数据结构总复习
文章目录
- 线性表
-
- 动态分配的顺序存储结构
- 链式存储
- 栈与队列
-
- 栈
-
- 顺序栈
- 链栈
- 队列
线性表
动态分配的顺序存储结构
通过分析代码,我们发现,要注意什么:
- 要分清你的下标
- Insert 函数是可以用来没有元素的时候,增加元素的
- Init(或者Create )函数一般只用来分配空间等的初始化
//动态分配空间的顺序存储结构的线性表
#include考点
- 两个有序递增的顺序表的合并
关键点,可以学到什么,就是分别用pa,pb,pc,来记录首地址,一句话,就是用辅助变量来方便操作
void Merge(Sqlist la,Sqlist lb,Sqlist &lc)
//目标,将原本有序递增的la,pb顺序表整合到lc ,lc认为有序递增的
{
pa = la.elem;
pb = la.elem;
lc.listsize = lc.length = la.length + lb.length;
pc =lc.elem = (ElemType *)malloc(lc.listsize*(sizeof(ElemType)));
if(!lc.elem)
exit OVERFLOW;
pa_last = pa + la.length-1;
pb_last = pb + lb.length-1;
while(pa<=pa_last&&pb<=pb_last)
{
if(*pa<*pb) *pc++ = *pa++;
else *pc++ = *pb++;
}
while(pa<=pa_last) *pc++ = *pa++;
while(pb<=pb_last) *pc++ = *pb++;
}
顺序表优点与缺点:
- 优点:可以随便进行数据的插入与删除
- 优点:占据较少的空间
- 缺点:需要连续的一串地址
- 缺点:在插入与删除时,要移动大量的元素
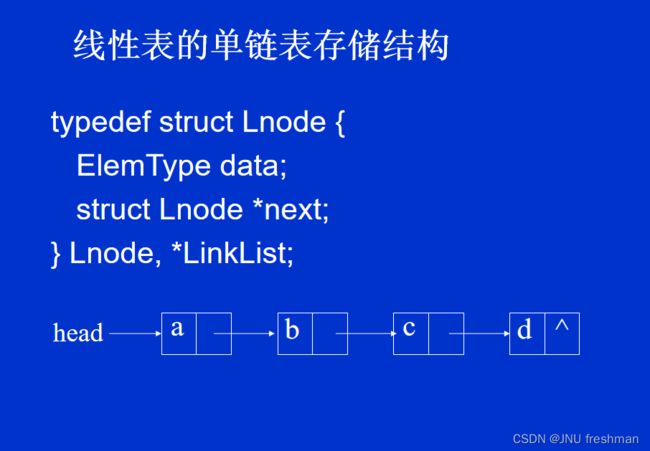
链式存储
//动态分配空间的顺序存储结构的线性表
#include应用:
- 有序非递减链表的整合
- 有序非递减链表求交集
- 有序
优点以及缺点
- 优点:插入与删除不用移动大量的元素
- 优点:不需要连续的地址
- 优点:采用动态链表不用固定最大长度
- 缺点:占用较大的内存
- 缺点:不可以随机访问某个元素
栈与队列
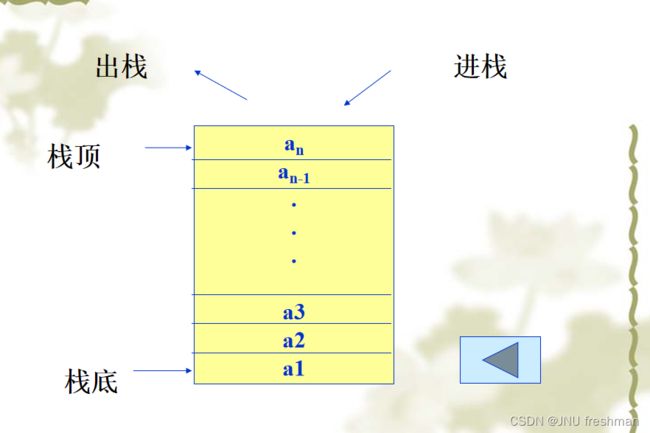
栈
定义:只能在表尾进行插入与删除的线性表(先进后出)
- 表尾是栈顶,表头是栈底
顺序栈
- 顺序栈的精髓就是通过S.top == S.base 来判断栈是否为空
- 用S.top-S.base >=stacksize 来判断栈是否满
#include链栈
- 相比之下,链栈的操作更为简单,
- 在初始化的时候给传递过来的头指针分配一个头结点
- 当S->next ==NULL 的时候,就说明栈为空
- 进行插入操作的时候,先分配空间LinkStack temp ,来存储数据,temp->next =S->next; S->next=S
- 删除操作的时候,temp = S-> next,e = temp ->data;S->next = temp ->next;
不过应该注意的是,链栈是在队头进行操作,区别于顺序栈的队尾,不过,可以这么记忆,你在哪边进行插入的就在哪边进行删除就可以
#include队列
- 链队列:判断为空的条件:Q.rear==Q.front 指向头结点
- 这也要求了,在删除操作的时候,要判断删除之后是否为空,要是为空就让两个指针相等
#include