【数据结构】栈和队列---C语言版
栈和队列
- 一、栈的概念
- 二、栈的实现
- 三、栈的应用
- 四、队列的概念
- 五、队列的实现
一、栈的概念
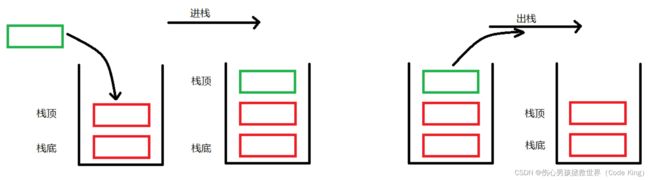
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
二、栈的实现
1.头文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include2.源文件:
#include "039-Stack.h"
//初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 4;
}
//销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
//插入元素
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * pst->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity *= 2;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//删除元素
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判断栈是否已满,空返回1,非空返回0
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//求栈中元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
3.测试文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "039-Stack.h"
void TestStack()
{
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
int main()
{
TestStack();
return 0;
}
三、栈的应用
1.有效的括号:链接
分析:
(1)将栈的实现可以直接copy进去(返回栈顶元素需要做小小的改动:如果栈为空,不能直接assert断言终止,而要返回’\0’),后面只需要实现括号的匹配即可。
(2)如何实现括号匹配?如果是左括号,那么入栈,如果是右括号就判断栈顶元素该右括号是否能够匹配,如果可以就从栈里弹出一个左括号,如果不匹配就直接返回false。
char pairs(char a) {
if (a == '}') return '{';
if (a == ']') return '[';
if (a == ')') return '(';
return 0;
}
bool isValid(char* s) {
int n = strlen(s);
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
int stk[n + 1], top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = pairs(s[i]);
if (ch) {
if (top == 0 || stk[top - 1] != ch) {
return false;
}
top--;
} else {
stk[top++] = s[i];
}
}
return top == 0;
}
四、队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出
FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头

五、队列的实现
1.头文件:
#pragma once
#include2.源文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "040-Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
//插入一个数据,尾指针+1,当尾指针为空时,队列为空
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newNode;
pq->tail = newNode;
}
}
//删除数据
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueRear(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
//判断队是否已满
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
//求队列元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
int size = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
3.测试文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"040-Queue.h"
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
TestQueue();
}
好了,今天的分享就到这里了
如果对你有帮助,记得点赞+关注哦!
我的主页还有其他文章,欢迎学习指点。关注我,让我们一起学习,一起成长吧!
