html中放大镜案列,Canvas实现放大镜效果完整案例分析(附代码)
本文主要记录 canvas 在图像、文字处理、离屏技术和放大镜特效的实现过程中使用到的api。先看下效果吧:
一张模糊的图片:
鼠标点击任意位置,产生放大效果:
哇塞~ 一个帅哥,哈哈哈哈~
1、放大镜原理
实现效果:如上图,点击或点击滑动鼠标显示一个区域,区域中显示对应点击部分范围的放大清晰图片。那么问题就可以肢解为3部分:
1、如何在canvas(模糊图)上再画出另外一个canvas(清晰放大图);
2、如何将canvas中显示的(清晰放大图)剪切出圆形区域。
3、如何在鼠标点击滑动的时候显示该区域;
2、显示模糊照片
其实一般的交互不是模糊照片,这里我只是为了夸张下效果,用了张模糊的原图,哈哈哈,canvas本身是可以对清晰的图片做滤镜处理,涉及到很多图形学的算法,然后我不会,默默的打开了ps手动高斯模糊了一张照片...嗯,没毛病!
首先定义一个 canvas 元素
//定义canvas画布
var canvas1 = document.getelementbyid('canvas1');
ctx1 = canvas.getcontext('2d');
//模糊图片加载
var image1 = new image();
image1.src = "./模糊.png";
//图片加载成功后绘制图片
image1.onload = function() {
//drawimage 在画布上绘制模糊图片
ctx1.drawimage(image1, 0, 0, canvas1.width, canvas1.height);
};
ctx1.drawimage(图片,x位置,y位置,图片显示宽度,图片显示高度)
3、加载清晰图片
我们再加一个canvas(放大镜看到的图片),初始隐藏:
var canvas2 = document.getelementbyid('canvas2'),
ctx2 = canvas2.getcontext('2d'),
scale = 2; // 放大倍数
// canvas2的图片大小是模糊图片的2倍
canvas2.width = canvas.width * scale;
canvas2.height = canvas.height * scale;
// 在canvas2中加载图片
var image2 = new image();
image2.src = "name2.png";
image2.onload = function() {
ctx2.drawimage(image2, 0, 0, canvas2.width, canvas2.height);
};
4、显示放大镜
4.1 绘制放大镜
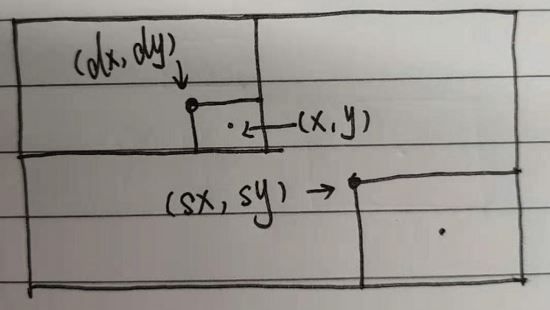
鼠标所处的位置点(x,y)是区域的中心,计算出清晰图所在的位置点,截取圆形
// 保存当前状态
ctx1.save();
// 边框
ctx1.strokestyle = "#9eddf1";
ctx1.linewidth = 3;
// 开始绘制
ctx1.beginpath();
// ⚪
ctx1.arc(x, y, mr, 0, math.pi * 2);
ctx1.stroke();
// 表示剪切
ctx1.clip();
// 画图
ctx1.drawimage(that.canvas2, sx, sy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr, dx, dy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr);
// 释放当前状态
ctx1.restore();
绘制状态的最佳搭档save()和restore():用于对当前状态的保存及释放不影响其他操作;可用于重复的绘制图形的变化过程;
clip():表示剪切区域
4.2 离屏技术
所谓的离屏技术就是在一个canvas上绘制另外一个canvas,前面使用的绘制图片的api是 drawimage() ,它分别可以支持,3个、5个和9个参数; 其中第一个参数既可以是图片,也可以是canvas对象!那么我们就可以使用这个方法,在圆上绘制出清晰图了~
// 圆的半径是mr
var mr = 100;
// 对应模糊图的左上角起点
var dx = x - mr,
dy = y - mr;
// 找出清晰图截图的左上角起点
var sx = x * scale - mr,
sy = y * scale- mr;
...
ctx.clip();
// 在对应的位置上重新绘制图片
//drawimage(img,sx,sy,swidth,sheight,x,y,width,height) 9个参数时
//img: 图片/canvas
//sx: 图片的x起点
//sy: 图片的y起点
//swidth:要绘制的图片选取的宽度
//sheight:要绘制的图片选取的高度
//x,y:图片在canvas上显示的位置
//width,height:在canvas上要显示的大小
ctx1.drawimage(canvas2, sx, sy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr, dx, dy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr);
...
5、鼠标交互事件
效果:鼠标点击并滑动鼠标产生反应,松开鼠标或者移除画布则失效。
//定义一个判断鼠标是否是点击滑动的标识符
var flag;
//鼠标点入事件
canvas.onmousedown = function(e) {
flag = true;
//显示放大镜
}
// 鼠标移动事件
canvas.onmousemove = function(e) {
if (flag) {
//显示放大镜
}
}
//鼠标松开事件
canvas.onmouseup = function(e) {
flag = false;
// 隐藏放大镜
}
//鼠标离开事件
canvas.onmouseout = function(e) {
flag = false;
// 隐藏放大镜
}
完整代码:
var scale = 3;
var mr = 150;
var photo = {
//初始化
init: function() {
var that = this;
that.canvas = document.getelementbyid('canvas');
that.ctx = that.canvas.getcontext('2d');
that.canvas2 = document.getelementbyid('canvas2');
that.ctx2 = that.canvas2.getcontext('2d');
that.canvas.width = 800;
that.canvas.height = 500;
that.canvas2.width = that.canvas.width * scale;
that.canvas2.height = that.canvas.height * scale;
that.image1 = new image();
that.image1.src = "./name3.jpg";
that.image2 = new image();
that.image2.src = "./name4.jpg";
that.image1.onload = function() {
that.ctx.drawimage(that.image1, 0, 0, that.canvas.width, that.canvas.height);
};
that.image2.onload = function() {
that.ctx2.drawimage(that.image2, 0, 0, that.canvas2.width, that.canvas2.height);
that.moveevt();
};
},
bigerimage: function(x, y) {
var that = this;
var imagex = x * scale,
imagey = y * scale,
sx = imagex - mr,
sy = imagey - mr;
var dx = x - mr,
dy = y - mr;
that.ctx.save();
that.ctx.strokestyle = "#9eddf1";
that.ctx.linewidth = 3;
that.ctx.beginpath();
that.ctx.arc(x, y, mr, 0, math.pi * 2);
that.ctx.shadowcolor = "#6ed25b";
that.ctx.shadowblur = 10;
that.ctx.stroke();
that.ctx.clip();
that.ctx.drawimage(that.canvas2, sx, sy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr, dx, dy, 2 * mr, 2 * mr);
that.ctx.restore();
},
//移动
moveevt: function() {
var that = this;
that.canvas.onmousedown = function(e) {
that.flag = true;
that.showimage(e);
}
that.canvas.onmousemove = function(e) {
if (that.flag) {
that.showimage(e)
}
}
that.canvas.onmouseup = function(e) {
that.hideimage(e)
}
that.canvas.onmouseout = function(e) {
that.hideimage(e)
}
},
showimage: function(e) {
e.preventdefault()
var x = e.offsetx,
y = e.offsety,
that = this;
that.ctx.clearrect(0, 0, that.canvas.width, that.canvas.height);
that.ctx.drawimage(that.image1, 0, 0, that.canvas.width, that.canvas.height);
that.bigerimage(x, y);
},
hideimage: function(e) {
e.preventdefault()
var that = this;
that.flag = false;
that.ctx.clearrect(0, 0, that.canvas.width, that.canvas.height);
that.ctx.drawimage(that.image1, 0, 0, that.canvas.width, that.canvas.height);
}
}
window.onload = function() {
photo.init();
}
到此这篇关于canvas实现放大镜效果完整案例分析(附代码)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关canvas 放大镜内容请搜索萬仟网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持萬仟网!