Java 中保持扩展性的几种套路和实现
在日常的开发中,作者总结了平常用到的一些低成本、保持扩展性的套路,分享出来,欢迎大家讨论。
前言
SOLID(单一、开闭、里式替换、接口隔离、依赖倒置)五大原则和23种设计模式(常见的单例、构建者、装饰、适配、代理、组合、模板等等),小伙伴们对这些肯定都很熟悉。这些原则和设计模式能够辅助我们,让我们在设计的时候有所抉择,从而达到高内聚、低耦合的目的。
那说到设计,肯定会提到架构两个字,常见的架构名词:分层架构、六边形架构、SOA架构、CQRS架构、EDA架构等等。我个人对架构的理解是边界的确认以及边界内部元素的组合,其实只要是程序员,他就一定是架构师,只不过是好的架构师还是不那么好的架构师;人人都是架构师,我认为这句话是没有问题的,区别在于他的认知决定了他所能确认的边界、如何更高效的组合内部元素;技术的架构师肯定侧重于技术,业务的架构师肯定侧重于业务,商品的架构师所能看到的边界大概率还是局限在商品域,ICBU架构组的架构师更多考虑是横向的业务支撑。以上是我个人对架构两个字的理解,今天我们不讨论具体架构,我们讨论一些套路,在日常的开发中,我总结了些我平常用到的一些低成本、保持扩展性的套路,分享出来,欢迎大家讨论。
基于管道(pipeline)的套路
关键点
- 管道(Pipeline)----用于串联阀门的管道通路
- 阀门(PipelineValue)----用于每一个节点处理实际业务诉求
- 管道上下文(PipelineContext)----用于管道上下文中数据的扭转
适用场景
- 当你的数据流需要经过很多同等逻辑处理时,可以考虑使用此套路,便于后续扩展
实现代码
- Pipeline/StandardPipeline
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:46
*/
public interface Pipeline {
/**
* 执行
*
* @return
*/
boolean invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext);
/**
* 添加值
*
* @param pipelineValue
* @return
*/
boolean addValue(PipelineValue pipelineValue);
/**
* 移除值
*
* @param pipelineValue
* @return
*/
boolean removeValue(PipelineValue pipelineValue);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:46
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
public class StandardPipeline implements Pipeline {
private List pipelineValueList = Lists.newArrayList();
@Override
public boolean invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) {
boolean isResult = true;
for (PipelineValue pipelineValue :
pipelineValueList) {
try {
isResult = pipelineValue.execute(pipelineContext);
if (!isResult) {
log.error("{},exec is wrong", pipelineValue.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
return isResult;
}
@Override
public boolean addValue(PipelineValue pipelineValue) {
if (pipelineValueList.contains(pipelineValue)) {
return true;
}
return pipelineValueList.add(pipelineValue);
}
@Override
public boolean removeValue(PipelineValue pipelineValue) {
return pipelineValueList.remove(pipelineValue);
}
} - PipelineContext/StandardPipelineContext
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:47
*/
public interface PipelineContext {
String FOR_TEST = "forTest";
/**
* 设置
*
* @param contextKey
* @param contextValue
*/
void set(String contextKey, Object contextValue);
/**
* 获取值
*
* @param contextKey
* @return
*/
Object get(String contextKey);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:47
*/
public class StandardPipelineContext implements PipelineContext {
private Map contentMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
@Override
public void set(String contextKey, Object contextValue) {
contentMap.put(contextKey, contextValue);
}
@Override
public Object get(String contextKey) {
return contentMap.get(contextKey);
}
} - PipelineValue/AbstractPipelineValue/GraySwitchValue/ForTestValue
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:47
*/
public interface PipelineValue {
/**
* 节点执行
*
* @param pipelineContext
* @return
*/
boolean execute(PipelineContext pipelineContext);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:48
*/
public abstract class AbstractPipelineValue implements PipelineValue {
@Override
public boolean execute(PipelineContext pipelineContext) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " start ");
boolean result = doExec(pipelineContext);
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " end ");
return result;
}
protected abstract boolean doExec(PipelineContext pipelineContext);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:48
*/
public class GraySwitchValue extends AbstractPipelineValue {
@Override
public boolean doExec(PipelineContext pipelineContext) {
pipelineContext.set(PipelineContext.FOR_TEST, true);
return true;
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:48
*/
public class ForTestValue extends AbstractPipelineValue {
@Override
public boolean doExec(PipelineContext pipelineContext) {
return true;
}
}- PipelineClient
package com.example.ownertest.dm.pipelline;
/**
* 入口类
*
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/25 19:48
*/
public class PipelineClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 管道初始化
Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline();
// value扩展
PipelineValue pipelineValue = new GraySwitchValue();
PipelineValue pipelineValue2 = new ForTestValue();
// 上下文
PipelineContext pipelineContext = new StandardPipelineContext();
pipeline.addValue(pipelineValue);
pipeline.addValue(pipelineValue2);
// 调用管道
pipeline.invoke(pipelineContext);
}
}常见框架中的应用
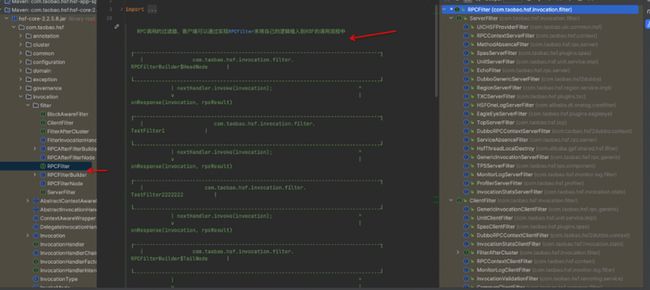
- 网络层的扛把子netty框架中,例如ChannelPipeline、ChannelHandler、ChannelHandlerContext,分别用于处理tcp拆包、加解码等等之类。
基于责任链(filterchain)的套路
关键点
来源--https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/intercepting-filter.html
- 过滤器(Filter)----实际处理业务的节点
- 过滤链(FilterChain)----串联过滤器的链条
适用场景
- 例如常见的web请求场景
实现代码
- Filter/ForTest1Filter/ForTest2Filter
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:22
*/
public interface Filter {
void doFilter(HttpRequest httpRequest,FilterChain filterChain);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:22
*/
public class ForTest1Filter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(HttpRequest httpRequest, FilterChain filterChain) {
// do
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " before " + System.currentTimeMillis());
filterChain.doFilter(httpRequest);
// after
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:22
*/
public class ForTest2Filter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(HttpRequest httpRequest, FilterChain filterChain) {
// do
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " before " + System.currentTimeMillis());
filterChain.doFilter(httpRequest);
// after
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}- FilterChain/StandardFilterChain
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:23
*/
public interface FilterChain {
void doFilter(HttpRequest httpRequest);
void addFilter(Filter filter);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:24
*/
public class StandardFilterChain implements FilterChain {
private List filterList = Lists.newArrayList();
private int currentIndex = 0;
@Override
public void doFilter(HttpRequest httpRequest) {
if (currentIndex == filterList.size()) { return; }
Filter filter = filterList.get(currentIndex);
currentIndex = currentIndex + 1;
filter.doFilter(httpRequest, this);
}
@Override
public void addFilter(Filter filter) {
if (filterList.contains(filter)) {
return;
}
filterList.add(filter);
}
} - HttpRequest/StandardHttpRequest
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:24
*/
public interface HttpRequest {
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:24
*/
public class StandardHttpRequest implements HttpRequest {
}- FilterClient----入口测试
package com.example.ownertest.dm.filter;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/26 19:25
*/
public class FilterClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FilterChain filterChain = new StandardFilterChain();
filterChain.addFilter(new ForTest1Filter());
filterChain.addFilter(new ForTest2Filter());
filterChain.doFilter(new StandardHttpRequest());
}
}常见框架中的应用
- hsf的filter机制,服务端扩展的ServerFilter和客户端扩展的ClientFilter;
- 开发过java web的小伙伴都知道的servlet,servlet的入口即是FilterChain、Filter;
基于组合/模板的套路
关键点
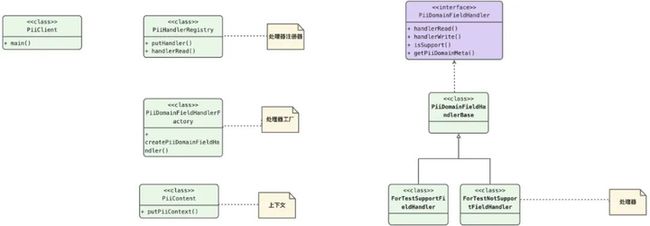
- 处理器注册器----用于存储处理器的集合
- 处理器工厂----用于创建处理器
- 处理器----实际的处理器以及扩展的实现
- 处理器上下文----处理器上下文,用于参数的传递
适用场景
- 适合于有共性、后续持续扩展的场景
实现代码
- PiiHandlerRegistry----处理器注册器
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:45
*/
@Slf4j
public class PiiHandlerRegistry {
private static Map piiDomainFieldHandlerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
public static void putHandler(String piiDomainFieldName, PiiDomainFieldHandler piiDomainFieldHandler) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(piiDomainFieldName)) {
log.warn(" piiDomainFieldName is null,continue");
return;
}
if (piiDomainFieldHandler == null) {
log.warn(piiDomainFieldName + " piiDomainFieldHandler is null,continue");
return;
}
if (!piiDomainFieldHandlerMap.containsKey(piiDomainFieldName)) {
piiDomainFieldHandlerMap.put(piiDomainFieldName, piiDomainFieldHandler);
}
}
public static int handlerRead(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent) {
int num = 0;
for (Map.Entry piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry :
piiDomainFieldHandlerMap.entrySet()) {
if (piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry.getValue().isSupport(domain, domainField)) {
piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry.getValue().handlerRead(domain, domainField, piiContent);
}
}
return num;
}
public static int handlerWrite(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent) {
int num = 0;
for (Map.Entry piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry :
piiDomainFieldHandlerMap.entrySet()) {
if (piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry.getValue().isSupport(domain, domainField)) {
piiDomainFieldHandlerEntry.getValue().handlerWrite(domain, domainField, piiContent);
}
}
return num;
}
public static Map getPiiDomainFieldHandlerMap() {
return piiDomainFieldHandlerMap;
}
public static void init() {
List piiDomainFieldHandlerList = PiiDomainFieldHandlerFactory
.createPiiDomainFieldHandler();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(piiDomainFieldHandlerList)) {
for (PiiDomainFieldHandler piiDomainFieldHandler :
piiDomainFieldHandlerList) {
putHandler(piiDomainFieldHandler.getPiiDomainMeta(), piiDomainFieldHandler);
}
}
}
} - PiiDomainFieldHandlerFactory----处理器工厂
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:46
*/
public class PiiDomainFieldHandlerFactory {
/**
* 创建领域处理器
*
* @return
*/
public static List createPiiDomainFieldHandler() {
List piiDomainFieldHandlerList = Lists.newArrayList();
//
piiDomainFieldHandlerList.add(new ForTestSupportFieldHandler());
piiDomainFieldHandlerList.add(new ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler());
return piiDomainFieldHandlerList;
}
} - PiiDomainFieldHandler/PiiDomainFieldHandlerBase/ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler/ForTestSupportFieldHandler----处理器
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:46
*/
public interface PiiDomainFieldHandler {
/**
* 处理实际操作
* 读----从PiiContent获取数据回填domain
*
* @param domain
* @param domainField
* @param piiContent
* @param
* @return
*/
boolean handlerRead(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent);
/**
* 处理实际操作
* 写----将domain中需要写入pii的字段数据写入PiiContent
*
* @param domain
* @param domainField
* @param piiContent
* @param
* @return
*/
boolean handlerWrite(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent);
/**
* 当前处理器是否支持该领域对象
*
* @param domain
* @param domainField
* @param
* @return
*/
boolean isSupport(T domain, Field domainField);
/**
* 获取处理器对应的元信息
*
* @return
*/
String getPiiDomainMeta();
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:47
*/
@Slf4j
public abstract class PiiDomainFieldHandlerBase implements PiiDomainFieldHandler {
@Override
public boolean handlerRead(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent) {
// to do business read
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean handlerWrite(T domain, Field domainField, PiiContent piiContent) {
// to do business write
return true;
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:47
*/
public class ForTestSupportFieldHandler extends PiiDomainFieldHandlerBase {
@Override
public boolean isSupport(T domain, Field domainField) {
if (this.getClass().getSimpleName().equalsIgnoreCase(domain.getClass().getSimpleName())) {
// to do business
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " is support, to do some business");
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String getPiiDomainMeta() {
return this.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:48
*/
public class ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler extends PiiDomainFieldHandlerBase {
@Override
public boolean isSupport(T domain, Field domainField) {
if (this.getClass().getSimpleName().equalsIgnoreCase(domain.getClass().getSimpleName())) {
// to do business
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " is support, to do some business");
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String getPiiDomainMeta() {
return this.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
} - PiiContent----上下文
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:48
*/
@Data
public class PiiContent {
public static String FORTEST="fortest";
private Map piiDataMap = Maps.newHashMap();
private Map piiContextMap = Maps.newHashMap();
public void putPiiData(String domainFieldName, Object domainFieldValue) {
piiDataMap.put(domainFieldName, domainFieldValue);
}
public Object getPiiData(String domainFieldName) {
return piiDataMap.get(domainFieldName);
}
public void putPiiContext(String contextName, Object contextNameValue) {
piiContextMap.put(contextName, contextNameValue);
}
public Object getPiiContext(String contextName) {
return piiContextMap.get(contextName);
}
} - PiiClient----入口的测试类
package com.example.ownertest.dm.comp;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/10/31 20:48
*/
public class PiiClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PiiHandlerRegistry.init();
// 遍历处理器
for (Map.Entry entryHandler :
PiiHandlerRegistry.getPiiDomainFieldHandlerMap().entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entryHandler.getKey() + "\t" + entryHandler.getValue().getPiiDomainMeta());
}
//
PiiContent piiContent = new PiiContent();
piiContent.putPiiContext(PiiContent.FORTEST, PiiContent.FORTEST);
// 请求处理
System.out.println("ForTestSupportFieldHandler start");
PiiHandlerRegistry.handlerRead(new ForTestSupportFieldHandler(), null, piiContent);
System.out.println("ForTestSupportFieldHandler end");
// 请求处理
System.out.println("ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler start");
PiiHandlerRegistry.handlerRead(new ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler(), null, piiContent);
System.out.println("ForTestNotSupportFieldHandler end");
}
} 常见框架中的应用
- 这个就太多了,例如spring最核心的BeanPostProcessor机制,通过org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#beanPostProcessors管理一些列的beanPostProcessors,在spring上下文org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh的时候,进行bean的init(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor)、解析注解(ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor)、解析aop(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)等等。
基于注解的套路
关键点
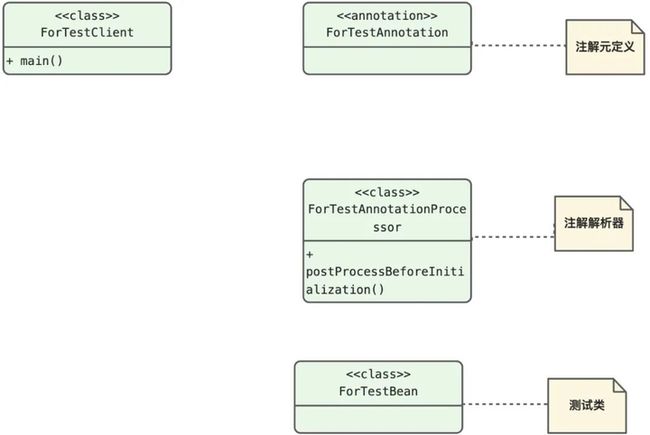
- 注解元定义----用来定义通用的元信息;
- 注解解析器----解析类上是否有指定的注解,进而进行对应的扩展操作;
- spring的BeanPostProcessor----这里是借用spring的BeanPostProcessor机制,在spring容器初始化的时候,进行回调,完成预期的扩展行为;
适用场景
- 简化内部使用
实现代码
- ForTestAnnotation----注解元定义
package com.example.ownertest.dm.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 用于测试的标识注解
*
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 10:21
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface ForTestAnnotation {
}- ForTestAnnotationProcessor----注解解析器
package com.example.ownertest.dm.annotation;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 注解解析器
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 10:25
*/
@Component
public class ForTestAnnotationProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 获取目标类是否有ForTestAnnotation注解
ForTestAnnotation annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean),
ForTestAnnotation.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return bean;
}
// 处理想要的扩展
System.out.println(beanName + " has ForTestAnnotation");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}- ForTestBean----测试bean
package com.example.ownertest.dm.annotation;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 10:26
*/
@ForTestAnnotation
public class ForTestBean {
public ForTestBean() {
System.out.println(ForTestBean.class.getSimpleName() + " init");
}
}- ForTestClient---测试入口
package com.example.ownertest.dm.annotation;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 10:26
*/
public class ForTestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(
"com.example.ownertest.dm.annotation");
System.out.println(ForTestClient.class.getSimpleName());
}
}常见框架中的应用
- 例如集团内部的spring-boot-alibaba-diamond-autoconfigure
基于事件分发的套路
关键点
- 事件源--事件触发者
- 事件--标识产生的来源
- 事件监听器--事件的关注者,即处理者
- 事件分发器--用于将事件源的事件转发给事件监听器
实现代码
- EventSource/EventSourceForTest/EventSourceForTest2
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* 发出事件
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:12
*/
public interface EventSource {
/**
* 发出事件
*
* @return
*/
Event fireEvent();
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:14
*/
public class EventSourceForTest implements EventSource {
@Override
public Event fireEvent() {
Event event = new EventForTest();
System.out.println(getClass().getSimpleName() + " \t fireEvent " + event.getName());
return event;
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:15
*/
public class EventSourceForTest2 implements EventSource {
@Override
public Event fireEvent() {
Event event = new EventForTest2();
System.out.println(getClass().getSimpleName() + " \t fireEvent " + event.getName());
return event;
}
}- Event/EventForTest/EventForTest2
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:15
*/
public interface Event {
/**
* 事件名称
*
* @return
*/
String getName();
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:17
*/
public class EventForTest implements Event {
@Override
public String getName() {
return getClass().getSimpleName();
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:17
*/
public class EventForTest2 implements Event {
@Override
public String getName() {
return getClass().getSimpleName();
}
}- EventListener/EventListenerForTest
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:17
*/
public interface EventListener {
/**
* 是否支持此事件
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
boolean supportEvent(Event event);
/**
* 处理事件
*
* @return
*/
boolean handlerEvent(Event event);
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:18
*/
public class EventListenerForTest implements EventListener {
@Override
public boolean supportEvent(Event event) {
return event.getName().contains("Test");
}
@Override
public boolean handlerEvent(Event event) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "\t handler " + event.getName());
return true;
}
}- EventDispatcher/EventListenerManager
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:18
*/
public class EventDispatcher {
/**
* 单例模式
*/
private static EventDispatcher eventDispatcher = new EventDispatcher();
private EventDispatcher() {
}
/**
* 分发事件
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
public static boolean dispatchEvent(Event event) {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(EventListenerManager.getEventListenerList())) {
for (EventListener eventListener :
EventListenerManager.getEventListenerList()) {
if (eventListener.supportEvent(event)) {
eventListener.handlerEvent(event);
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:18
*/
public class EventListenerManager {
private static List eventListenerList = Lists.newArrayList();
/**
* 添加事件监听器
*
* @param eventListener
* @return
*/
public static boolean addEventListener(EventListener eventListener) {
if (!eventListenerList.contains(eventListener)) {
return eventListenerList.add(eventListener);
}
return true;
}
/**
* 移除事件监听器
*
* @param eventListener
* @return
*/
public static boolean removeEventListener(EventListener eventListener) {
if (eventListenerList.contains(eventListener)) {
return eventListenerList.remove(eventListener);
}
return true;
}
public static List getEventListenerList() {
return eventListenerList;
}
} - EventClient
package com.example.ownertest.dm.event;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 14:19
*/
public class EventClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建事件源
EventSource eventSourceForTest = new EventSourceForTest();
EventSource eventSourceForTest2 = new EventSourceForTest2();
// 创建事件监听器
EventListener eventListener = new EventListenerForTest();
EventListenerManager.addEventListener(eventListener);
// 发布事件
EventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(eventSourceForTest.fireEvent());
EventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(eventSourceForTest2.fireEvent());
}
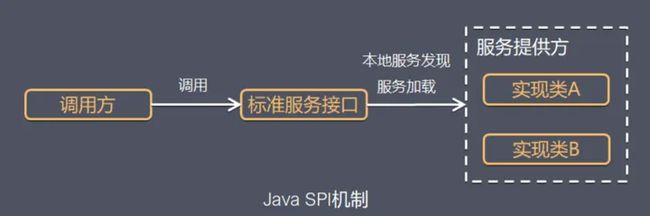
}基于SPI机制的套路
关键点
- 服务调用方
- 服务实现方----以接口名称为文件名称,放在META-INF/services,值为该接口的实现
- 标准服务接口
适用场景
实现代码
- SpiServiceLoaderHelper
package com.example.ownertest.dm.spi;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 15:32
*/
public class SpiServiceLoaderHelper {
public static ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface getProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface() {
// 先从缓存中加载
Object serviceCache = DependServiceRegistryHelper.getDependObject(ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface.class);
if (serviceCache != null) {
return (ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface) serviceCache;
}
// spi 方式加载
ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface serviceInterface = loadSpiImpl(ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface.class);
// 防止注入的bean为空 提前进行判断 以免业务执行出现问题
boolean isExist = true;
if (Objects.isNull(serviceInterface)) {
isExist = false;
} else if (Objects.isNull(serviceInterface.getProductPackageRemoteService())) {
isExist = false;
}
if (!isExist) {
throw new RuntimeException("getProductPackageRemoteService load impl failed,please check spi service");
}
// 添加进统一的依赖管理
DependServiceRegistryHelper.registry(ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface.class, serviceInterface);
return serviceInterface;
}
/**
* 以spi的方式加载实现类
*
* @param cls
* @param
* @return
*/
private static
P loadSpiImpl(Class
cls) {
ServiceLoader
spiLoader = ServiceLoader.load(cls);
Iterator
iaIterator = spiLoader.iterator();
if (iaIterator.hasNext()) {
return iaIterator.next();
}
return null;
}
}
- DependServiceRegistryHelper
package com.example.ownertest.dm.spi;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 15:35
*/
public class DependServiceRegistryHelper {
/**
* 存储策略依赖的服务,统一管理
*/
private static Map dependManagerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
public static boolean registryMap(Map dependManagerMap) {
for (Map.Entry dependEntry :
dependManagerMap.entrySet()) {
registry(dependEntry.getKey(), dependEntry.getValue());
}
return true;
}
public static boolean registry(Class cls, Object dependObject) {
dependManagerMap.put(cls.getCanonicalName(), dependObject);
return true;
}
public static Object getDependObject(Class cls) {
return dependManagerMap.get(cls.getCanonicalName());
}
} - SpiServiceLoaderClientTest
package com.example.ownertest.dm.spi;
/**
* @Author: linear.zw
* @Date: 2023/11/1 15:37
*/
public class SpiServiceLoaderClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface productPackageRemoteServiceInterface
= SpiServiceLoaderHelper.getProductPackageRemoteServiceInterface();
}
}常见框架中的应用
- 目前大多数中台的策略包,都是基于spi方式的,动态加载业务的实现,进而达到扩展的目的;
- 例如google开源的auto-service,通过注解的方式,自动生成spi的实现目录;
最后
程序员大多数都是实干派,所以,你的套路有哪些,评论区有你的位置,Show me the code。
作者|高止
原文链接
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。