集合体系概述(Collection、List、Set)
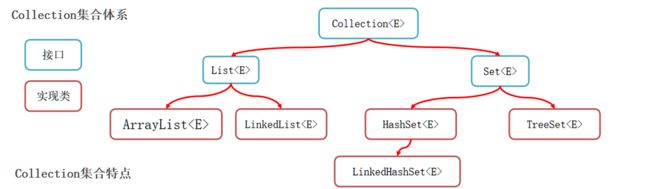
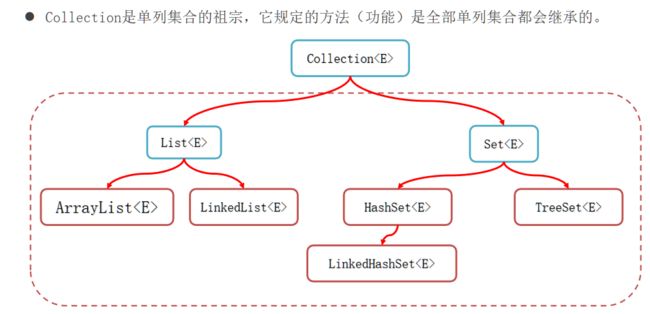
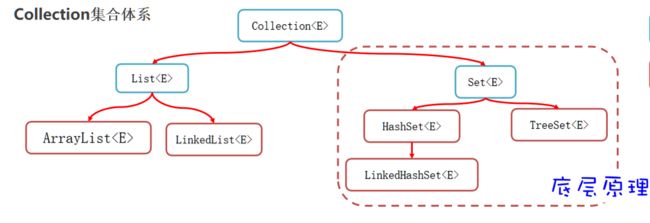
集合体系概述
- Collection代表单列集合,每个元素(数据)只包含一个值。
- Map代表双列集合,每个元素包含两个值(键值对)。
- List系列集合:添加的元素是有序、可重复、有索引。
- Set系列集合:添加的元素是无序、不重复、无索引。
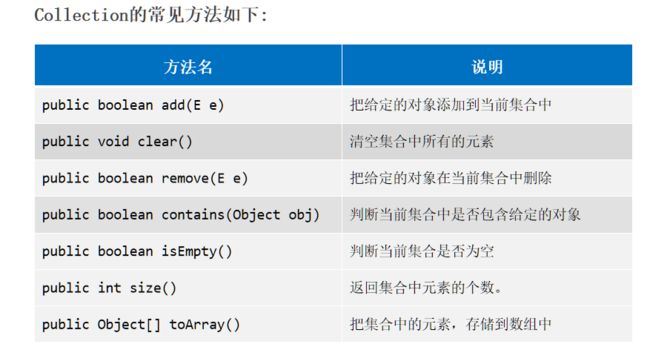
Collection的常用方法
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
//1.public boolean add(E e): 添加元素到集合
c.add("java1");
c.add("java1");
c.add("java2");
c.add("java2");
c.add("java3");
System.out.println(c); //打印: [java1, java1, java2, java2, java3]
//2.public int size(): 获取集合的大小
System.out.println(c.size()); //5
//3.public boolean contains(Object obj): 判断集合中是否包含某个元素
System.out.println(c.contains("java1")); //true
System.out.println(c.contains("Java1")); //false
//4.pubilc boolean remove(E e): 删除某个元素,如果有多个重复元素只能删除第一个
System.out.println(c.remove("java1")); //true
System.out.println(c); //打印: [java1,java2, java2, java3]
//5.public void clear(): 清空集合的元素
c.clear();
System.out.println(c); //打印:[]
//6.public boolean isEmpty(): 判断集合是否为空 是空返回true 反之返回false
System.out.println(c.isEmpty()); //true
//7.public Object[] toArray(): 把集合转换为数组
Object[] array = c.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); //[java1,java2, java2, java3]
//8.如果想把集合转换为指定类型的数组,可以使用下面的代码
String[] array1 = c.toArray(new String[c.size()]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1)); //[java1,java2, java2, java3]
//9.还可以把一个集合中的元素,添加到另一个集合中
Collection c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("java1");
c1.add("java2");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("java3");
c2.add("java4");
c1.addAll(c2); //把c2集合中的全部元素,添加到c1集合中去
System.out.println(c1); //[java1, java2, java3, java4] Collection的遍历方式
迭代器
- 迭代器概述:
迭代器是用来遍历集合的专用方式(数组没有迭代器),在Java中迭代器的代表是Iterator。
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("赵敏");
c.add("小昭");
c.add("素素");
c.add("灭绝");
System.out.println(c); //[赵敏, 小昭, 素素, 灭绝]
//第一步:先获取迭代器对象
//解释:Iterator就是迭代器对象,用于遍历集合的工具)
Iterator it = c.iterator();
//第二步:用于判断当前位置是否有元素可以获取
//解释:hasNext()方法返回true,说明有元素可以获取;反之没有
while(it.hasNext()){
//第三步:获取当前位置的元素,然后自动指向下一个元素.
String e = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
} 迭代器代码的原理如下:
- 当调用iterator()方法获取迭代器时,当前指向第一个元素
- hasNext()方法则判断这个位置是否有元素,如果有则返回true,进入循环
- 调用next()方法获取元素,并将当月元素指向下一个位置,
- 等下次循环时,则获取下一个元素,依此内推
注意:当取元素越界时,会报空指针异常(NoSuchElementException)
增强for
- 格式:
for (元素的数据类型 变量名 : 数组或者集合) { }
增强for可以用来遍历集合或者数组。
增强for遍历集合,本质就是迭代器遍历集合的简化写法。(底层就是迭代器)
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("赵敏");
c.add("小昭");
c.add("素素");
c.add("灭绝");
//1.使用增强for遍历集合
for(String s: c){
System.out.println(s);
}
//2.再尝试使用增强for遍历数组
String[] arr = {"迪丽热巴", "古力娜扎", "稀奇哈哈"};
for(String name: arr){
System.out.println(name);
} lambda表达式
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("赵敏");
c.add("小昭");
c.add("素素");
c.add("灭绝");
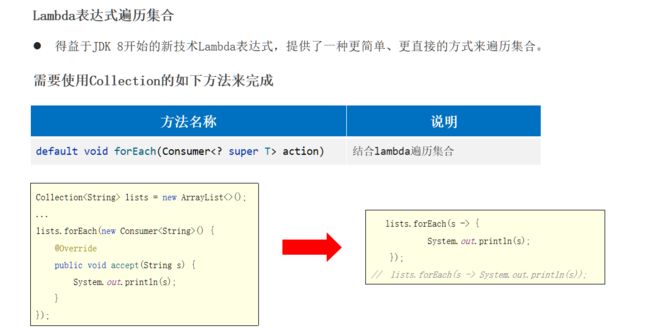
//调用forEach方法
//由于参数是一个Consumer接口,所以可以传递匿名内部类
c.forEach(new Consumer{
@Override
public void accept(String s){
System.out.println(s);
}
});
//也可以使用lambda表达式对匿名内部类进行简化
c.forEach(s->System.out.println(s)); //[赵敏, 小昭, 素素, 灭绝] 遍历自定义对象集合案例
ublic class Movie{
private String name; //电影名称
private double score; //评分
private String actor; //演员
//无参数构造方法
public Movie(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Movie(String name, double score, String actor){
this.name=name;
this.score=score;
this.actor=actor;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection movies = new ArrayList<>();
movies.add(new MOvie("《肖申克的救赎》", 9.7, "罗宾斯"));
movies.add(new MOvie("《霸王别姬》", 9.6, "张国荣、张丰毅"));
movies.add(new MOvie("《阿甘正传》", 9.5, "汤姆汉克斯"));
for(Movie movie : movies){
System.out.println("电影名:" + movie.getName());
System.out.println("评分:" + movie.getScore());
System.out.println("主演:" + movie.getActor());
}
}
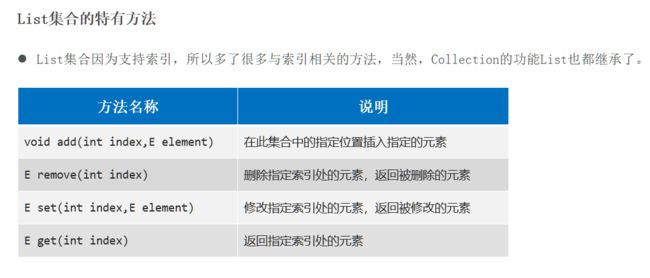
} List集合
特点、特有方法
List系列集合特点: 有序,可重复,有索引
ArrayList:有序,可重复,有索引。
LinkedList:有序,可重复,有索引。
//1.创建一个ArrayList集合对象(有序、有索引、可以重复)
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蜘蛛精");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("牛夫人");
System.out.println(list); //[蜘蛛精, 至尊宝, 至尊宝, 牛夫人]
//2.public void add(int index, E element): 在某个索引位置插入元素
list.add(2, "紫霞仙子");
System.out.println(list); //[蜘蛛精, 至尊宝, 紫霞仙子, 至尊宝, 牛夫人]
//3.public E remove(int index): 根据索引删除元素, 返回被删除的元素
System.out.println(list.remove(2)); //紫霞仙子
System.out.println(list);//[蜘蛛精, 至尊宝, 至尊宝, 牛夫人]
//4.public E get(int index): 返回集合中指定位置的元素
System.out.println(list.get(3));
//5.public E set(int index, E e): 修改索引位置处的元素,修改后,会返回原数据
System.out.println(list.set(3,"牛魔王")); //牛夫人
System.out.println(list); //[蜘蛛精, 至尊宝, 至尊宝, 牛魔王] 遍历方式
- List集合支持的遍历方式
- for循环(因为List集合有索引)
- 迭代器
- 增强for循环
- Lambda表达式
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蜘蛛精");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("糖宝宝");
//1.普通for循环
for(int i = 0; i< list.size(); i++){
//i = 0, 1, 2
String e = list.get(i);
System.out.println(e);
}
//2.增强for遍历
for(String s : list){
System.out.println(s);
}
//3.迭代器遍历
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
//4.lambda表达式遍历
list.forEach(s->System.out.println(s)); ArrayList集合的底层原理
ArrayList集合底层是基于数组结构实现的,也就是说当你往集合容器中存储元素时,底层本质上是往数组中存储元素。
查询速度快(注意:是根据索引查询数据快):查询数据通过地址值和索引定位,查询任意数据耗时相同。
删除效率低:可能需要把后面很多的数据进行前移。
添加效率极低:可能需要把后面很多的数据后移,再添加元素;或者也可能需要进行数组的扩容。
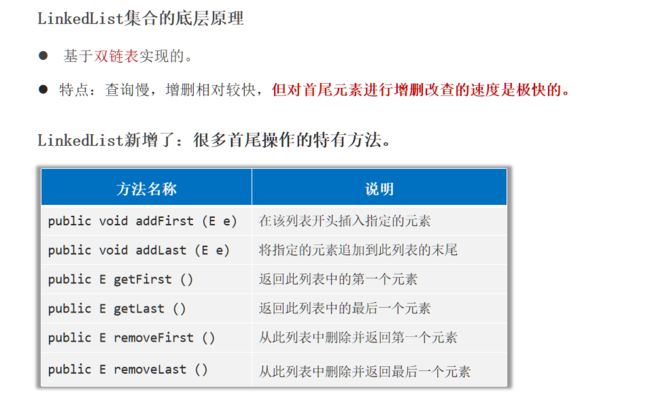
LinkedList集合的底层原理
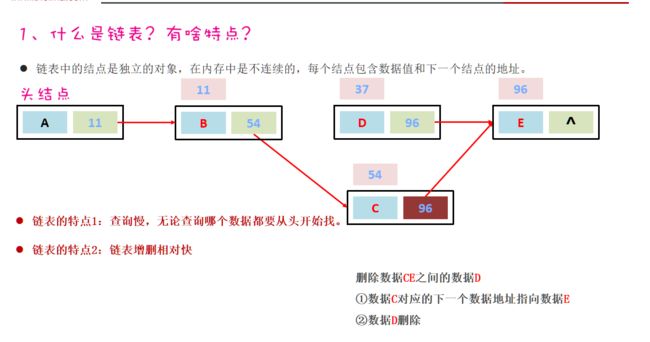
- LinkedList底层是链表结构,链表结构是由一个一个的节点组成,一个节点由数据值、下一个元素的地址组成。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo04 {
/*
目标: 弄清楚LinkedList的头尾操作
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.addFirst("bb"); // [bb , aa]
list.addFirst("cc"); // [cc , bb , aa]
list.addLast("dd"); //[cc , bb , aa , dd]
System.out.println(list.getFirst()); // cc
System.out.println(list.getLast()); // dd
list.removeFirst(); // [bb , aa , dd]
list.removeLast(); // [bb , aa ]
System.out.println(list);
}
}
LinkedList的应用场景之一:可以用来设计队列(先进先出)
//1.创建一个队列:先进先出、后进后出
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
//入对列
queue.addLast("第1号人");
queue.addLast("第2号人");
queue.addLast("第3号人");
queue.addLast("第4号人");
System.out.println(queue);
//出队列
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst()); //第4号人
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst()); //第3号人
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst()); //第2号人
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst()); //第1号人 LinkedList的应用场景之一:可以用来设计栈(先进后出)
//1.创建一个栈对象
LinkedList stack = new ArrayList<>();
//压栈(push) 等价于 addFirst()
stack.push("第1颗子弹");
stack.push("第2颗子弹");
stack.push("第3颗子弹");
stack.push("第4颗子弹");
System.out.println(stack); //[第4颗子弹, 第3颗子弹, 第2颗子弹,第1颗子弹]
//弹栈(pop) 等价于 removeFirst()
System.out.println(statck.pop()); //第4颗子弹
System.out.println(statck.pop()); //第3颗子弹
System.out.println(statck.pop()); //第2颗子弹
System.out.println(statck.pop()); //第1颗子弹
//弹栈完了,集合中就没有元素了
System.out.println(list); //[] Set集合
特点
Set系列集合的特点: 无序:添加数据的顺序和获取出的数据顺序不一致; 不重复; 无索引;
HashSet : 无序、不重复、无索引。
LinkedHashSet:有序、不重复、无索引。
TreeSet:排序、不重复、无索引。
注意:
Set要用到的常用方法,基本上就是Collection提供的!!自己几乎没有额外新增一些常用功能!
HashSet集合的底层原理
特点:无序,不重复,无索引
- 哈希值
- 就是一个int类型的数值,Java中每个对象都有一个哈希值。
- Java中的所有对象,都可以调用Obejct类提供的hashCode方法,返回该对象自己的哈希值。
public int hashCode():返回对象的哈希码值。
- 对象哈希值的特点
- 同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的。
- 不同的对象,它们的哈希值一般不相同,但也有可能会相同(哈希碰撞)。
- HashSet集合底层是基于哈希表实现的,哈希表根据JDK版本的不同,也是有点区别的
- JDK8以前:哈希表 = 数组+链表
- JDK8以后:哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树
要想保证在HashSet集合中没有重复元素,我们需要重写元素类的hashCode和equals方法。
public class Student{
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
private double height; //身高
//无参数构造方法
public Student(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Student(String name, int age, double height){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.height=height;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
//按快捷键生成hashCode和equals方法
//alt+insert 选择 hashCode and equals
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
if (Double.compare(student.height, height) != 0) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result;
long temp;
result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(height);
result = 31 * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
return result;
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Set students = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s : students){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
} LinkedHashSet集合的底层原理
特点:有序,不重复,无索引
LinkedHashSet它底层采用的是也是哈希表结构,只不过额外新增了一个双向链表来维护元素的存取顺序。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Set students = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s : students){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
} TreeSet集合
特点:可排序(默认升序排序 ,按照元素的大小,由小到大排序),不重复,无索引
- 对于数值类型:Integer , Double,默认按照数值本身的大小进行升序排序。
- 对于字符串类型:默认按照首字符的编号升序排序。
- 对于自定义类型如Student对象,TreeSet默认是无法直接排序的。
自定义排序规
方式一 :让自定义的类实现Comparable接口,重写里面的compareTo方法来指定比较规则。
//第一步:先让Student类,实现Comparable接口
//注意:Student类的对象是作为TreeSet集合的元素的
public class Student implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
//无参数构造方法
public Student(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Student(String name, int age, double height){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.height=height;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
//第二步:重写compareTo方法
//按照年龄进行比较,只需要在方法中让this.age和o.age相减就可以。
/*
原理:
在往TreeSet集合中添加元素时,add方法底层会调用compareTo方法,根据该方法的
结果是正数、负数、还是零,决定元素放在后面、前面还是不存。
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//this:表示将要添加进去的Student对象
//o: 表示集合中已有的Student对象
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
//创建TreeSet集合,元素为Student类型
Set students = new TreeSet<>();
//创建4个Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("紫霞",23, 169.8);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
//添加Studnet对象到集合
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students); 方式二:通过调用TreeSet集合有参数构造器,可以设置Comparator对象(比较器对象,用于指定比较规则)。
//创建TreeSet集合时,传递比较器对象排序
/*
原理:当调用add方法时,底层会先用比较器,根据Comparator的compare方是正数、负数、还是零,决定谁在后,谁在前,谁不存。
*/
//下面代码中是按照学生的年龄升序排序
Set students = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2){
//需求:按照学生的身高排序
return Double.compare(o1,o2);
}
});
//创建4个Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("紫霞",23, 169.8);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
//添加Studnet对象到集合
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students); 注意事项:集合的并发修改异常问题
- 使用迭代器遍历集合时,又同时在删除集合中的数据,程序就会出现并发修改异常的错误。
- 由于增强for循环遍历集合就是迭代器遍历集合的简化写法,因此,使用增强for循环遍历集合,又在同时删除集合中的数据时,程序也会出现并发修改异常的错误
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("王麻子");
list.add("小李子");
list.add("李爱花");
list.add("张全蛋");
list.add("晓李");
list.add("李玉刚");
System.out.println(list); // [王麻子, 小李子, 李爱花, 张全蛋, 晓李, 李玉刚]
//需求:找出集合中带"李"字的姓名,并从集合中删除
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String name = it.next();
if(name.contains("李")){
list.remove(name); //这时候是不允许集合删除元素的(b报异常)
}
}
System.out.println(list); List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("王麻子");
list.add("小李子");
list.add("李爱花");
list.add("张全蛋");
list.add("晓李");
list.add("李玉刚");
System.out.println(list); // [王麻子, 小李子, 李爱花, 张全蛋, 晓李, 李玉刚]
//需求:找出集合中带"李"字的姓名,并从集合中删除
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String name = it.next();
if(name.contains("李")){
//list.remove(name);
it.remove(); //当前迭代器指向谁,就删除谁
}
}
System.out.println(list);