阿里的easyexcal包实现表格动态导出
阿里的easyexcal包实现表格动态导出
1.介绍
在日常开发中,我们或多或少会遇到导入excal,导出excal等业务需求,那么了解这一技能就很有必要了。
市场中针对这个,我知道的有两个包,一个是poi(Poor Obfuscation Implementation),一个是easyexcal(阿里的);但poi存在oom内存溢出的风险,在正式环境中,导出的数据往往成千上万条,很容易就触发oom,所以,一般情况下公司都不建议使用poi,阿里的easyexcal包的底层实现也是使用了poi,也就是说easyexcal是对poi的进一步封装改造,成功规避了oom。
2.场景需求
现在有一个需求:实现表头信息动态,表数据动态,表中单元格具有各自的样式(比如背景颜色,字体样式,字体颜色等)。
3.设计方案思路
我这里使用easyexcal包实现该需求,首先注意表头信息是变动的,那也就意味着没法使用easyexcal的一系列注解(就是常规的先创建一个导出的实体类,然后再加注解),这里有个坑:我最开始的想法是,创建包含所有表头信息的导出实体,然后通过反射的技术对具体需要展示的表头字段进行标识,然后发现easyexcal中的注解@ExcelIgnore 忽略项是没有value属性的,这样就出现了尴尬的情况:反射能给字段添加或删除注解吗???,我查了很多资料,最后是没找到,应该不能实现添加或删除,但给注解中的属性值修改是可以做到的,但@ExcelIgnore没有属性供我们修改,至此,该方法行不通了;然后我看了easyexcal源码,大致知道了导出excal的流程:先渲染表头,再渲染数据,他们都是一个个单元格,每一个单元格有自己的行列数,一个excal表就是由一个个单元格以此拼接起来的。于是,我就使用单独给表头数据,表体数据,需要给单元格加样式的行列坐标数据和样式数据。需要注意的是表头和表体数据格式是二维数组,我是用list中套list,外层list中的元素是一行,内部list中的元素是列。
4.具体代码实现
我这里分别使用了3.0.5和2.2.8的easyexcal包,需要注意的是3.0版本之前和之后有较大改动,其实现的方法不一样,注意:以下案例在springboot项目中实现
4.1easyexcal3.0.5版本实现代码
4.1.1导核心依赖
com.alibaba
easyexcel
3.0.5
4.1.2写一个类继承AbstractCellWriteHandler或者也可以实现CellWriteHandler接口
public class MyCellStyleWriteHandler extends AbstractCellWriteHandler {
private List xyInfo;
/*
给样式模板两个
*/
private CellStyle style1;
private CellStyle style2;
public MyCellStyleWriteHandler(){
}
public MyCellStyleWriteHandler(List xyInfo){
this.xyInfo=xyInfo;
}
@Override
public void beforeCellCreate(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, WriteTableHolder writeTableHolder,
Row row, Head head, Integer columnIndex, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
// 设置行高测试
}
@Override
public void afterCellDispose(CellWriteHandlerContext context) {
Cell cell = context.getCell();
// 拿到poi的workbook
Workbook workbook = context.getWriteWorkbookHolder().getWorkbook();
// 自定义宽度处理
// 自定义样式处理
// 当前事件会在 数据设置到poi的cell里面才会回调
// 判断不是头的情况 如果是fill 的情况 这里会==null 所以用not true
if (BooleanUtils.isNotTrue(context.getHead())) {
//循环样式信息,进行横纵坐标的匹配,给对应的单元格样式
for (XyInfo item:xyInfo
) {
if (cell.getRowIndex() == item.getX() && cell.getColumnIndex() == item.getY()) {
//现在已经锁定的单元格,下面只需要给样式
//样式: 1:红字,紫色背景;2:黄字,红色背景
// 这里千万记住 想办法能复用的地方把他缓存起来 一个表格最多创建6W个样式,我这就直接样式模板化,避免其发生
if(item.getContent()==1){
cell.setCellStyle(this.getCellStyle(workbook,1));
}
if(item.getContent()==2){
cell.setCellStyle(this.getCellStyle(workbook,2));
}
// 由于这里没有指定dataformat 最后展示的数据 格式可能会不太正确
// 这里要把 WriteCellData的样式清空, 不然后面还有一个拦截器 FillStyleCellWriteHandler 默认会将 WriteCellStyle 设置到
// cell里面去 会导致自己设置的不一样(很关键)
context.getFirstCellData().setWriteCellStyle(null);
}
}
}
}
//优化代码,给个样式方法
/**
* 对于可确定的样式,进行样式模板化,避免每一个单元格都创建一个样式
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param content 具体设置样式信息
* @return
*/
public CellStyle getCellStyle(Workbook workbook,Integer content){
//样式: 1:红字,紫色背景;2:黄字,红色背景
if(null==this.style1 && content==1){
//避免多次创建
//这里有个坑:我最初的想法是自己创建CellStyle 对象,通过new的方式,然后这个地方不认他,设置完全不起效果,所以这里只能从weekbook中拿。
style1=workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font=workbook.createFont();
//红字
font.setColor((short)016);
//蓝色背景
style1.setFillForegroundColor((short)030);
//加载字体
style1.setFont(font);
// 这里需要指定 FillPatternType 为FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND
style1.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
}
if(null==style2 && content==2){
//避免多次创建
style2=workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font=workbook.createFont();
//白字
font.setColor((short)011);
//红色背景
style2.setFillForegroundColor((short)016);
//加载字体
style2.setFont(font);
// 这里需要指定 FillPatternType 为FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND
style2.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
}
//返回样式模板
if(content==1){
return this.style1;
}
if (content==2){
return this.style2;
}
return null;
}
}
4.1.3导出关键代码
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//你要导出的文件存放路径和文件名字
String filePath = "D:\\ttt\\Download\\";
String fileName=System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs();
}
//解析表头容器
List>headss=new LinkedList<>();
//解析数据容器
List>datas=new LinkedList<>();
//解析单元格样式容器
ListxyInfo=new LinkedList<>();
//手动添加假数据模拟真实数据(表头信息)
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("A","AA"))));
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("B","AAA"))));
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("C","A2","A3","A4"))));
//手动添加假数据模拟真实数据(标体数据)
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","")));
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc")));
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","","")));
//手动添加需要设置样式的单元格信息
xyInfo.add(new XyInfo(6,0,1));
xyInfo.add(new XyInfo(5,1,2));
EasyExcel.write(filePath+fileName)
// 这里放入动态头
.head(headss).sheet("模板(sheet名字)")
//加载单元格样式
.registerWriteHandler(new MyCellStyleWriteHandler(xyInfo))
.doWrite(datas);
System.out.println("导出成功");
}
}
XyInfo实体类
@Data
public class XyInfo {
/**
* 行
*/
private Integer x=0;
/**
* 列
*/
private Integer y=0;
/**
* 样式: 1:红字,紫色背景;2:黄字,红色背景
*/
private Integer content;
public XyInfo(Integer x,Integer y,Integer content){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.content=content;
}
}
4.1.4效果展示


4.2easyexcal2.2.8版本实现代码
4.2.1导核心依赖
com.alibaba
easyexcel
2.2.8
4.2.2写一个类实现CellWriteHandler接口
public class My2 implements CellWriteHandler {
private List xyInfo;
/*
给样式模板两个
*/
private CellStyle style1;
private CellStyle style2;
public My2(List xyInfo){
this.xyInfo=xyInfo;
}
/**
* 在创建单元格之前调用
*/
@Override
public void beforeCellCreate(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, WriteTableHolder writeTableHolder, Row row, Head head, Integer columnIndex, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
}
/**
* 在单元格创建后调用
*/
@Override
public void afterCellCreate(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, WriteTableHolder writeTableHolder, Cell cell, Head head, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
}
/**
* 在单元上的所有操作完成后调用
*/
@Override
public void afterCellDispose(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, WriteTableHolder writeTableHolder, List> cellDataList, Cell cell, Head head, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
// 拿到poi的workbook
Workbook workbook = cell.getSheet().getWorkbook();
// 自定义宽度处理
// 自定义样式处理
// 当前事件会在 数据设置到poi的cell里面才会回调
// 判断不是头的情况 如果是fill 的情况 这里会==null 所以用not true
//循环样式信息,进行横纵坐标的匹配,给对应的单元格样式
for (XyInfo item:xyInfo
) {
if (cell.getRowIndex() == item.getX() && cell.getColumnIndex() == item.getY()) {
//现在已经锁定的单元格,下面只需要给样式
//样式: 1:红字,紫色背景;2:黄字,红色背景
// 这里千万记住 想办法能复用的地方把他缓存起来 一个表格最多创建6W个样式,我这就直接样式模板化,避免其发生
if(item.getContent()==1){
cell.setCellStyle(this.getCellStyle(workbook,1));
}
if(item.getContent()==2){
cell.setCellStyle(this.getCellStyle(workbook,2));
}
}
}
}
//优化代码,给个样式方法
/**
* 对于可确定的样式,进行样式模板化,避免每一个单元格都创建一个样式
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param content 具体设置样式信息
* @return
*/
public CellStyle getCellStyle(Workbook workbook,Integer content){
//样式: 1:红字,紫色背景;2:黄字,红色背景
if(null==this.style1 && content==1){
//避免多次创建
style1=workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font=workbook.createFont();
//红字
font.setColor((short)016);
//蓝色背景
style1.setFillForegroundColor((short)030);
//加载字体
style1.setFont(font);
// 这里需要指定 FillPatternType 为FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND
style1.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
}
if(null==style2 && content==2){
//避免多次创建
style2=workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font=workbook.createFont();
//白字
font.setColor((short)011);
//红色背景
style2.setFillForegroundColor((short)016);
//加载字体
style2.setFont(font);
// 这里需要指定 FillPatternType 为FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND
style2.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
}
//返回样式模板
if(content==1){
return this.style1;
}
if (content==2){
return this.style2;
}
return null;
}
}
4.2.3导出关键代码
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//你要导出的文件存放路径和文件名字
String filePath = "D:\\ttt\\Download\\";
String fileName=System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs();
}
//解析表头容器
List>headss=new LinkedList<>();
//解析数据容器
List>datas=new LinkedList<>();
//解析单元格样式容器
ListxyInfo=new LinkedList<>();
//手动添加假数据模拟真实数据(表头信息)
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("A","AA"))));
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("B","AAA"))));
headss.add( new ArrayList(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("C","A2","A3","A4"))));
//手动添加假数据模拟真实数据(标体数据)
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","")));
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc")));
datas.add(new LinkedList(Arrays.asList("aaa","","")));
//手动添加需要设置样式的单元格信息
xyInfo.add(new XyInfo(6,0,1));
xyInfo.add(new XyInfo(5,1,2));
EasyExcel.write(filePath+fileName)
// 这里放入动态头
.head(headss).sheet("模板(sheet名字)")
//加载单元格样式
.registerWriteHandler(new My2(xyInfo))
.doWrite(datas);
System.out.println("导出成功");
}
}
4.2.3效果展示
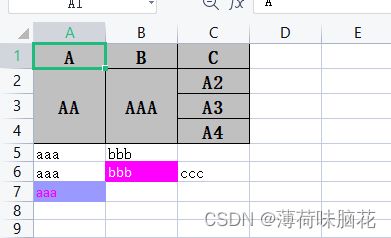
5.总结
到此,该需求基本实现,现在就简单说说easyexcal包中的技术,使用了拦截器技术,aop思想,动态代理等,具体的,我后续会做整理,目前还在研究源码,最后希望此文章能给你带来灵感。