异步编程:线程池和CompletableFuture
最近写业务逻辑的时候遇到一些请求需要处理数据,过程很长但是这个过程需要后台去完成,开始处理就给前端返一个处理中的状态,后续处理完成通过RocketMQ来订阅修改状态。
最开始想这个问题的时候觉得代码都是从上到下,return了的话怎么运行后续处理数据,那肯定是要启线程,我们看看最终实现,利用了juc的CompletableFuture,一种不需要返回值,一种需要返回值。
String batchNo = String.valueOf(SnowFlakeUtil.nextId());
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
//处理逻辑
});
return SingleApiResult.of(batchNo);CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
return riskEngineService.batchStartingStorageAll(qos, batdchNo);
}).whenComplete((r,e) -> {
BatchNoDTO batchNoDTO = new BatchNoDTO();
BatchStartResultDTO batchStartResultDTO = Optional.ofNullable(r).orElse(new BatchStartResultDTO());
batchNoDTO.setBatchNo(batchStartResultDTO.getBatchNo());
if(e == null) {
variablesTree.callBackDefaultMQ(batchStartAsyncDTO.getCallBackUrl(), batchNoDTO);
} else {
log.error("该批次:{},执行存在异常信息:{}", r.getBatchNo(), e);
variablesTree.callBackDefaultMQ(batchStartAsyncDTO.getCallBackUrl(), batchNoDTO);
}
});写代码的时候顺便看了看线程池和CompletableFuture,所以写篇文章总结一下。
线程池
什么是线程池?
线程池是一种利用池化技术思想来实现的线程管理技术,主要是为了复用线程、便利地管理线程和任务、并将线程的创建和任务的执行解耦开来。我们可以创建线程池来复用已经创建的线程来降低频繁创建和销毁线程所带来的资源消耗。在JAVA中主要是使用ThreadPoolExecutor类来创建线程池,并且JDK中也提供了Executors工厂类来创建线程池(不推荐使用)。
线程池的优点:
降低资源消耗,复用已创建的线程来降低创建和销毁线程的消耗。
提高响应速度,任务到达时,可以不需要等待线程的创建立即执行。
提高线程的可管理性,使用线程池能够统一的分配、调优和监控。
为什么用线程池?
假如我们每一次执行都需要新建一个线程,那就有两个问题
- 不受控制风险,对于每个创建的线程没有统一管理的地方,每个线程创建后我们不知道线程的去向。
- 每执行一个任务都需要创建新的线程来执行,创建线程对系统来说开销很高
JAVA线程池继承关系
java中线程池的核心实现类是ThreadPoolExecutor,可以通过该类地构造方法来构造一个线程池。
ThreadPoolExecutor<-AbstractExecutorService<-ExecutorService<-Executor
Executor接口提供了将任务的执行和线程的创建以及使用解耦开来的抽象ExecutorService接口继承了Executor接口,在Executor的基础上,增加了一些关于管理线程池本身的一些方法,比如查看任务的状态、stop/terminal线程池、获取线程池的状态等等。
ThreadPoolExecutor的构造组成
corePoolSize:核心线程数量,决定是否创建新的线程来处理到来的任务maximumPoolSize:最大线程数量,线程池中允许创建线程地最大数量keepAliveTime:线程空闲时存活的时间unit:空闲存活时间单位workQueue:任务队列,用于存放已提交的任务threadFactory:线程工厂,用于创建线程执行任务handler:拒绝策略,当线程池处于饱和时,使用某种策略来拒绝任务提交
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
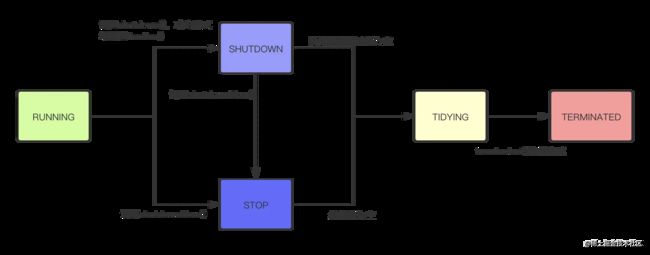
线程池的生命周期
五种状态
- RUNNING:处于RUNNING状态下的线程池能够接收新的任务以及处理阻塞队列中的任务SHUTDOWN:处于SHUTDOWN状态下的线程池,不再接收新到来的任务,但是依然能够处理阻塞队列中的任务
- STOP:处于STOP状态下的线程池,不再接收新到来的任务,但是依然能够处理阻塞队列中的任务
- TIDYING:所有任务已经终止,有效线程数为0,线程转换到TIDYING状态会运行terminated钩子方法
- TERMINATED:terminated方法执行完成后进入TERMINATED状态
生命周期
ThreadPoolExecutor中表示线程池状态设计
在ThreadPoolExecutor中使用一个AtomicInteger类型的ctl字段来描述线程池地运行状态和线程数量,通过ctl的高三位来表示线程池的5种状态,低29位表示线程池中现有的线程数量。使用最少的变量来减少锁竞争,提高并发效率。
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
// 线程池线程数地bit数
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
// 线程池中最大线程容量
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
// 获取线程池地运行状态
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
// 获取有效工作线程地数量
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
// 组装线程数量和线程池状态
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
线程池执行流程
- 如果workerCount < corePoolSize ==> 创建线程执行提交的任务
- 如果workerCount >= corePoolSize && 阻塞队列未满 ==> 添加至阻塞队列,等待后续线程来执行提交地任务
- 如果workerCount >= corePoolSize && workerCount < maxinumPoolSize && 阻塞队列已满 ==> 创建非核心线程执行提交的任务
- 如果workerCount >= maxinumPoolSize && 阻塞队列已满 ==> 执行拒绝策略
execute 提交任务
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
// 工作线程数量 < corePoolSize => 直接创建线程执行任务
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 工作线程数量 >= corePoolSize && 线程池处于运行状态 => 将任务添加至阻塞队列中
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
/**
* 为什么需要double check线程池地状态?
* 在往阻塞队列中添加任务地时候,有可能阻塞队列已满,需要等待其他的任务移出队列,在这个过程中,线程池的状态可能会发生变化,所以需要doublecheck
* 如果在往阻塞队列中添加任务地时候,线程池地状态发生变化,则需要将任务remove
*/
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
addWorker 创建线程加入线程池
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
// 线程池状态处于非RUNNING状态,添加worker失败
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
// 判断线程池中线程数量是否处于该线程池允许的最大线程数量,如果允许创建线程,则cas更新线程池中线程数量,并退出循环检查,执行下面创建线程地逻辑
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
// 创建线程
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
// 如果线程池处于RUNNING状态,并且线程已经启动则提前抛出线程异常启动异常
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
// 将线程加入已创建地线程集合,更新用于追踪线程池中线程数量largestPoolSize字段
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 启动线程执行任务
if (workerAdded) {
// 启动线程会调用Worker中地runWorker()来执行任务
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
runWorker 执行任务
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
// 获取执行任务线程
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取执行任务
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
// 将worker中的任务置空
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
// 双重检查线程池是否正在停止,如果线程池停止,并且当前线程能够中断,则中断线程
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
// 前置执行任务钩子函数
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
// 执行当前任务
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
// 后置只sing任务钩子函数
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
// 回收线程
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
线程池拒绝策略
当线程池中的线程和阻塞队列中的任务已经处于饱和状态,线程池则需要执行给定的拒绝策略来拒绝正在提交的任务,ThreadPoolExecutor主要提供了一下四种拒绝策略来拒绝任务。
- AbortPolicy:抛出异常让用户可根据具体任务来做出具体的判断,默认的拒绝策略
- DiscardPolicy:什么也不做,直接丢弃任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy:将阻塞队列中的任务poll出来,然后执行当前任务
- CallerRunsPolicy:让提交任务的线程来执行任务
- new RejectedExecutionHandler():自定义拒绝策略
CompletableFuture
假如我们之前要另启线程执行代码,我们需要继承Thread方法或者实现Runnable接口,如果需要返回值就实现Callable接口,当然我们还需要创建线程池来执行线程,非常麻烦,具体可以看(6条消息) java创建线程(Thread)的5种方式_创建thread_强强爱java的博客-CSDN博客
这时候我们就要使用Java8推出的异步编程神器CompletableFuture,CompletableFuture自己维护了一个线程池ForkJoin,也可以传入自定义的线程池,任务的创建也非常方便。
创建任务
- supplyAsync方法,支持返回值
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier)
//自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier, Executor executor)- runAsync方法,不支持返回值
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
eg:
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以自定义线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//runAsync的使用
CompletableFuture runFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("run,关注公众号:loquat分享站"), executor);
//supplyAsync的使用
CompletableFuture supplyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.print("supply,关注公众号:loquat分享站");
return "loquat分享站"; }, executor);
//runAsync的future没有返回值,输出null
System.out.println(runFuture.join());
//supplyAsync的future,有返回值
System.out.println(supplyFuture.join());
executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭
}
}
//输出
run,关注公众号:loquat分享站
null
supply,关注公众号:loquat分享站loquat分享站 任务回调
- thenRun/thenRunAsync,做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务。某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法;但是前后两个任务没有参数传递,第二个任务也没有返回值
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
Async就是在执行第两个任务时,第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池;thenRun使用的是同一个,其他方法也一样
eg:
public class FutureThenRunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("先执行第一个CompletableFuture方法任务");
return "loquat分享站";
}
);
CompletableFuture thenRunFuture = orgFuture.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");
});
System.out.println(thenRunFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
先执行第一个CompletableFuture方法任务
接着执行第二个任务
null
- thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
public class FutureThenAcceptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("原始CompletableFuture方法任务");
return "loquat分享站";
}
);
CompletableFuture thenAcceptFuture = orgFuture.thenAccept((a) -> {
if ("loquat分享站".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("关注了");
}
System.out.println("先考虑考虑");
});
System.out.println(thenAcceptFuture.get());
}
}
- ForkJoin线程池,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
public class FutureThenApplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("原始CompletableFuture方法任务");
return "loquat分享站";
}
);
CompletableFuture thenApplyFuture = orgFuture.thenApply((a) -> {
if ("loquat分享站".equals(a)) {
return "关注了";
}
return "先考虑考虑";
});
System.out.println(thenApplyFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
原始CompletableFuture方法任务
关注了
- exceptionally,某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调方法;并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。
public class FutureExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
throw new RuntimeException();
}
);
CompletableFuture exceptionFuture = orgFuture.exceptionally((e) -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return "你的程序异常啦";
});
System.out.println(exceptionFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:273)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:280)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1592)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.exec(CompletableFuture.java:1582)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:289)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.runTask(ForkJoinPool.java:1056)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1692)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:157)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException
at cn.eovie.future.FutureWhenTest.lambda$main$0(FutureWhenTest.java:13)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1590)
... 5 more
你的程序异常啦
- whenComplete方法 ,某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
public class FutureWhenTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "loquat分享站";
}
);
CompletableFuture rstFuture = orgFuture.whenComplete((a, throwable) -> {
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("上个任务执行完啦,还把" + a + "传过来");
if ("loquat分享站".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("666");
}
System.out.println("233333");
});
System.out.println(rstFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
上个任务执行完啦,还把loquat分享站传过来
666
233333
loquat分享站
- handle方法 ,某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且是有返回值的;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法执行的结果。
public class FutureHandlerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "loquat分享站";
}
);
CompletableFuture rstFuture = orgFuture.handle((a, throwable) -> {
System.out.println("上个任务执行完啦,还把" + a + "传过来");
if ("loquat分享站".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("666");
return "关注了";
}
System.out.println("233333");
return null;
});
System.out.println(rstFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
上个任务执行完啦,还把loquat分享站传过来
666
关注了
线程池与CompletableFuture配合使用
这里使用了自定义的线程工厂,开发中方便定位问题
package Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @description:
* @author: zxy
* @createDate: 2023/5/28
*/
public class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
/**
* 构造函数传入我们想业务需要的线程名字threadName,方便发生异常是追溯
* @param threadName
*/
public MyThreadFactory(String threadName) {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
if (threadName == null || threadName.isEmpty()){
threadName = "pool";
}
namePrefix = threadName +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
package Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @description:
* @author: zxy
* @createDate: 2023/5/25
*/
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadFactory loquat = new MyThreadFactory("loquat");
final ThreadPoolExecutor pool =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(
20,
100,
5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),
loquat
);
System.out.println("111" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
System.out.println("222" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, pool);
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
System.out.println("333" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, pool);
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
pool.shutdown();
}
}
参考文章:异步编程利器:CompletableFuture详解 |Java 开发实战 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
线程池详解 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)