第二十章总结
20.1 线程简介
20.2 创建线程
20.2.1 继承 Thread 类
例题20.1
package 二十章;
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// Thread th = new Thread() {
// publicvoid run() {
// System.out.println("happy"); } }; th.start(); }
public void run() {
for(int i = 0;i <= 10;i++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadTest th = new ThreadTest();
th.start();
}
}20.2.2 实现 Runnable 接口
例题20.2
package 二十章;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
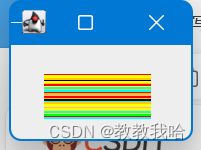
public class SwingAndThread extends JFrame {
int count = 0;
public SwingAndThread() {
setBounds(300,200,250,100);
Container container = getContentPane();
container.setLayout(null);
Icon icon = new ImageIcon("src/二十章/1.gif");
JLabel jl = new JLabel(icon);
jl.setBounds(10,10,200,50);
Thread t = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true) {
jl.setBounds(count,10,200,50);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
count += 4;
if (count >= 200){
count = 10;
}
}
}
};
t.start();
container.add(jl);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SwingAndThread();
}
}
20.3 线程的生命周期
20.4 操作线程的方法
20.4.1 线程的休眠
例题20.3
package 二十章;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Random;
public class SleepMethodTest extends JFrame {
private static Color[] color = {
Color.BLACK,Color.CYAN,Color.GREEN,Color.ORANGE,Color.YELLOW,Color.RED,Color.PINK,Color.LIGHT_GRAY,
};
private static final Random rand = new Random();
private static Color getC(){
return color[rand.nextInt(color.length)];
}
public SleepMethodTest() {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
int x = 30;
int y = 50;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
Graphics graphics = getGraphics();
graphics.setColor(getC());
graphics.drawLine(x,y,100,y++);
if (y >= 80) {
y = 50;
}
}
}
});
t.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
init(new SleepMethodTest(),100,100);
}
public static void init(JFrame frame,int width,int height) {
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(width,height);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}20.4.2 线程的加入
例题20.4
package 二十章;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
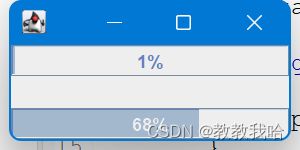
public class JoinTest extends JFrame {
private Thread threadA;
private Thread threadB; //定义两个线程
private JProgressBar progressBar = new JProgressBar(); //定义两个进度条组件
private JProgressBar progressBar2 = new JProgressBar();
public static void main(String[] args) {
JoinTest test = new JoinTest();
test.setVisible(true);
}
public JoinTest() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(200,200,200,100);
getContentPane().add(progressBar, BorderLayout.NORTH); //将进度条设置再窗体最北面
getContentPane().add(progressBar2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); //将进度条设置再窗体最南面
progressBar.setStringPainted(true); //设置进度条显示数字字符
progressBar2.setStringPainted(true);
threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() { //使用匿名内部类形式初始化 Thread 实例
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() { //重写run()方法
while (true) {
progressBar.setValue(++count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
threadB.join();
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
progressBar2.setValue(++count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (count == 100)
break;
}
}
});
threadB.start();
}
}
20.4.3 线程的中断
例题20.5
package 二十章;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
public class InterruptedSwing extends JFrame {
public InterruptedSwing(){
JProgressBar progressBar = new JProgressBar();
getContentPane().add(progressBar, BorderLayout.NORTH);
JButton button = new JButton("停止");
getContentPane().add(button,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
progressBar.setStringPainted(true);
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
progressBar.setValue(++count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("当前线程序被中断");
break;
}
}
}
});
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
t.interrupt();
}
});
t.start();
}
public static void init(JFrame frame,int width,int height) {
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(width,height);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
init(new InterruptedSwing(),100,100);
}
}20.5 线程的优先级
例题20.6
package 二十章;
public class PriorityTest implements Runnable{
String name;
public PriorityTest(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String tmp = "";
for (int i = 0;i < 50000;i++) {
tmp += i;
}
System.out.println(name + "线程完成任务");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread a = new Thread(new PriorityTest("A"));
a.setPriority(1);
Thread b = new Thread(new PriorityTest("B"));
b.setPriority(3);
Thread c = new Thread(new PriorityTest("C"));
c.setPriority(7);
Thread d = new Thread(new PriorityTest("D"));
d.setPriority(10);
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
d.start();
}
}
20.6 线程同步
20.6.1 线程安全
例
package untitled1.src;
public class ThreadSafeTest implements Runnable{
int num = 10;
public void run (){
while (true) {
//synchronized (this) {
if (num > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
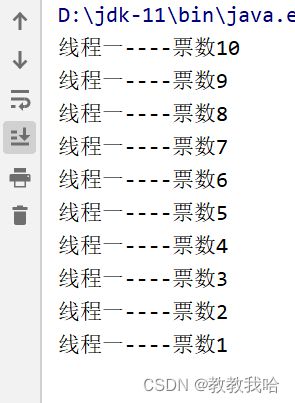
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----票数" + num--);
}
//}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSafeTest t = new ThreadSafeTest();
Thread tA = new Thread(t,"线程一");
Thread tB = new Thread(t,"线程二");
Thread tC = new Thread(t,"线程三");
Thread tD = new Thread(t,"线程四");
tA.start();
tB.start();
tC.start();
tD.start();
}
}20.6.2 线程同步机制
例
package untitled1.src;
public class ThreadSafeTest implements Runnable{
int num = 10;
public void run (){
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
if (num > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----票数" + num--);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSafeTest t = new ThreadSafeTest();
Thread tA = new Thread(t,"线程一");
Thread tB = new Thread(t,"线程二");
Thread tC = new Thread(t,"线程三");
Thread tD = new Thread(t,"线程四");
tA.start();
tB.start();
tC.start();
tD.start();
}
}