SpringCloud-Ribbon负载均衡
1.Ribbon
参考:尚硅谷
1.1Ribbon的负载均衡策略
1.轮询RoundRobinRule:按照服务列表轮流选择(默认)
2.随机RandomRule:按照服务列表随机选择
3.RetryRule:先按照RoundRobinRule获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内进行重试,获取可用的服务。
4.WeightedResponseTimeRule 对RoundRobinRule的扩展,响应速度越快实例选择权重越大,越容易被选择。
5.BestAvailableRule:会过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
6.AvailabilityFilteringRule:先过滤掉故障实例,在选择并发量较小的实例。
7.ZooAvoidanceRule:默认规则,复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务器。
1.2Ribbon负载均衡替换
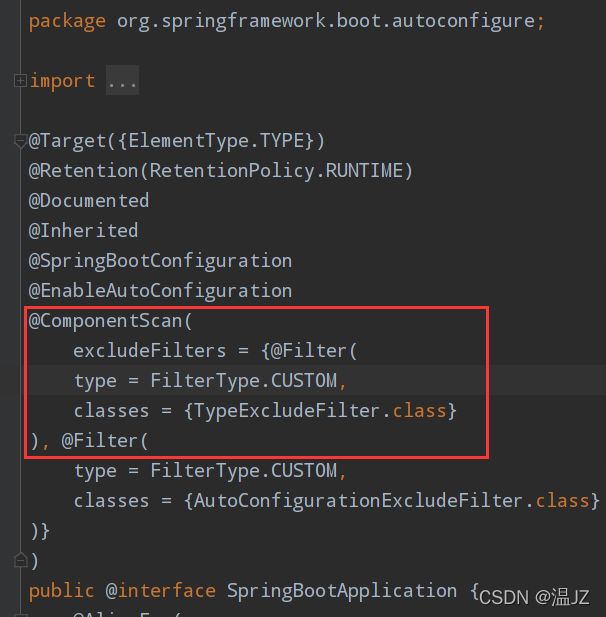
这个配置类不能放在@ComponentScan所扫描的当前包以及子包下否则我们自定义的这个配置类就会被所有的Ribbon客户端所共享,达不到特殊化定制的目的了。
主启动类上面的@SpringBootApplication注解上面有@ComponentScan注解,所以这个启动类所在的包及其子包都是在@CompentScan这个注解的扫描范围内。
所以我们要另外在这个包之外再建一个包。
然后在这个Myrule配置类里写上新的负载均衡的规则。
@Configuration
public class Myrule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RandomRule();//将默认轮询负载均衡策略设置为随机
}
}
然后我们还要告诉主启动类你的负载均衡策略用的到底是哪一个在启动类上加上注解@RibbonClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = Myrule.class)
public class OrderMain80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args);
}
}
name我现在这个服务消费者要访问CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE这个微服务,configuration是新加了一个配置类,调整负载均衡的策略。
1.3Ribbon负载均衡轮询算法原理
负载均衡算法:rest接口第几次请求数 % 服务器集群数量 = 实际调用服务器位置下标,每次服务重启后rest接口从1开始。List instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(微服务服务名);
例:List[0] instances = 127.0.0.1:8002,List[1] instances = 127.0.0.1:8001,
8001和8002两台机器构成集群,他们共计两台机器,集群总数为2
按照轮询算法原理:当请求总数为1时:1%2=1对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001
当请求总数为2时:2%2 = 0对应下标位置为0,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8002,
当请求总数为3时:3%2 = 0对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001,
以此类推…
如果这时候服务器重启了那就从1开始算。
1.4RoundRobinRule源码分析
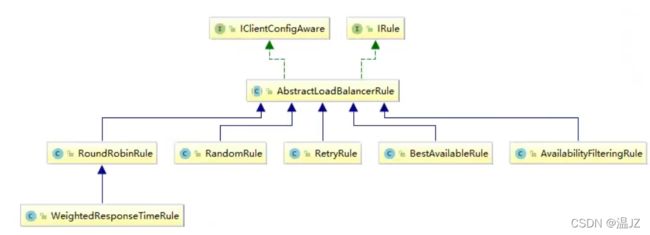
一切规则都是IRule这个接口,AbstractLoadBalancerRule是它的抽象类一切具体的措施都继承这个抽象类。
package com.netflix.loadbalancer;
public interface IRule {
Server choose(Object var1);//选择哪一台服务器提供服务
void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer var1);
ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}
IRule这个接口中的choose是具体选择哪一台机器提供服务我们下面具体分析的RoundRobinRule的思想也集中在这个函数里。下面我们来看一下RoundRobinRule中的相关代码(只与choose有关的)
public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule{
private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter;//代表第几次访问
public RoundRobinRule() {
this.nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
public RoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {
this();
this.setLoadBalancer(lb);
}//设置负载均衡策略
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {//如果负载均衡策略为空则它没有选择任何策略返回空
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
} else {
Server server = null;
int count = 0;//设置轮询次数
while(true) {
if (server == null && count++ < 10) {//如果轮询次数超过10
List reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();//拿到所有活着的服务器
List allServers = lb.getAllServers();//拿到服务器集群上的所有服务器
int upCount = reachableServers.size();//拿到活着服务器的数量
int serverCount = allServers.size();//拿到服务器集群上的所有服务器数量
if (upCount != 0 && serverCount != 0) {
int nextServerIndex = this.incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);//计算下一个服务器的节点坐标
server = (Server)allServers.get(nextServerIndex);//拿到节点服务器的下标
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
} else {
if (server.isAlive() && server.isReadyToServe()) {
return server;
}
server = null;
}
continue;
}
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb);
}
return server;
}
}
}
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
int current;
int next;
do {
current = this.nextServerCyclicCounter.get();//获得当前已有的请求总数
next = (current + 1) % modulo;//加1取模得到下一个机器的下标
} while(!this.nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next));比较并交换
return next;
}
}