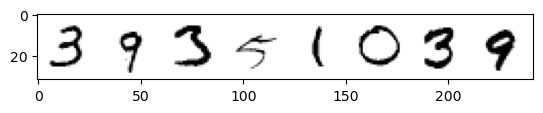扩散模型(1)代码
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f'Using device: {device}')
Using device: cuda
dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="mnist/",train=True,download=True,transform=torchvision.transforms. ToTensor())
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
x,y =next(iter(train_dataloader))
print('Input shape:', x.shape)
Input shape: torch.Size([8, 1, 28, 28])
print('Lable shape:', y.shape)
Lable shape: torch.Size([8])
plt.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x)[0], cmap='Greys')
扩散模型之退化过程 控制内容损坏程度,引入一个参数控制输入的“噪声量”
def corrupt(x, amount):
# 根据amount为输入x加入噪声
# 如果amount=0则返回输入,不做任何更改,如果amount=1那么就返回一个纯粹的噪声
noise = torch.rand_like(x)
amount = amount.view(-1, 1, 1, 1)
# noisy_like = (1-amount)*x+amount*noise
return x*(1-amount)+amount*noise
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(12,5))
axs[0].set_title('Input data')
axs[0].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x)[0], cmap='Greys')
# 加入噪声
amount = torch.linspace(0,1,x.shape[0])
noise_x = corrupt(x,amount)
axs[1].set_title('Corrupted data (----amount increases ---->)')
axs[1].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(noise_x)[0], cmap='Greys')
class BasicUnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=1):
super().__init__()
self.down_layers = torch.nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
]
)
# 下行路径
self.up_layers = torch.nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.Conv2d(32, out_channels, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
]
)
# 上行路径
self.act = nn.SiLU()# 激活函数
self.downscale = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.upscale = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2)
def forward(self, x):
h = []
for i, l in enumerate(self.down_layers):
x = self.act(l(x)) # 通过运算层与激活函数
if i < 2: # 选择下行路径的前两层
h.append(x) # 供残差连接使用的数据
x = self.downscale(x) # 选择下采样适配下一层的输入
for i, l in enumerate(self.up_layers):
if i > 0:
x = self.upscale(x)
x += h.pop()
x = self.act(l(x))
return x
net = BasicUnet()
x = torch.rand(8, 1, 28, 28)
net(x).shape
torch.Size([8, 1, 28, 28])
sum([p.numel() for p in net.parameters()])
309057
diffusion model有什么用-也就是说给定一个带噪声的noise_x的输入,扩散模型的输出其对原始输入x的最佳预测。
需要通过均方误差对预测值与真实值进行比较
# 流程:1、获取数据 2、添加随机噪声 3、数据输入模型 4、预测和初始图像进行比较 计算损失更新模型的参数
batch_size = 128
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
n_epochs = 3
net = BasicUnet()
net.to(device)
# 损失函数
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
#优化器
opt = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr=1e-3)
losses = []
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for x,y in train_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
noise_amount = torch.rand(x.shape[0]).to(device)
noisy_x = corrupt(x,noise_amount) # 创建带噪声的NOISY_X
# 得到模型的预测结果
pred = net(noisy_x)
loss = loss_fn(pred, x)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
# 储存损失,供后期查看
losses.append(loss.item())
avg_loss = sum(losses[-len(train_dataloader):])/len(train_dataloader)
print(f'Finished epoch {epoch}. Average loss for this epoch:{avg_loss:05f}')
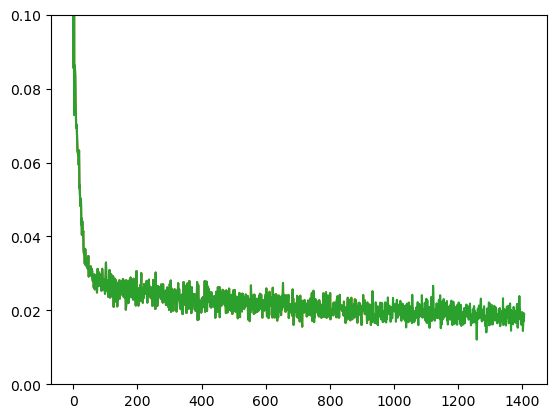
plt.plot(losses)
plt.ylim(0,0.1);
Finished epoch 0. Average loss for this epoch:0.027834
Finished epoch 1. Average loss for this epoch:0.021065
Finished epoch 2. Average loss for this epoch:0.019122
# 可视化模型在“带噪“输入上的表现
# 初始数据
x, y = next(iter(train_dataloader))
x = x[:8]
# 在(0-1)之间取噪声量
amount = torch.linspace(0,1, x.shape[0])
noised_x = corrupt(x, amount)
# 模型预测结果
with torch.no_grad():
preds = net(noised_x.to(device)).detach().cpu()
# 绘图
fig,axs = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(12,7))
axs[0].set_title('Input data')
axs[0].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x)[0].clip(0, 1), cmap='Greys')
axs[1].set_title('Corrupted data')
axs[1].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(noised_x)[0].clip(0, 1), cmap='Greys')
axs[2].set_title('prediction data')
axs[2].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(preds)[0].clip(0, 1), cmap='Greys')
采样过程
模型在高噪声量下的预测不好该怎么办呢?
从完全随机噪声开始,检测预测效果,然后朝着预测效果移动一部分,比如20%,可能新的预测效果就比上一侧的预测效果好一点,那么么就可以继续向前移动。
# 采样策略 把采样过程拆解为5步,每次只前进一步
n_steps = 5
x = torch.rand(8,1,28,28).to(device)
step_history = [x.detach().cpu()]
pred_output_history = []
for i in range(n_steps):
with torch.no_grad():
pred = net(x) # 预测去噪后图像
pred_output_history.append(pred.detach().cpu()) # 保存模型
mix_factor = 1/(n_steps - i) # 设置朝着预测方向移动多少
x = x*(1-mix_factor)+pred*mix_factor # 移动过程
step_history.append(x.detach().cpu()) # 记录每一次移动
fig, axs = plt.subplots(n_steps, 2, figsize=(9,4), sharex=True)
axs[0,0].set_title('x (model input)')
axs[0,1].set_title('model prediction')
for i in range(n_steps):
axs[i,0].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(step_history[i])[0].clip(0,1), cmap='Greys')
axs[i,1].imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(pred_output_history[i])[0].clip(0,1), cmap='Greys')
n_steps = 20
x = torch.rand(64,1,28,28).to(device)
for i in range(n_steps):
noise_amount = torch.ones((x.shape[0],)).to(device) * (1-(i/n_steps))# 噪声从高到低
with torch.no_grad():
pred = net(x)
mix_factor = 1/(n_steps - i) # 设置朝着预测方向移动多少
x = x*(1-mix_factor)+pred*mix_factor # 移动过程
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12,12))
ax.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x.detach().cpu(),nrow=8)[0].clip(0,1), cmap='Greys')
退化过程
在每个时间步都为输入图像添加少量噪声的退化过程。
如果在某个时间步给定 x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1,就可以得到一个噪声稍微增强的 x t x_{t} xt:
( x t ∣ x t − 1 ) = N ( x t ; 1 − β i x t − 1 , β t I ) q ( x 1 ∣ x 0 ) = ∏ t = 1 T q ( x t ∣ x t − 1 ) \left(x_{t} \mid x_{t-1}\right)=\mathcal{N}\left(x_{t} ; \sqrt{1-\beta_{i}} x_{t-1}, \beta_{t} I\right) q\left(x_{1} \mid x_{0}\right)=\prod_{t=1}^{T} q\left(x_{t} \mid x_{t-1}\right) (xt∣xt−1)=N(xt;1−βixt−1,βtI)q(x1∣x0)=t=1∏Tq(xt∣xt−1)
你可以这样理解,取 x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1,。给它一个系数 1 − β t \sqrt{1-\beta_{t}} 1−βt,然后将其与一个带有系数 β t \beta_{t} βt的噪声相加。其中, β \beta β是我们根据调度器为每个时划设定的参数,用于决定在每个时间步添加的噪声量。我们并不想通过把这个推演重复 500 次来得到,而是希望利用另一个公式,根据给出的 x 0 x_{0} x0计算得到任意时刻 t t t的 x t x_{t} xt:
q ( x t ∣ x 0 ) = N ( x t ; α i x 0 , ( 1 − α ˉ t ) I ) ; 其中 α ˉ t = ∏ T α i , α i = 1 − β i q\left(x_{t} \mid x_{0}\right)=\mathcal{N}\left(x_{t} ; \sqrt{\alpha_{i}} x_{0},\left(1-\bar{\alpha}_{t}\right) \boldsymbol{I}\right) ; \text { 其中 } \bar{\alpha}_{t}=\prod^{T} \alpha_{i}, \alpha_{i}=1-\beta_{i} q(xt∣x0)=N(xt;αix0,(1−αˉt)I); 其中 αˉt=∏Tαi,αi=1−βi