ThreadLocal类的使用
一.使用场景描述
1.每个线程需要一个独享的对象
public class ThreadLocalDemo1 {
public static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int finalI = i;
threadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String date = new ThreadLocalDemo1().date(finalI);
System.out.println(date);
}
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
public String date(int seconds) {
Date date = new Date(1000 * seconds);
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = ThreadSafeFormatter.dateFormatThreadLocal2.get();
return dateFormat.format(date);
}
}
class ThreadSafeFormatter {
//java8之前
// public static ThreadLocal dateFormatThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal() {
// @Override
// protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() {
// return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// }
// };
//java8语法
public static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormatThreadLocal2 = ThreadLocal
.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
}
2.每个线程内需要保存全局变量
public class ThreadLocalDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Service1().process("");
}
}
class Service1 {
public void process(String name) {
User user = new User("lele");
UserContextHolder.holder.set(user);
new Service2().process();
}
}
class Service2 {
public void process() {
User user = UserContextHolder.holder.get();
System.out.println("Service2拿到用户名:" + user.name);
new Service3().process();
}
}
class Service3 {
public void process() {
User user = UserContextHolder.holder.get();
System.out.println("Service3拿到用户名:" + user.name);
UserContextHolder.holder.remove();
}
}
class UserContextHolder {
public static ThreadLocal<User> holder = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
class User {
String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
二.ThreadLocal相关方法详解
1.T initialvalue():初始化
具体流程如下图:

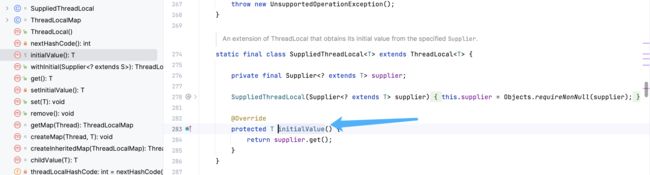


由上述流程可知:
initialValue()方法的作用是为ThreadLocal变量提供初始值。我们可能需要在创建ThreadLocal变量时为其指定初始值,这时就可以通过重写initialValue()方法来实现。
2.void set(T value):为线程设置新的值
相关源码如下:
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
通过调用Thread.currentThread()获取当前线程,然后通过调用getMap(t)方法获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象。如果当前线程没有ThreadLocalMap对象,则调用createMap(t, value)方法创建一个新的ThreadLocalMap对象,并将其设置到当前线程中。
3. T get() :得到这个线程对应的value
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
通过调用Thread.currentThread()获取当前线程,然后通过调用getMap(t)方法获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象。如果当前线程没有ThreadLocalMap对象,则直接调用setInitialValue()方法初始化并返回一个默认值。如果当前线程已经有了ThreadLocalMap对象,则通过调用map.getEntry(this)方法来获取对应的Entry对象。this指的是调用get方法的ThreadLocal对象。如果找到了对应的Entry对象,则返回其value值,这个值就是之前通过set方法设置的值。
4.void remove():删除当前线程的本地变量
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
通过调用Thread.currentThread()获取当前线程,然后通过调用getMap(t)方法获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象。如果当前线程没有ThreadLocalMap对象,则直接返回。
如果当前线程已经有了ThreadLocalMap对象,则调用map.remove(this)方法将调用该方法的ThreadLocal对象所对应的键值对从ThreadLocalMap中删除。这里的this指的是调用remove方法的ThreadLocal对象。
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
首先获取ThreadLocalMap内部的Entry数组tab,以及数组长度len。然后,根据指定ThreadLocal对象的threadLocalHashCode计算出在数组中的索引位置i。这里的threadLocalHashCode是ThreadLocal对象的一个属性,用于计算哈希值。
接下来,通过一个for循环来查找指定ThreadLocal对象所对应的键值对。在循环中,通过nextIndex方法计算出下一个可能的索引位置,并依次遍历数组中的每个元素。如果找到了与指定ThreadLocal对象相等的键值对,则调用e.clear()方法清除该键值对的值,并调用expungeStaleEntry(i)方法删除数组中所有陈旧的键值对。这里的陈旧键值对指的是已经被删除(值为null)但是仍然占据数组空间的键值对。
需要注意的是,由于ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal类内部使用的一个工具类,因此它的实现方式与常规的HashMap等Map实现方式略有不同。在ThreadLocalMap中,每个键值对的键都是一个弱引用(WeakReference),这意味着当键所引用的对象没有任何强引用指向它时,它会被垃圾回收器回收。因此,在使用ThreadLocal时需要注意避免内存泄漏问题。
5.ThreadLocalMap类说明
public class ThreadLocalMap {
// 存储键值对的数组
private Entry[] table;
// 当前 size
private int size;
// 阈值,达到该值则进行扩容
private int threshold;
// Entry 类表示键值对
static class Entry {
// 键值对中的 key
final ThreadLocal<?> key;
// 键值对中的 value
Object value;
// 构造函数
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
// 构造函数,初始化 table 和 threshold
ThreadLocalMap(int initialCapacity, int threshold) {
table = new Entry[initialCapacity];
this.threshold = threshold;
}
// 将 key-value 对插入到 table 中
public Object put(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// 获取当前线程的 Entry 数组索引
int index = hash(key);
// 获取该索引位置的 Entry
Entry[] table = this.table;
Entry e = table[index];
// 如果该位置为空,则直接插入新的 Entry
if (e == null) {
if (table.length <= index) { // 数组长度小于索引,需要扩容
int newSize = table.length << 1;
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newSize];
System.arraycopy(table, 0, newTable, 0, table.length);
table = this.table = newTable;
}
// 插入新的 Entry,并设置 size 加一
table[index] = e = new Entry(key, value);
this.size++;
// 如果 size 大于 threshold,则进行 rehash
if (size > threshold) {
rehash();
}
return null;
} else { // 如果该位置不为空,则更新旧的 Entry 的 value
Object oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value; // 设置新的 value
return oldValue; // 返回旧的 value
}
}
}
ThreadLocalMap的主要功能是将 ThreadLocal 变量与对应的值存储起来,实现线程隔离。它内部维护了一个 Entry 数组 table,每个 Entry 包含一个 ThreadLocal 对象和一个值。当一个线程访问 ThreadLocal 变量时,会首先从 ThreadLocalMap 中查找对应的值。如果找到了,则直接返回该值;如果没找到,则可以在 ThreadLocalMap 中添加一个新的键值对。在添加键值对时,如果 Entry 数组的长度小于索引,则需要扩容;如果数组长度大于等于索引,则直接在指定位置插入新的 Entry。如果数组中的某个位置为空,则直接插入新的 Entry;如果该位置不为空,则更新旧的 Entry 的值。当数组中的元素数量大于一定的阈值时,会进行 rehash,以优化性能。
三.总结
使用ThreadLocal好处:
- 达到线程安全;
- 不需要加锁,提高执行效率;
- 更高效地利用内存,节省开销;
- 免去传参数的麻烦;
主要注意:内存泄漏的问题
四.参考
ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap源码深度解析