Stream流中collect方法
Stream流中collect方法
- 一、收集Stream流到集合和指定集和中
-
- 1、示例
- 2、结果
- 二、收集 Stream 流中的数据到数组中
-
- 1、示例
- 2、结果
- 三、Stream流中数据聚合/分组/分区/拼接操作
-
- 1、聚合操作
- 2、分组操作
- 3、多级分组操作
- 4、分区操作
- 5、拼接操作
一、收集Stream流到集合和指定集和中
Stream 流提供了一个 collect() 方法,可以收集流中的数据到【集合】或者【数组】中去。
//1.收集数据到list集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toList())
//2.收集数据到set集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toSet())
//3.收集数据到指定的集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(Supplier<C> collectionFactory))
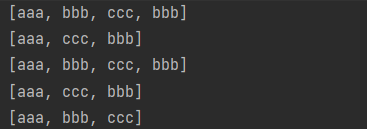
1、示例
public void test2() {
//Stream 流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//收集流中的数据到集合中
//1.收集流中的数据到 list
List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//Stream 流
stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//2.收集流中的数据到 set
Set<String> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
//Stream 流
stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//3.收集流中的数据(ArrayList)(不收集到list,set等集合中,而是)收集到指定的集合中
ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
//Stream 流
stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//4.收集流中的数据到 HashSet
HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println(hashSet);
//Stream 流
stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//distinct()不重复
List<String> distinctCollect = stream.distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(distinctCollect);
}
2、结果
public void test3() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<People>();
People people1 = new People("张三", 18);
People people2 = new People("王五", 19);
peopleList.add(people1);
peopleList.add(people2);
List<People> collect = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList<People>::new));
System.out.println(collect);
}
![]()
二、收集 Stream 流中的数据到数组中
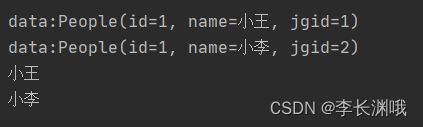
1、示例
void test2() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<People>();
People people1 = new People(1, "小王", 1);
People people2 = new People(1, "小李", 2);
peopleList.add(people1);
peopleList.add(people2);
//1.使用无参,收集到数组,返回值为 Object[](Object类型将不好操作)
Object[] objects = peopleList.stream().toArray();
for (Object o : objects) {//此处无法使用.length() 等方法
System.out.println("data:" + o);
}
//2.使用有参,可以指定将数据收集到指定类型数组,方便后续对数组的操作
People[] people = peopleList.stream().toArray(People[]::new);
for (People str : people) {
System.out.println(str.getName());
}
}
2、结果
三、Stream流中数据聚合/分组/分区/拼接操作
//最大值
Collectors.maxBy();
//最小值
Collectors.minBy();
//总和
Collectors.summingInt();/Collectors.summingDouble();/Collectors.summingLong();
//平均值
Collectors.averagingInt();/Collectors.averagingDouble();/Collectors.averagingLong();
//总个数
Collectors.counting();
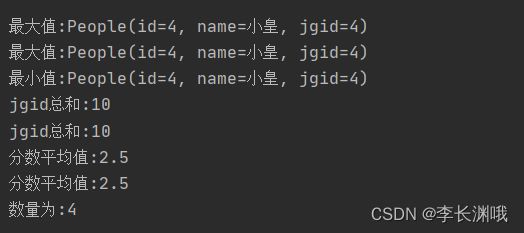
1、聚合操作
@Test
void test3() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 1));
peopleList.add(new People(3, "小李", 3));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小张", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(4, "小皇", 4));
//取最大值
Optional<People> maxCollect1 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(
new Comparator<People>() {
@Override
public int compare(People o1, People o2) {
//比大小前值比后值大则返回非负数
if (o1.getJgid() > o2.getJgid()) {
return 0;
} else {
return -1;
}
// return o1.getJgid() - o2.getJgid();
}
}
));
//或者使用lambda表达式取最大值
Optional<People> maxCollect2 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getJgid() - s2.getJgid()));
//或者使用lambda表达式取最小值
Optional<People> minCollect = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getJgid() - s2.getJgid()));
//取jgid总和
Integer sumCollect1 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(new ToIntFunction<People>() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(People value) {
return value.getJgid();
}
}));
//或者使用lambda表达式取jgid总和
Integer sumCollect2 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(People::getJgid));
Double avgScore1 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(new ToIntFunction<People>() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(People value) {
return value.getJgid();
}
}));
//或者使用lambda表达式取jgid平均值
Double avgScore2 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(People::getJgid));
//(聚合)统计数量
Long count = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("最大值:" + maxCollect1.get());
System.out.println("最大值:" + maxCollect2.get());
System.out.println("最小值:" + minCollect.get());
System.out.println("jgid总和:" + sumCollect1);
System.out.println("jgid总和:" + sumCollect2);
System.out.println("分数平均值:"+avgScore1);
System.out.println("分数平均值:"+avgScore2);
System.out.println("数量为:"+count);
}
2、分组操作
当我们使用 Stream 流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性来将数据进行分组。
//接收一个 Function 参数
groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier)
@Test
void test4() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 1));
peopleList.add(new People(3, "小李", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小张", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(4, "小皇", 1));
//根据年龄分组
Map<Integer, List<People>> jgidMap1 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(new Function<People, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(People people) {
return people.getJgid();
}
}));
//或者使用lambda表达式
Map<Integer, List<People>> jgidMap2 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getJgid));
System.out.println("根据年龄分组");
jgidMap1.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
//jgid奇数一组偶数一组
Map<String, List<People>> jgidMap3 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> {
if (s.getJgid() % 2 == 0) {
return "jgid为偶数";
} else {
return "jgid为奇数";
}
}));
System.out.println("jgid奇数一组偶数一组");
jgidMap3.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
//根据jgid分组且规定为最大一组(规约:reducing)
Map<Integer, Optional<People>> jgidMap4 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getJgid,
Collectors.reducing(BinaryOperator.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(People::getJgid)))
));
System.out.println("jgid分组后最大值");
jgidMap4.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
}
}
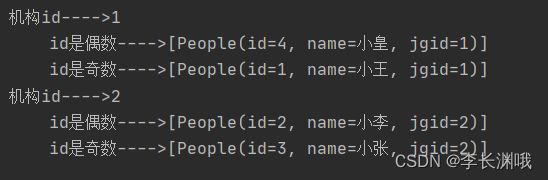
3、多级分组操作
当我们使用 Stream 流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性来将数据进行分组。
//接收两个参数: 1.Function 参数 2.Collector多级分组
groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier,Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)
@Test
void test5() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 1));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小李", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(3, "小张", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(4, "小皇", 1));
Map<Integer, Map<String, List<People>>> collect = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getJgid,
Collectors.groupingBy(people -> {
if (people.getId() % 2 == 0) {
return "id是偶数";
} else {
return "id是奇数";
}
})));
collect.forEach((key1, value1) -> {
System.out.println("机构id" + "---->" + key1);
value1.forEach((key2, value2) -> {
System.out.println("\t" + key2 + "---->" + value2);
});
});
}
4、分区操作
分区操作,通过使用 Collectors.partitioningBy() ,根据返回值是否为 true,把集合分为两个列表,一个 true 列表,一个 false 列表。
分组和分区的区别就在:分组可以有多个组。分区只会有两个区( true 和 false)
//1.一个参数
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
//2.两个参数(多级分区)
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate, Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)
@Test
void test6() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 1));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小李", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(3, "小张", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(4, "小皇", 1));
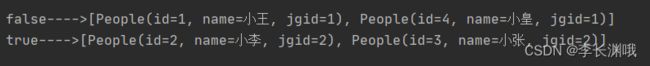
Map<Boolean, List<People>> collect = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> {
return s.getJgid() % 2 == 0;
}));
collect.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
}
5、拼接操作
Collectors.joining() 会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
//无参数--等价于 joining("");
joining()
//一个参数
joining(CharSequence delimiter)
//三个参数(连接符+前缀+后缀)
joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)
@Test
void test7() {
List<People> peopleList = new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 1));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小李", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(3, "小张", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(4, "小皇", 1));
String collect1 = peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(collect1);
String collect2 = peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(collect2);
String collect3 = peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("_", "开始<", ">结束"));
System.out.println(collect3);
}