)
print("evaluating trained model……")
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(testloader, 1):
inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
pred = output.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
percent = '%.2f' % (100*correct/total)
print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct}/{total} {percent}%')
return correct/total