jdbc连接数据库
文章目录
-
- @[TOC](文章目录)
- 一、jdbc快速入门
-
- (1)Jdbc原理
- (2)Jdbc带来的好处
- (3)Jdbc API
- (4)Jdbc快速入门
- 二、连接jdbc的5种方式及SQL注入问题
-
- (1)连接jdbc的5种方式
- (2)ResultSet底层
- (3)SQL注入问题
- (4)预处理PreparedStatement
- 三、JDBCUtils工具类
-
- (1)API
- (2)JDBCUtils工具类
- (3)JDBCUtils工具类的使用
- 四、事务及批处理
-
- (1)事务介绍
- (2)使用事务模拟转账业务
- (3)批处理应用
文章目录
-
- @[TOC](文章目录)
- 一、jdbc快速入门
-
- (1)Jdbc原理
- (2)Jdbc带来的好处
- (3)Jdbc API
- (4)Jdbc快速入门
- 二、连接jdbc的5种方式及SQL注入问题
-
- (1)连接jdbc的5种方式
- (2)ResultSet底层
- (3)SQL注入问题
- (4)预处理PreparedStatement
- 三、JDBCUtils工具类
-
- (1)API
- (2)JDBCUtils工具类
- (3)JDBCUtils工具类的使用
- 四、事务及批处理
-
- (1)事务介绍
- (2)使用事务模拟转账业务
- (3)批处理应用
一、jdbc快速入门
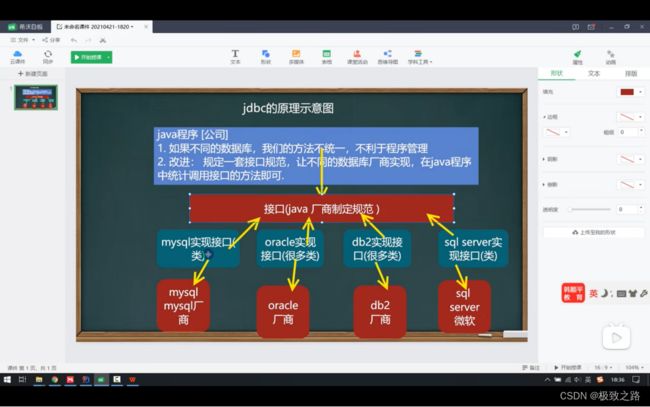
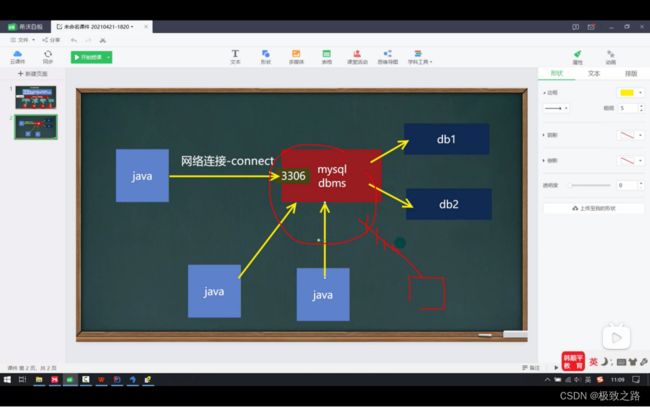
(1)Jdbc原理
Java程序只是定义了一套规范,让不同的数据库自己具体实现,这样就比让java程序自己实现直接操作数据库要方便很多。
每个数据库将 接口实现之后形成的类 会打包成.jar文件。
所以叫加载驱动,也叫该类叫驱动类,实际上是各个数据库对java定义的操作数据库规范的自己的具体实现类。
因此如果需要java文件能够使用mysql,需要将对应数据库的jar文件引入项目才可以。
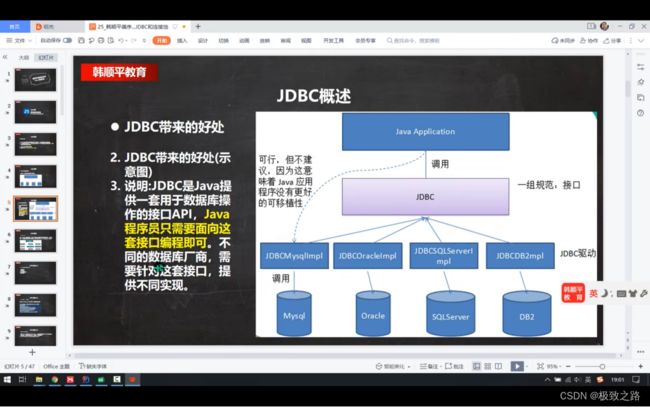
(2)Jdbc带来的好处
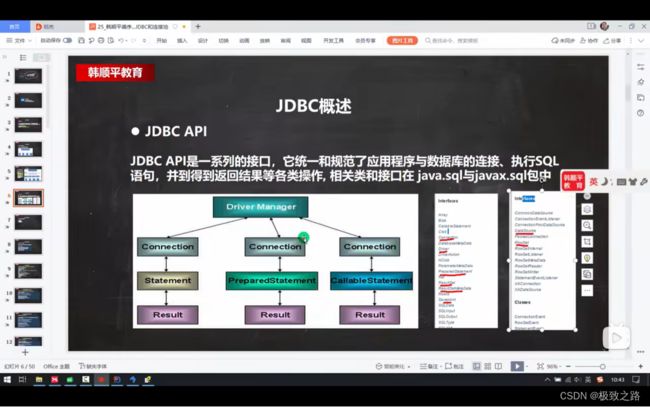
(3)Jdbc API
Javax.sql里面主要是对一些数据源(连接池中)操作的。
(4)Jdbc快速入门
/**
* 第一个jdbc程序完成简单的操作
*/
public class Jdbc01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.前置工作:项目下创建一个文件夹,比如libs
//将mysql.jar拷贝到该目录下,点击add to project...
//1..注册驱动
Driver driver = new Driver();
//2.得到连接
// jdbc:mysql:// 规定表示协议,通过jdbc的方式连接mysql
//hsp_db03: 连接到dbms的哪个数据库?
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03";
//将用户名和密码放到Properties对象中
Properties properties = new Properties();
//user和password是规定好的,不可变。
properties.setProperty("user", "root");//用户
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");//密码
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
//3.执行sql
String sql = "insert into actor values(null,'张飞','男',now(),'17328721782')";
// String sql = "update actor set name = '江南'";
// String sql = "delete from actor where id=1";
//Statement:用于执行静态sql语句,并返回执行的结果的对象
Statement statement = connect.createStatement();
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
// 4.释放资源
statement.close();
connect.close();
}
}
如果不关闭连接,就会导致连接非常多。到一定程度,再来一个连接就连不上了。
二、连接jdbc的5种方式及SQL注入问题
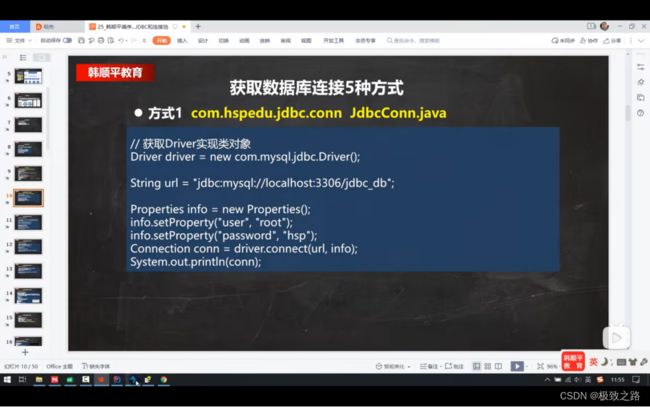
(1)连接jdbc的5种方式
方式1 问题:直接new了一个driver,该driver是第三方的,并且是静态加载,灵活性不强。依赖性比较高。
方式三相比方式二:注册驱动和获取连接都是用的DriverManager。
但多了一种使用user和password登录的方式。
方式4少了使用DriverManager.registerDriver注册。
因为加载这个Driver类的时候,这个类有一个静态代码,会自动完成注册驱动。
Mysql5.1.6之后,不需要显示调用去注册了。而是自动调用驱动jar包下的一个文本中的类名称去注册。
/**
* 获取数据库连接的5种方式
*/
public class JdbcConn {
@Test
public void connect01() throws SQLException {
//1.前置工作:项目下创建一个文件夹,比如libs
//将mysql.jar拷贝到该目录下,点击add to project...
//1..注册驱动
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
//2.得到连接
// jdbc:mysql:// 规定表示协议,通过jdbc的方式连接mysql
//hsp_db03: 连接到dbms的哪个数据库?
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03";
//将用户名和密码放到Properties对象中
Properties properties = new Properties();
//user和password是规定好的,不可变。
properties.setProperty("user", "root");//用户
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");//密码
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
//3.执行sql
String sql = "insert into actor values(null,'张飞','男',now(),'17328721782')";
// String sql = "update actor set name = '江南'";
// String sql = "delete from actor where id=1";
//Statement:用于执行静态sql语句,并返回执行的结果的对象
Statement statement = connect.createStatement();
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
// 4.释放资源
statement.close();
connect.close();
}
@Test
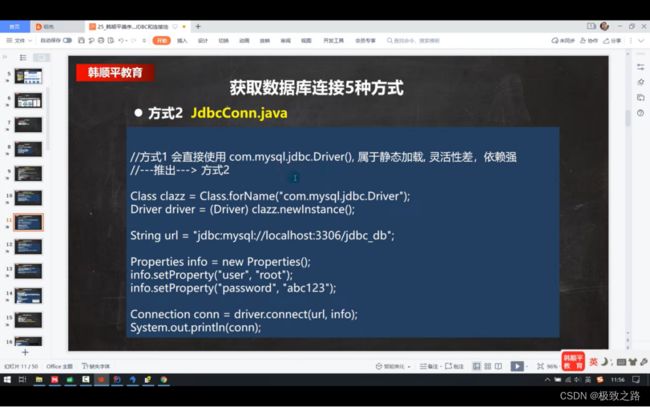
public void connect02() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
//使用反射加载Driver类,动态加载,更加的灵活,减少依赖性。
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) aClass.newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
System.out.println("方式二=" + connect);
connect.close();
}
//方式二相比方式一:加载Driver驱动的时候使用的是动态加载。
@Test
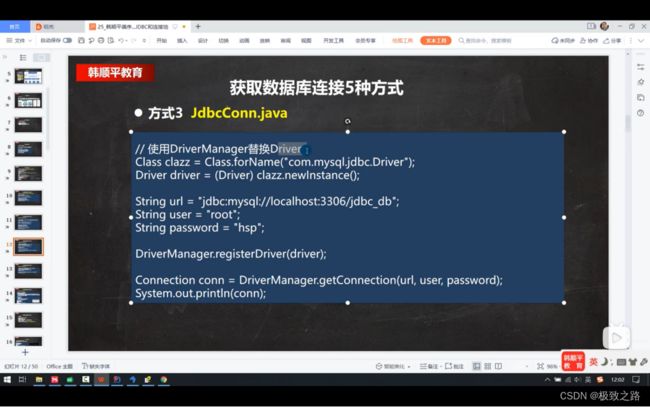
public void connect03() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) aClass.newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); //注册驱动
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//获取连接
System.out.println("第三种方式:" + connection);
connection.close();
}
/*
方式三相比方式二:注册驱动和获取连接都是用的DriverManager。
但多了一种使用user和password登录的方式。
*/
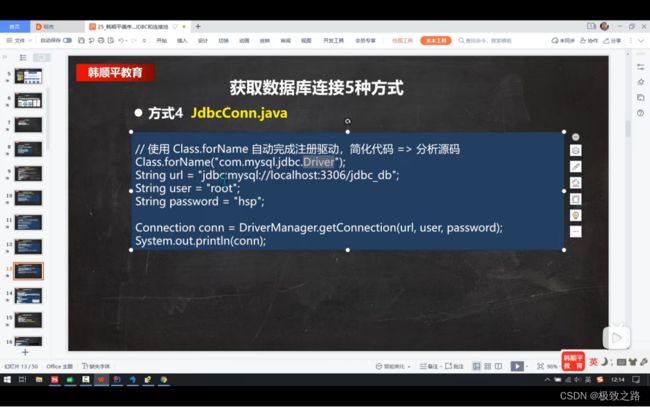
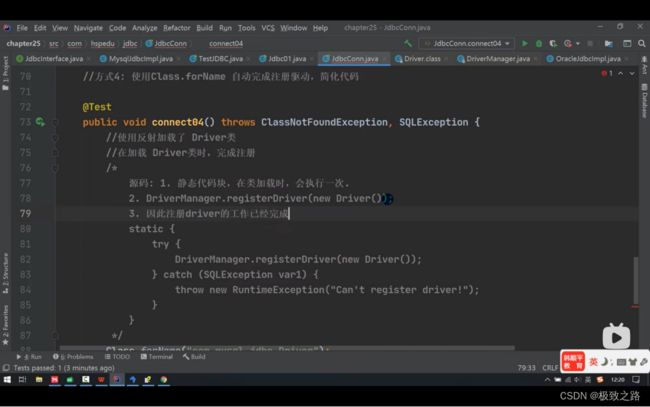
//方式四:使用Class.forName()自动完成注册驱动,简化代码。
@Test
public void connect4() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//创建url和user ,password
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("第四种方式:" + conn);
conn.close();
}
/*
方式四相比方式三是自动完成注册驱动。底层在静态代码块中。
*/
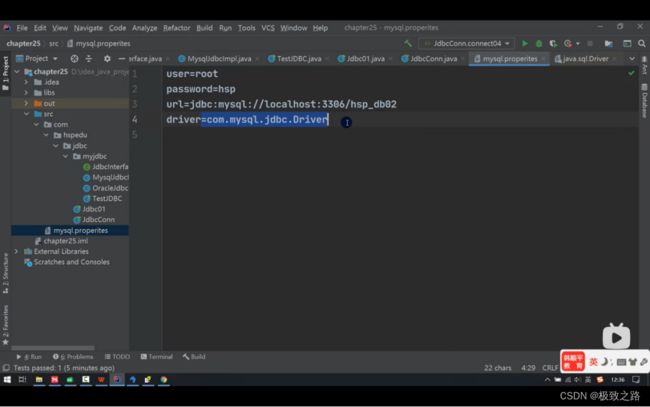
/*
在方式四的基础上改进,增加配置文件,让连接mysql更加灵活。
*/
@Test
public void connect5() throws Exception{
Properties properties = new Properties();
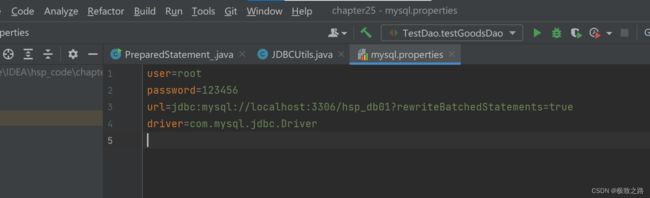
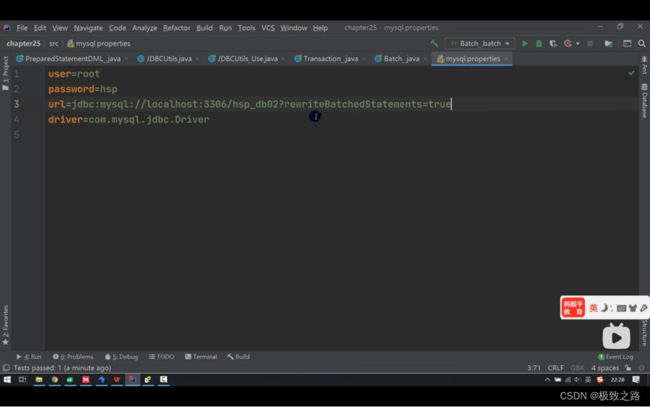
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//mysql.properties"));
//获取相关的值
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driver);//建议写上
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("第五种方式:"+conn);
conn.close();
}
}
/*
学习并且还要思考:
比如
1.jdbc为什么要先引入一个jar文件
2.涉及的类,如DriverManager及各种方法的功能是什么?
3.有什么要改进的。
*/
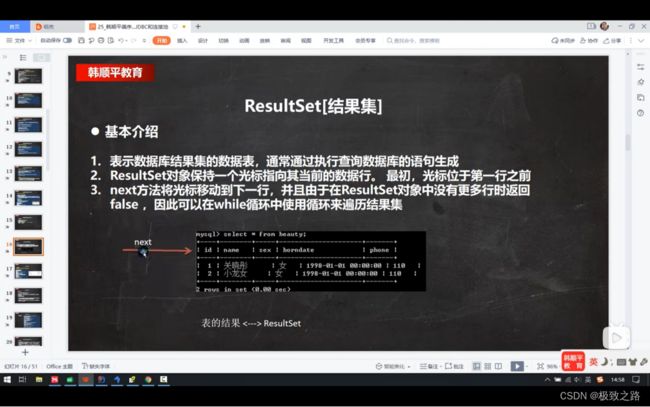
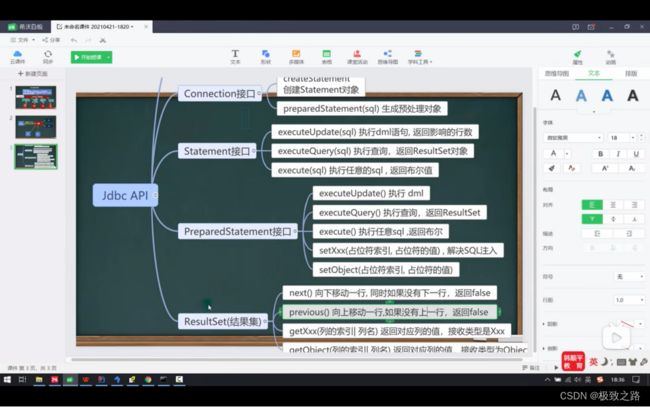
(2)ResultSet底层
刚开始光标位于表头,这样可以防止表是空表的情况。

ResultSet也是一个接口,具体由实现类实现这个接口。
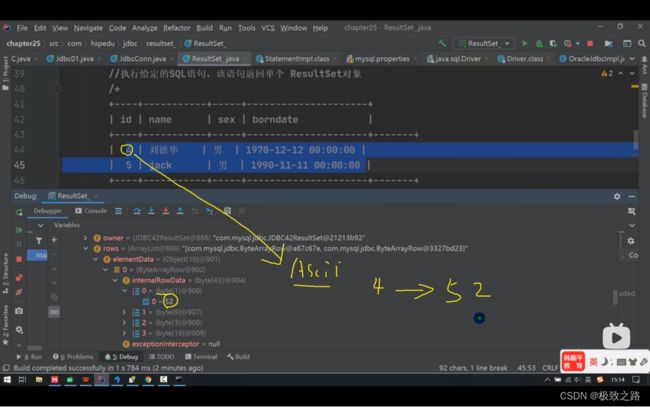
4对应的ASCll码值就是52.
里面存的是byte类型。
name是utf-8编码的,3个汉字占3个字节。这里面存的便是ASCLL码的一个组合。
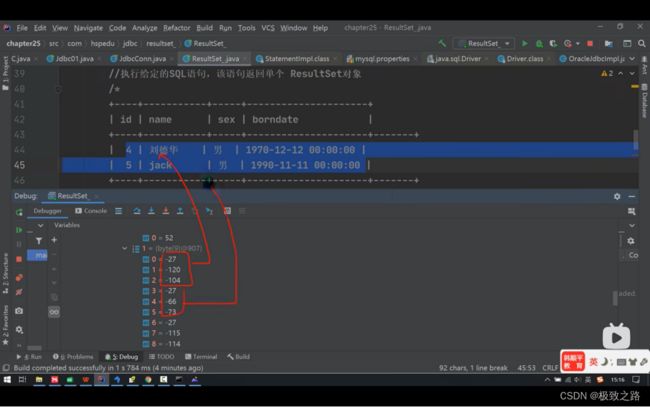
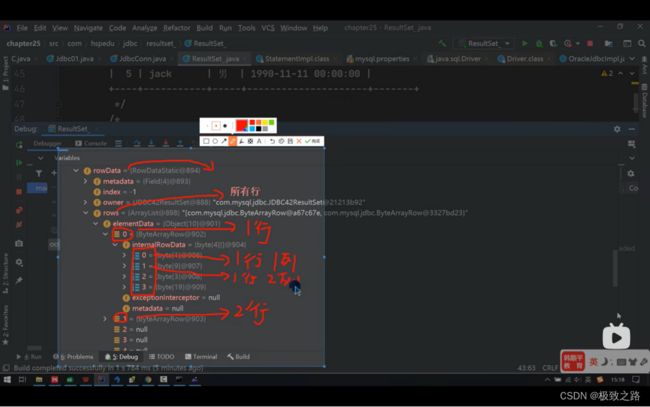
因此resultSet里面表中的数据就在elementData里面存放着。
并且所以行用一个ArrayList存放。
(3)SQL注入问题
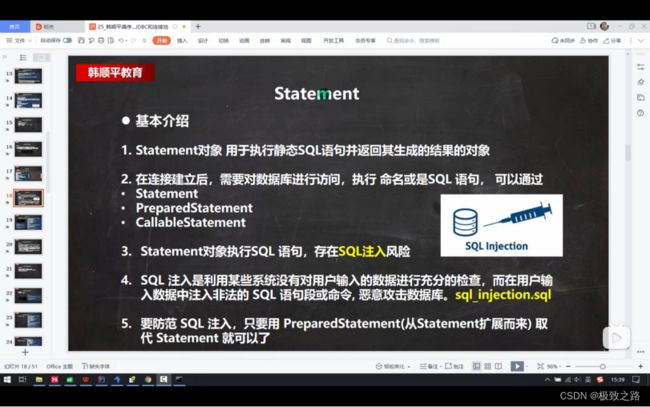
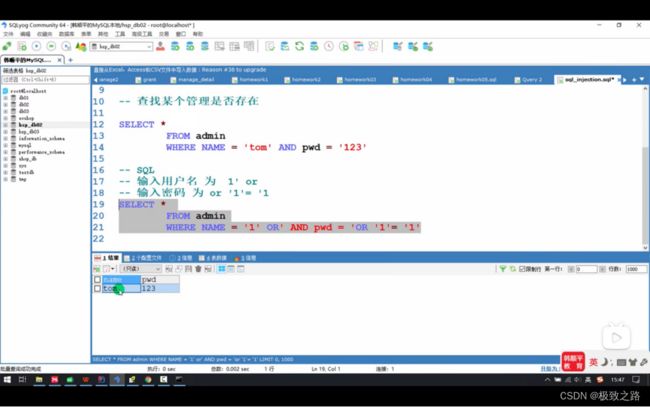
这就是SQL注入的问题,将用户名改为了1’ or 密码改成了’1’=’1。
这样不管怎么样,只要这个人存在都能登录成功。
而PreparedStatement就没有sql注入的问题。
/**
*
*/
public class Statement {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//让用户输入管理员名和密码
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String admin_name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String admin_pwd = sc.nextLine();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//mysql.properties"));
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql="select * from admin where `name`='"+admin_name+"' and pwd='"+admin_pwd+"';";
java.sql.Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
java.sql.ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// if (resultSet.next()){
// System.out.println("登录成功");
// }else {
// System.out.println("登录失败");
// }
while (resultSet.next()){
String name = resultSet.getString(1);
String pwd = resultSet.getString(2);
System.out.println("[ "+name+"\t"+pwd+" ]");
}
//释放资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
conn.close();
}
}
(4)预处理PreparedStatement
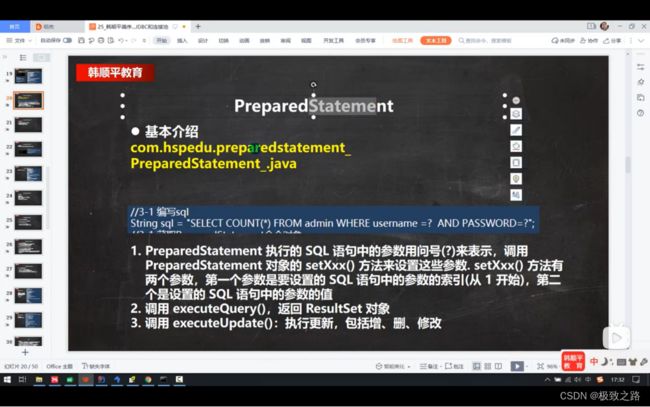
1.PreparedStatement可以给sql语句设置占位符并赋值。
2.PreparedStatement解决了sql注入的问题,并且会对sql语句进行预编译,减少了sql语句在mysql中编译的次数。
3.
executeQuery():执行的是查询。
executeUpdate():执行的是增删改。
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql="select * from admin where `name`=? and pwd=?";
PreparedStatement pstm=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.setString(1,admin_name);
pstm.setString(2,admin_pwd);
ResultSet resultSet = pstm.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
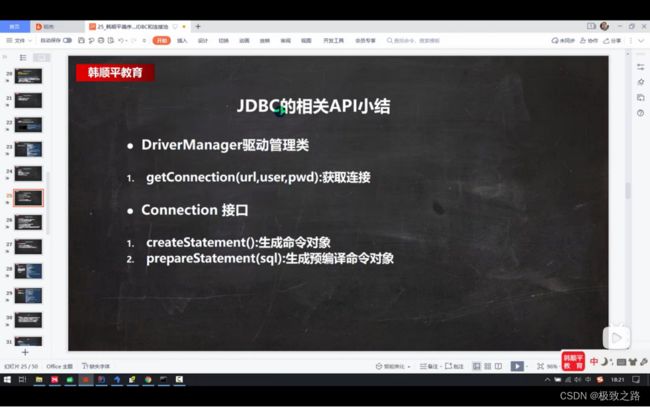
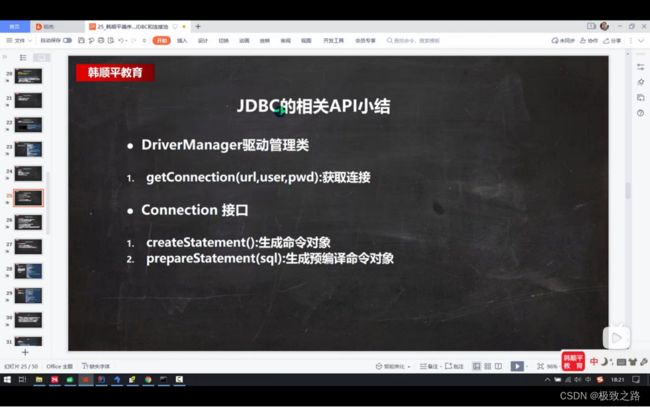
三、JDBCUtils工具类
(1)API
(2)JDBCUtils工具类
package com.hspedu.jdbc.utils;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
*这是一个工具类,完成mysql的连接和关闭资源
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
//定义相关的属性(4个) ,因为只需要1份,因此,需要做成static
private static String url;
private static String user;// 用户名
private static String password; //密码
private static String driver; //驱动名
//在static代码块中去初始化
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//mysql.properties"));
//读取相关的属性值
url=properties.getProperty("url");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
} catch (IOException e) {
//在实际开发中,可以这样去处理
//1.将编译异常 转成 运行异常
//2.调用者 可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便。
throw new RuntimeException(e);
//throw 手动生成异常对象的关键字。
}
}
//连接数据库,返回Connection
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/*
关闭相关资源
1.ResultSet结果集
2.Statement或者PreparedStatement
3.Connection
4.如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入null
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement statement,Connection connection){
//判断释放为null
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (statement!=null){
statement.close();
}
if (connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//异常处理,运行时异常和编译时异常?
/*
五大运行时异常:空指针异常,算数异常,类型转换异常,数组下标超限异常,还要一个数字格式异常。
编译时异常:类没有找到,文件没有找到。
*/
对应的properties配置文件:
(3)JDBCUtils工具类的使用
获取连接和释放资源是两个同样的操作,可以封装到一个类里面。
package com.hspedu.jdbc;
import com.hspedu.jdbc.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*
*/
public class JDBCUtils_Use {
@Test
public void testDML(){
//1.得到连接
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
//2.组织一个sql
String sql="update admin set name=? where name=?";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符赋值。
pstm.setString(1,"authdey");
pstm.setString(2,"jack");
//执行
int i = pstm.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i>0?"成功":"失败");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
}
@Test
public void testSel(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql="select * from admin";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
String name = rs.getString("name");
String pwd = rs.getString("pwd");
System.out.println(name+"\t"+pwd);
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs,pstm,conn);
}
}
}
四、事务及批处理
(1)事务介绍

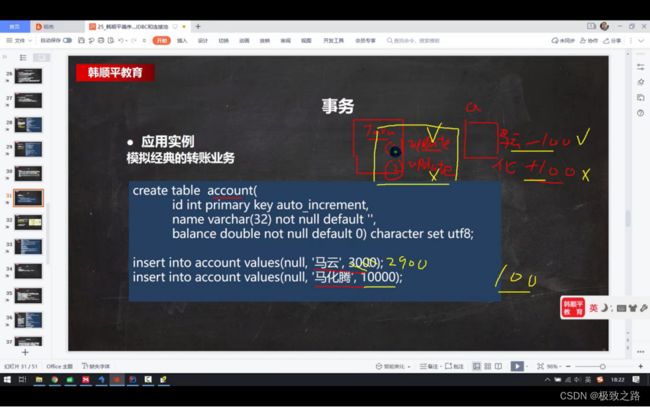
事务对应一组sql语句的执行。如果有单个sql语句没有执行成功,可以回滚到之前的状态。
默认mysql数据库每执行一条sql语句就自动提交。
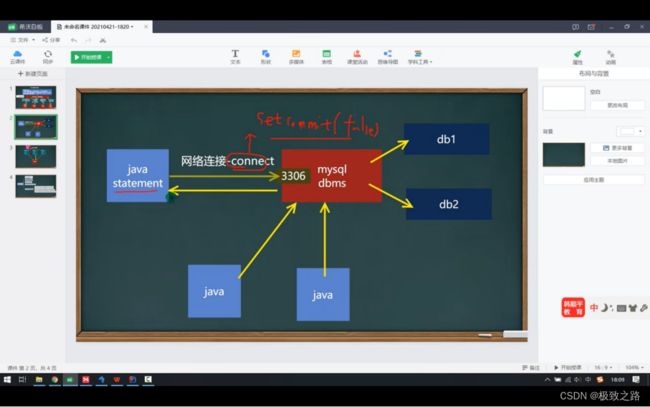
(2)使用事务模拟转账业务
package com.hspedu.jdbc.transaction_;
import com.hspedu.jdbc.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*演示 jdbc中如何使用事务
*/
public class Transaction_ {
@Test
public void noTransaction(){
//操作转账的业务
//1.得到连接
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
String sql="update accounts set balance = balance-100 where id=1";
String sql2="update accounts set balance = balance+100 where id=2";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.组织一个sql
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.executeUpdate();
int i=1/0;
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
pstm.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
}
@Test
public void useTransaction(){
//操作转账的业务
//1.得到连接
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
String sql="update accounts set balance = balance-100 where id=1";
String sql2="update accounts set balance = balance+100 where id=2";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//1.开启一个事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.executeUpdate();
int i=1/0;
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
pstm.executeUpdate();
//在这里提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
//进行回滚,默认回滚到事务最开始的状态。
System.out.println("执行发送了异常,撤销执行的sql");
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
}
}
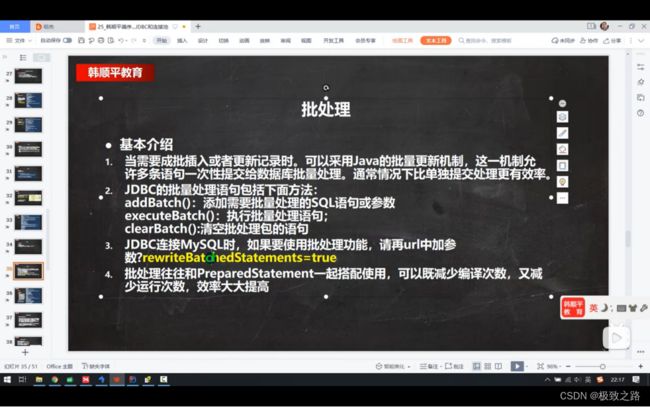
(3)批处理应用
如果数据量比较大,就需要清空一批,然后再执行一批。 如果在进行批处理机制的时候,如果没有指定参数,是无效的。
package com.hspedu.jdbc.batch_;
import com.hspedu.jdbc.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*演示java的批处理
*/
public class Batch_ {
//传统方法,添加1000条数据到admin2
@Test
public void noBatch(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql="insert into admin2 values(null,?,?)";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pstm.setString(1,"tom"+i);
pstm.setString(2,"555");
pstm.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间为"+(end-start));
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
//6160ms
}
@Test
public void usePatch(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql="insert into admin2 values(null,?,?)";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pstm.setString(1,"tom"+i);
pstm.setString(2,"555");
//addBatch:添加需要批量处理的sql语句或参数
pstm.addBatch();
if (i % 1000==0){//满一千条sql执行一次
pstm.executeBatch();
pstm.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间为"+(end-start));
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql="insert into admin2 values(null,?,?)";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pstm.setString(1,"tom"+i);
pstm.setString(2,"555");
//addBatch:添加需要批量处理的sql语句或参数
pstm.addBatch();
if (i % 1000==0){//满一千条sql执行一次
pstm.executeBatch();
pstm.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间为"+(end-start));
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null,pstm,conn);
}
}
}