遗传算法(GA)
理论:
遗传算法是一种通过模拟生物进化的方式来寻找最优解的一类优化算法。这种算法主要依靠遗传、突变和自然选择的机制对问题求解进行高效的迭代搜索。
遗传算法的基本思想是将问题的解表示成一个个个体,然后根据适应度函数的定义来评估每个个体的适应性并确定其在繁殖中的概率。经过交叉与变异等操作,新的代替原有的个体,继续与其他生成的个体竞争下去。这一过程不断迭代直至找到最优解或达到迭代次数上限。
遗传算法具有全局搜索能力强、对复杂非线性问题较为适用、支持并行优化计算等特点,在许多领域中得到了广泛的应用,如机器学习、图像处理、网络优化、工程设计等等。
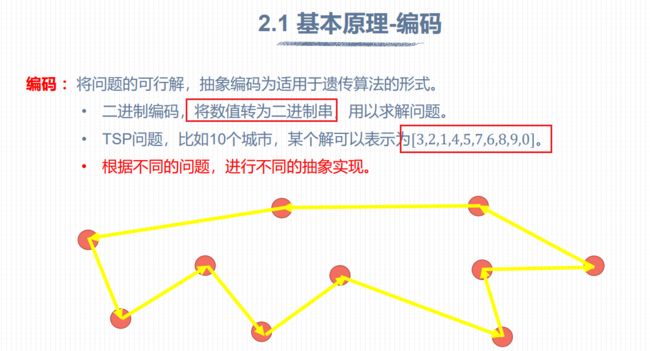


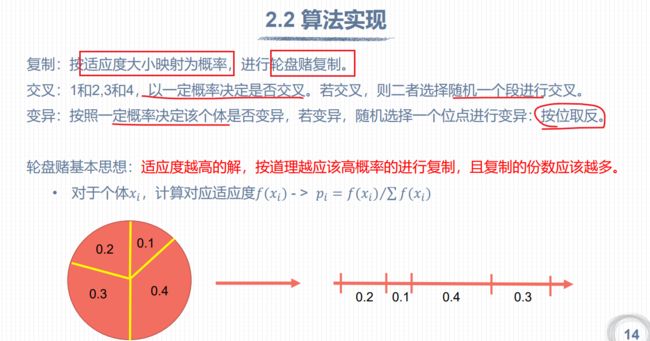
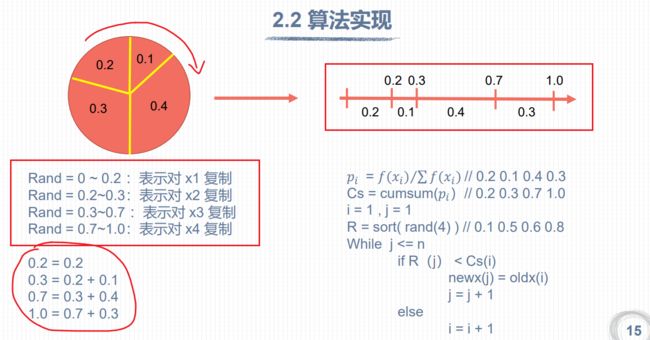
顺时针转动:0.2 0.1 0.4 0.3




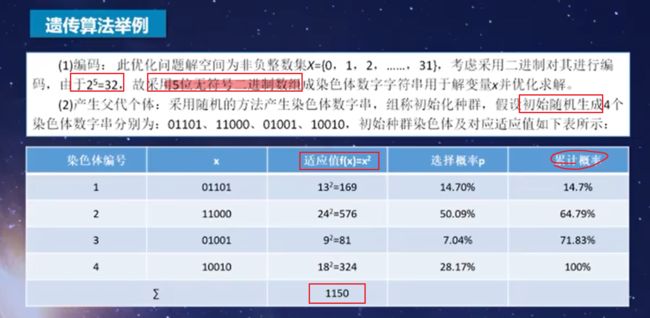
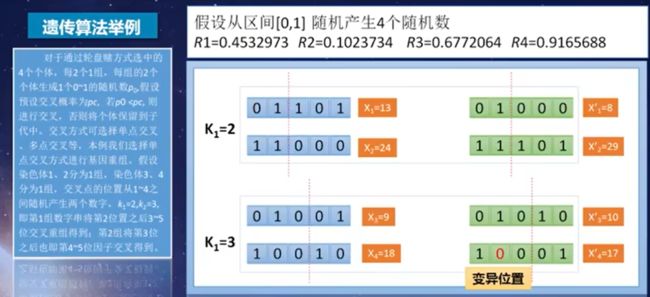
从区间[0,1]随机产生4个随机数:R1=45.3% ,14.7%<45.3%<64.79,所以选择个体2
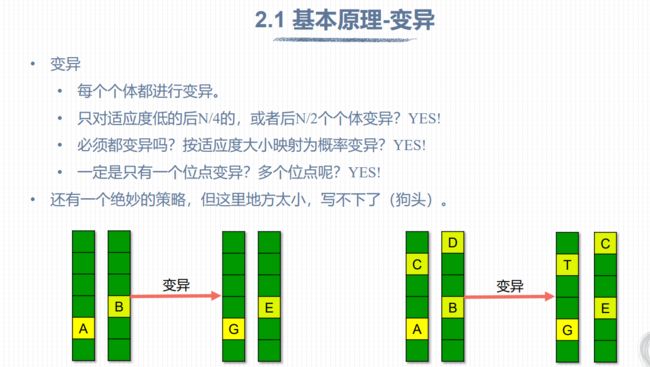
为了避免陷入局部最优的情况,我们通常会按照一定的概率对少量个体进行变异操作
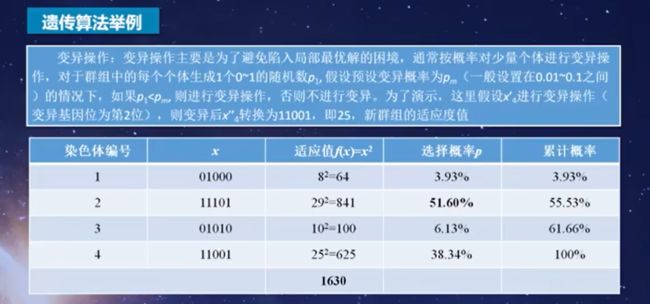
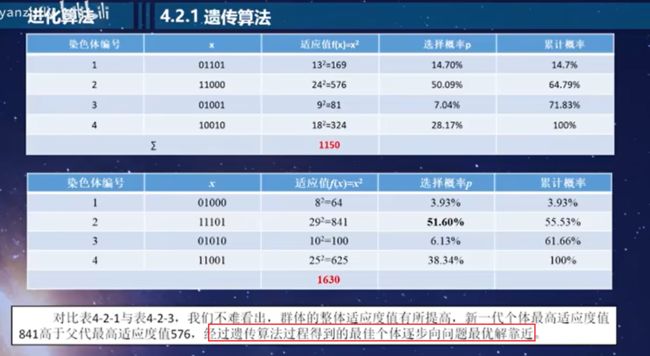
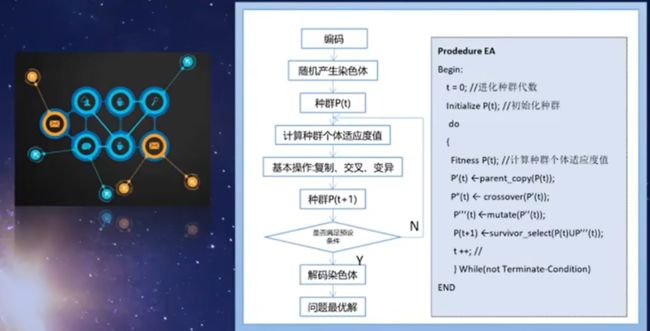
总结:遗传算法是通过对种群个体迭代的复制、交叉、变异的过程,是新种群继承父带种群的优良特征,而不断完善和优化的过程,我们将它称为遗传算法。
遗传算法中对个体操作有哪些?
在遗传算法中,对个体的操作主要包括选择、交叉和变异三种类型。以下是对这三种操作的简要介绍:
-
选择(Selection):根据适应度函数,从种群中选择一部分个体作为下一代的父代。选择的方式一般有轮盘赌选择、竞赛选择、锦标赛选择等。
-
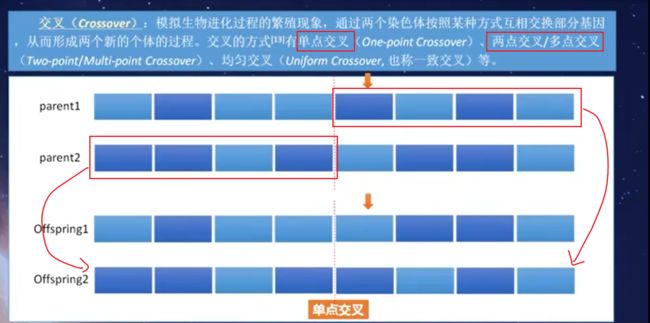
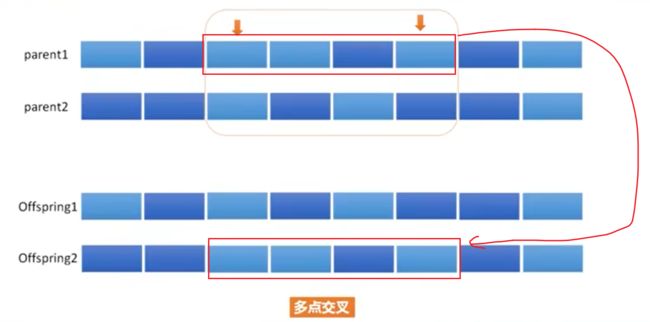
交叉(Crossover):将上一步选择出的父代个体进行交叉,生成新的子代个体。交叉的方式有单点交叉、多点交叉、均匀交叉等。
-
变异(Mutation):在交叉后生成的子代个体中,以一定的概率对某些基因进行变异操作,引入新的遗传信息。变异一般采用随机的方式,如单点变异、多点变异、位变异等。
以上三种操作结合起来,就可以产生出一组新的个体来进行下一代的优化。在遗传算法中,这些操作的选择和调整会影响算法的搜索效率和结果质量。
遗传算法中对种群操作有哪些?
在遗传算法中,对种群的操作主要包括初始化和淘汰两类。
-
初始化(Initialization):在遗传算法开始前,需要先生成一个初始的种群。一般来说,这个种群是由一些随机的个体组成的。随机程度要适当,不能过于杂乱,也不能过于单一。
-
淘汰(Survival of the fittest):在遗传算法的迭代过程中,需要通过一些策略对种群进行淘汰,以避免种群陷入局部最优解。常见的淘汰策略有精英保留、种群大小控制、截断选择等。
其中,精英保留的策略是将前几代中表现最好的个体直接留用到下一代种群中,以保持种群中的优秀个体,提升算法的搜索效率。
种群大小控制的策略是设定一个种群大小的上限,当种群中个体数目超过这个数值时,需要淘汰一部分个体,保持种群规模的合适。
截断选择的策略是按一定比例将个体按照适应度的大小从高到低排序,只保留前面的几个个体,淘汰后面的个体。
对种群操作要灵活,不同的问题需要采用不同的操作策略。
算法:
Individual
public class Individual {
private int[] chromosome; // chromosome染色体
private double fitness = -1;
public Individual(int[] chromosome) {
// 创造单个染色体
this.chromosome = chromosome;
}
public Individual(int chromosomeLength) { // 初始化随机个体
this.chromosome = new int[chromosomeLength];
for (int gene = 0; gene < chromosomeLength; gene++) {
if (0.7 < Math.random()) {
this.setGene(gene, 2);
} else if(0.4 < Math.random()){
this.setGene(gene, 1);
}
else
{
this.setGene(gene, 0);
}
}
}
public int[] getChromosome() { // 获得个体的染色体
return this.chromosome;
}
public int getChromosomeLength() { // 得到个体的染色体长度
return this.chromosome.length;
}
public void setGene(int offset, int gene) { // 将基因置于偏移位置
this.chromosome[offset] = gene;
}
public int getGene(int offset) { // 获得基因偏移
return this.chromosome[offset];
}
public void setFitness(double fitness) { // 储存个体适合度
this.fitness = fitness;
}
public double getFitness() { // 得到个体的适合度
return this.fitness;
}
public String toString() { // 将染色体显示为字符串。
String output = "";
for (int gene = 0; gene < this.chromosome.length; gene++) {
output += this.chromosome[gene];
}
return output; // 染色体的字符串表示
}
}
Population
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Random;
// 种群是个体的抽象集合。人口类通常用于对其个人执行组级操作,比如找到最强壮的个体,收集种群的统计数据作为一个整体,选择个体进行变异或交叉。
public class Population {
private Individual population[];
private double populationFitness = -1;
public Population(int populationSize) { // 种群中个体的数量
this.population = new Individual[populationSize];
}
public Population(int populationSize, int chromosomeLength) { // 种群中个体的数量 染色体长度
// 将种群初始化为个体数组
this.population = new Individual[populationSize];
// 依次创建每个个体
for (int individualCount = 0; individualCount < populationSize; individualCount++) {
// 创建一个个体,将其染色体初始化为给定的
Individual individual = new Individual(chromosomeLength);
// 将个体添加到种群中
this.population[individualCount] = individual;
}
}
public Individual[] getIndividuals() { // 从种群中挑选个体
return this.population;
}
/**
* 根据适应度在种群中找到一个个体
*
根据适应度在种群中找到一个个体。
这个方法可以让你按照适合度的顺序选择个体。
这可以用来表示最强壮的个体(例如,如果你是。测试解决方案),但它也可以用来寻找弱势个体(如果你想剔除种群)或者一些最强的个人(如果你用的是“精英主义”的话)。
*
* @param offset
* The offset of the individual you want, sorted by fitness. 0 is
* the strongest, population.length - 1 is the weakest.
* 你想要的个体的偏移量,根据适应度排序。0是最强的,人口。长度- 1是最弱的。
* @return individual Individual at offset
*/
public Individual getFittest(int offset) {
// 适应度排序种群
Arrays.sort(this.population, new Comparator<Individual>() {
@Override
public int compare(Individual o1, Individual o2) {
if (o1.getFitness() > o2.getFitness()) {
return -1;
} else if (o1.getFitness() < o2.getFitness()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
});
return this.population[offset]; // 返回最适合的个体
}
public void setPopulationFitness(double fitness) { // 设置种群的群体适应度
this.populationFitness = fitness;
}
public double getPopulationFitness() { // 得到种群的群体适应度
return this.populationFitness;
}
public int size() { // 得到种群的规模
return this.population.length;
}
public Individual setIndividual(int offset, Individual individual) { // 设置个体的偏移量
return population[offset] = individual;
}
public Individual getIndividual(int offset) {
return population[offset];
}
public void shuffle() { // 变换位置
Random rnd = new Random();
for (int i = population.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int index = rnd.nextInt(i + 1);
Individual a = population[index];
population[index] = population[i];
population[i] = a;
}
}
}
GeneticAlgorithm
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.CloudletSchedulerTimeShared;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.UtilizationModel;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.UtilizationModelFull;
public class GeneticAlgorithm {
private int populationSize; // 种群规模
private double mutationRate; // 突变率
private double crossoverRate; // 交叉
private int elitismCount; // 精英数
public GeneticAlgorithm(int populationSize, double mutationRate, double crossoverRate, int elitismCount) {
this.populationSize = populationSize;
this.mutationRate = mutationRate;
this.crossoverRate = crossoverRate;
this.elitismCount = elitismCount;
}
public Population initPopulation(int chromosomeLength) {
// Initialize population 初始化种群数
Population population = new Population(this.populationSize, chromosomeLength);
return population;
}
public double calcFitness(Individual individual) { // 计算个体的适应度
ArrayList<vm3> vmlist = new ArrayList<vm3>();
//VM description
int vmid = 0;
int mips = 250;
long size = 10000; //image size (MB)
int ram = 2048; //vm memory (MB)
long bw = 1000;
int pesNumber = 1; //number of cpus
String vmm = "Xen"; //VMM name
double[] executioncost1= {1.23,1.12,1.15};
int[] datasize1= {30,30};
vm3 Vm1 = new vm3(vmid, brokerId, mips, pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared(), executioncost1, datasize1);
// the second VM will have twice the priority of VM1 and so will receive twice CPU time
// 第二个VM的优先级将是VM1的两倍,因此将获得两倍的CPU时间
vmid++;
double[] executioncost2= {1.17,1.17,1.28};
int[] datasize2= {10,10};
vm3 Vm2 = new vm3(vmid, brokerId, mips , pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared(), executioncost2, datasize2);
vmid++;
double[] executioncost3= {1.13,1.11,1.11};
int[] datasize3= {10,10};
vm3 Vm3 = new vm3(vmid, brokerId, mips, pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared(), executioncost3, datasize3);
vmid++;
double[] executioncost4= {1.26,1.12,1.14};
int[] datasize4= {10,10};
vm3 Vm4 = new vm3(vmid, brokerId, mips , pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared(), executioncost4, datasize4);
vmid++;
double[] executioncost5= {1.19,1.14,1.22};
int[] datasize5= {10,10};
vm3 Vm5 = new vm3(vmid, brokerId, mips , pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared(), executioncost5, datasize5);
//add the VMs to the vmList
vmlist.add(Vm1);
vmlist.add(Vm2);
vmlist.add(Vm3);
vmlist.add(Vm4);
vmlist.add(Vm5);
//submit vm list to the broker
broker.submitVmList(vmlist);
// properties 属性
int id = 0;
long length = 40000;
long fileSize = 300;
long outputSize = 300;
UtilizationModel utilizationModel = new UtilizationModelFull();
double[] comcost1= {0.00,0.17,0.21};
cloudlet3 Cloudlet1 = new cloudlet3(id, length, pesNumber, fileSize, outputSize, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, comcost1);
Cloudlet1.setUserId(brokerId);
id++;
double[] comcost2= {0.17,0.00,0.22};
cloudlet3 Cloudlet2 = new cloudlet3(id, length, pesNumber, fileSize, outputSize, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, comcost2);
Cloudlet2.setUserId(brokerId);
id++;
double[] comcost3= {0.21,0.22,0.00};
cloudlet3 Cloudlet3 = new cloudlet3(id, length, pesNumber, fileSize, outputSize, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, comcost3);
Cloudlet3.setUserId(brokerId);
List<cloudlet3> cloudletList=new ArrayList<cloudlet3>();
//将Cloudlet添加到列表中
cloudletList.add(Cloudlet1);
cloudletList.add(Cloudlet2);
cloudletList.add(Cloudlet3);
// 正确基因的轨迹数
double cost = 0.0;
// 计算的成本
for (int geneIndex = 0; geneIndex < individual.getChromosomeLength(); geneIndex++) {
// 每找到一个“1”,就增加一个适应度点
cost=cost+vmlist[geneIndex].executioncost[individual[geneIndex]];
}
// 通信成本
for(int geneIndex = 1; geneIndex < individual.getChromosomeLength(); geneIndex++)
{
cost=cost+cloudletList[individual[geneIndex]].comcost[individual[geneIndex-1]]*vmlist[geneIndex].datasize[0];
}
// 计算适应度
double fitness = (double) cost;
// 存储适应度
individual.setFitness(fitness);
return fitness;
}
// 本质上,就是循环遍历种群中的个体,计算每个个体的适应度,然后计算整个种群的适应度。种群的适合度可能重要也可能不重要,但重要的是确保每个个体都得到评估。
public void evalPopulation(Population population) { // 评估整个群体
double populationFitness = 0;
// 在种群上循环评估个体和种群适应度
for (Individual individual : population.getIndividuals()) {
populationFitness += calcFitness(individual);
}
population.setPopulationFitness(populationFitness);
}
/**
* 检查种群是否满足终止条件
*
* 对于这个简单的问题,我们知道完美的解决方案是什么样子的,所以我们可以简单地停止进化,一旦我们达到了一个适应度。
*
* @param population
* @return boolean True if termination condition met, otherwise, false
*/
/**
* Select parent for crossover 选择父级进行交叉
*
* @param population
* The population to select parent from
* @return The individual selected as a parent
*/
public Individual selectParent(Population population) {
// Get individuals
Individual individuals[] = population.getIndividuals();
// 旋转轮盘赌
double populationFitness = population.getPopulationFitness();
double rouletteWheelPosition = Math.random() * populationFitness;
// Find parent
double spinWheel = 0;
for (Individual individual : individuals) {
spinWheel += individual.getFitness();
if (spinWheel >= rouletteWheelPosition) {
return individual;
}
}
return individuals[population.size() - 1];
}
/**
* Apply crossover to population 将交叉应用于种群
*
*
*
* @param population
* The population to apply crossover to
* @return The new population
*/
public Population crossoverPopulation(Population population) {
// 创造新种群
Population newPopulation = new Population(population.size());
// 根据适应度对当前种群进行循环
for (int populationIndex = 0; populationIndex < population.size(); populationIndex++) {
Individual parent1 = population.getFittest(populationIndex);
// 把交叉应用到个体身上
if (this.crossoverRate > Math.random() && populationIndex >= this.elitismCount) {
// 初始化的后代
Individual offspring = new Individual(parent1.getChromosomeLength());
// Find second parent
Individual parent2 = selectParent(population);
// 基因组环
for (int geneIndex = 0; geneIndex < parent1.getChromosomeLength(); geneIndex++) {
// Use half of parent1's genes and half of parent2's genes
if (0.5 > Math.random()) {
offspring.setGene(geneIndex, parent1.getGene(geneIndex));
} else {
offspring.setGene(geneIndex, parent2.getGene(geneIndex));
}
}
// 给新种群增加后代
newPopulation.setIndividual(populationIndex, offspring);
} else {
// 在不使用交叉的情况下将个体添加到新种群中
newPopulation.setIndividual(populationIndex, parent1);
}
}
return newPopulation;
}
/**
* 将突变应用于种群
*
* This method will consider the GeneticAlgorithm instance's mutationRate
* and elitismCount
*
* @param population
* The population to apply mutation to
* @return The mutated population
*/
public Population mutatePopulation(Population population) {
// 初始化新种群
Population newPopulation = new Population(this.populationSize);
// 根据适应度对当前种群进行循环
for (int populationIndex = 0; populationIndex < population.size(); populationIndex++) {
Individual individual = population.getFittest(populationIndex);
// 在个体基因上进行循环
for (int geneIndex = 0; geneIndex < individual.getChromosomeLength(); geneIndex++) {
// 如果这是一个精英个体,跳过突变
if (populationIndex > this.elitismCount) {
// Does this gene need mutation?
if (this.mutationRate > Math.random()) {
// 获得新基因
int newGene = 1;
if (individual.getGene(geneIndex) == 1) {
newGene = 0;
}
// 变异的基因
individual.setGene(geneIndex, newGene);
}
}
}
// 将个体添加到种群中
newPopulation.setIndividual(populationIndex, individual);
}
// 返回突变种群
return newPopulation;
}
}