Python的海龟 turtle 库使用详细介绍(画任意多边形,全网最详细)
学Turtle库,其实就是学数学,而且还能提高对数学和学习的兴趣。Turtle库还能够帮助孩子更好地理解几何学和数学概念,比如角度、比例、几何图形的性质等等,是Python中一个很有趣的库。
前言
Turtle库是Python中一个很有趣的库,可以用来绘制各种图形,比如直线、圆、正方形等等。掌握Turtle库的意义在于可以培养孩子的创造力和想象力,让他们通过编写代码来实现自己的创意,同时也可以提高他们的编程能力和逻辑思维能力。此外,Turtle库还能够帮助孩子更好地理解几何学和数学概念,比如角度、比例、几何图形的性质等等,学Turtle库其实就是学数学,但更有趣味性。
turtle库介绍
Turtle库是Python的一个标准库,提供了一个绘图的海龟机器人,可以使用Python代码控制海龟机器人的移动和动作,从而实现绘制图形的功能。Turtle库支持绘制直线、圆、椭圆、曲线、填充颜色等功能,可以用来绘制各种各样的图形和图案。使用Turtle库可以加深对Python语言的理解和掌握,同时也可以进行艺术创作和教育活动。
Python内置了turtle库。在1966年,Seymour Papert和Wally Feurzig发明了一种专门给儿童学习编程的语言——LOGO语言,它的特色就是通过编程指挥一个小海龟(turtle)在屏幕上绘图。海龟绘图(Turtle Graphics)后来被移植到各种高级语言中,Python内置了turtle,基本上100%复制了原始的Turtle Graphics的所有功能。
- turtle的帮助文档:turtle
- turtle绘图作品:海龟绘图
turtle库的使用
使用前需先引入库,可以使用 from turtle import * 或者 import turtle。前者使用方法不需要加 turtle,后者需要加turtle。
简单示例:
import turtle
# 创建一个Turtle对象
t = turtle.Turtle()
#turtle.setup(width,height,startx,starty)
# 移动Turtle对象前进100步
t.forward(100)
# 向左旋转Turtle对象90度
t.left(90)
# 移动Turtle对象前进50步
t.forward(50)
# 创建另一个Turtle对象
t2 = turtle.Turtle()
# 移动Turtle对象t2前进80步
t2.forward(80)
# 绘制线段连接两个Turtle对象的位置
t2.goto(t.xcor(), t.ycor())
# 调用done()使得窗口等待被关闭,否则将立刻关闭窗口:
turtle.done()
画出长方形
从简单的开始,画个长方形。
# 导入turtle包的所有内容:
from turtle import *
# 设置笔刷宽度:
width(4)
# 前进:
forward(200)
# 右转90度:
right(90)
# 笔刷颜色:
pencolor('red')
forward(100)
right(90)
pencolor('green')
forward(200)
right(90)
pencolor('blue')
forward(100)
right(90)
# 调用done()使得窗口等待被关闭,否则将立刻关闭窗口:
done()从程序代码可以看出,海龟绘图就是指挥海龟前进、转向,海龟移动的轨迹就是绘制的线条。要绘制一个长方形,只需要让海龟前进、右转90度,反复4次。
调用width()函数可以设置笔刷宽度,调用pencolor()函数可以设置颜色。更多操作请参考turtle库的说明。绘图完成后,记得调用done()函数,让窗口进入消息循环,等待被关闭。否则,由于Python进程会立刻结束,将导致窗口被立刻关闭。
绘制任意多边形
增加点难度,学习下数学的几何知识。
多边形的内角公式: 内角 = (n-2) * 180 / n,其中n是多边形的边数。
多边形的所有内角之和等于 180*(n - 2),其中 n 是多边形的边数。
以正五边形为例,将n设置为5,代入公式得到 (5-2) * 180 / 5 = 3 * 180 / 5 = 108度,因此,正五边形的每个内角为108度。
其实类似这类画图问题,都是数学问题,算对了角度,就很容易画了。
多边形内角公式的推导,来学习下数数学知识。
多边形的内角是指多边形内部的任意两个相邻顶点之间的夹角。
证法一:
因为每个三角形的内角之和为 180°,一个n边行,可以分为n-2个三角形。因此,多边形的内角和等于 180*(n - 2)。那么每个内角= (n-2) * 180 / n。
证法二:
任意凸多边形的外角和都为360°,在一个n边形中,每个顶点的外角度数为360度/n。由于多边形有n个顶点,所以外角度数的总和为360度。因此可以得到公式:n * 外角度数 = 360度,即外角度数 = 360度 / n。内角+外角=180度,可以得到多边形的内角公式:内角 = 180度 - (360度 / n) = (n - 2) * 180度 / n。
例如,在一个三角形中,每个顶点的外角度数为 360° / 3 = 120°。 在一个四边形中,每个顶点的外角度数为 360° / 4 = 90°。 在一个五边形中,每个顶点的外角度数为 360° / 5 = 72°。
举例,画几个正五边形:
from turtle import *
import time
def draw5(x, y):
pu()
goto(x, y)
pd()
# set heading: 0
seth(0)
for i in range(5):
fd(40)
rt(72)
time.sleep(1)
for x in range(0, 250, 50):
draw5(x, 0)
done()出题,如何绘制出五角星?
根据上述公式,如果要绘制五角星,关键是得知道每次转向多少角度?
五角星是144度。为什么是144度,你知道吗?因为正五边形的内角是108度,则它的的补角是72度,五角星的每个角是180-72-72=36度,因此 每次转向180-36 = 144 度。
#绘制一个五角星
from turtle import *
import time
def drawStar(x, y):
pu()
goto(x, y)
pd()
# set heading: 0
seth(0)
for i in range(5):
fd(110)
rt(144)
time.sleep(1)
drawStar(0,0)
done()以此类推,你能绘制出六角星吗?
也很简单,关键是知道六角星的每个角的角度,求得转向角度。根据多边形的内角公式,多边形内角 = (n-2) * 180 / n,其中n是多边形的边数。
先画出每个小三角形,每次转向60度,再画出剩余5个小三角形,总共是6个小三角形组成了六边形。
from turtle import *
def triangle():
pensize(2)
pencolor('black')
for i in range(3):
fd(60)
right(120)
def test():
colors=['green','red','yellow','pink','purple','orange']
speed(1)
for i in range(6):
begin_fill()
fillcolor(colors[i])
triangle()
fd(60)
left(60) #以坐标系为基准,左转60°
end_fill()
#填充中心颜色
fillcolor("blue")
begin_fill()
for i in range(6):
fd(60)
left(60)
end_fill()
ht()#隐藏画笔
done()
test()
from turtle import *
def triangle(x):
pensize(2)
pencolor('black')
for i in range(3):
fd(x)
right(120)
def main():
speed(8)
colors=['green','red','yellow','blue']
for j in range(1,7):
for i in range(4):
if j >= 2:
triangle(160 + j * 10)
left(90)
else:
fillcolor(colors[i])
begin_fill()
triangle(160)
left(90)
end_fill()
ht()
main()
done()猜一猜以下代码将画出什么图形?
from turtle import *
def triangle():
pensize(2)
pencolor('black')
for i in range(3):
fd(160)
right(120)
def test():
penup()
setpos(-100,140)#画笔移动到一个绝对坐标。(开始默认画笔居中)
pendown()
speed(5)
colors=['green','red','pink','purple','blue','yellow','orange']
for i in range(6):
fillcolor(colors[i])
begin_fill()
triangle()
fd(160)
right(60)
end_fill()
ht()
#执行
test()
done()
出题,你能画出如下的风车吗?
画个龙卷风
from turtle import *
# 龙卷风
setup(800,600)
pensize(1)
speed(6)
colors=['green','red','yellow','grey','orange','blue','pink','purple']
bgcolor('black')
for i in range(1,10):
pencolor(colors[i%8])
penup()
goto(5*i,0)
pendown()
circle(10*i)
done()
同心圆(箭靶)
# 同心圆
from turtle import *
setup(800, 600, 450, 50)
pensize(5)
bgcolor('white')
speed('fastest')
colors = ['blue', 'yellow', 'red', 'green', 'white', 'black', 'orange', 'grey']
for i in range(10, 1, -1):
penup()
goto(0, -20 * i)
pendown()
begin_fill()
fillcolor(colors[i % 4])
circle(20 * i)
end_fill()
hideturtle()
done()
turtle主要函数介绍
绝对坐标
海龟初始位置为(0,0),位于画布中央。
海龟默认朝向右侧。(在turtle模块中,可使用setheading()函数(可简写为seth)用于设置海龟的朝向。它的作用是设置海龟当前的前进方向,参数是一个0-360之间的整数,表示海龟的朝向角度。例如setheading(90)将使海龟朝向上方,seth(180)将使朝向指向左方。
行进函数
turtle.goto(x,y,从当前位置到达任何位置(X,Y)。
海龟无论何处,面对的方向是前进方向。
前进函数:turtle.fd(),向前移动指定的距离。
后退函数:turtle.bk(),向后移动指定的距离。
画弧函数:turtle.circle(r, angle) 以左侧r像素处为圆心,逆时针旋转angle的角度。
朝向函数:turtle.seth(angle)朝向绝对方向angle。(海龟默认朝向右侧,设置90,则逆时针转向指向正上方,设置为180则将使朝向指向左侧。)
right()和left()函数用于设置海龟的转向角度。
right(angle)函数用于将海龟向右旋转指定的角度。参数angle是一个整数,表示海龟要旋转的角度。例如,right(90)将使海龟向右旋转90度。
left(angle)函数用于将海龟向左旋转指定的角度。参数angle是一个整数,表示海龟要旋转的角度。例如left(90)将使海龟向左旋转90度。 这两个函数可以用于控制海龟的行走方向和绘制图形的方向。在使用这两个函数时,需要注意它们设置的是海龟的相对转向角度,而不是绝对转向角度。也就是说,调用right()函数后,海龟的面向方向会向右旋转,而调用left()函数后,海龟的面向方向会向左旋转。
turtle.penup() 画笔抬起
turtle.pendown() 画笔落下
turtle.pensize() 海龟腰围
turtle.pencolor() 画笔颜色
turtle.speed() 设置移动速度,其中的参数值表示海龟的速度等级,取值范围为[0, 10],注意其中0也是表示最快的速度,1则是最慢,10也是表示最快的速度,默认速度应该是5(normal)。
- 如果输入的数字大于10或小于0.5,则速度设置为0。
- 速度字符串通过以下方式映射到速度值:
- ‘fastest’:0
- ‘fast’:10
- ‘normal’:6
- ‘slow’:3
- ‘slowest’:1
turtle.home() 返回原点(0,0)位置(屏幕正中央),朝向右。
绘制复杂的图形
注:部分资源引用自《Python创意编程100例turtle篇》。如有侵权请告知删除。
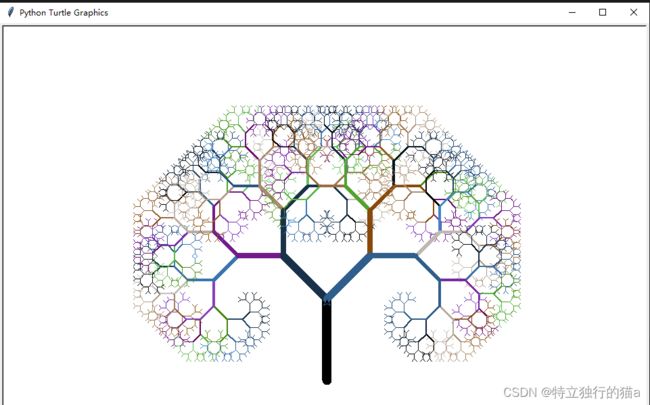
美丽的树
from turtle import *
# 设置色彩模式是RGB:
colormode(255)
lt(90)
lv = 14
l = 120
s = 45
width(lv)
# 初始化RGB颜色:
r = 0
g = 0
b = 0
pencolor(r, g, b)
penup()
bk(l)
pendown()
fd(l)
def draw_tree(l, level):
global r, g, b
# save the current pen width
w = width()
# narrow the pen width
width(w * 3.0 / 4.0)
# set color:
r = r + 1
g = g + 2
b = b + 3
pencolor(r % 200, g % 200, b % 200)
l = 3.0 / 4.0 * l
lt(s)
fd(l)
if level < lv:
draw_tree(l, level + 1)
bk(l)
rt(2 * s)
fd(l)
if level < lv:
draw_tree(l, level + 1)
bk(l)
lt(s)
# restore the previous pen width
width(w)
speed("fastest")
draw_tree(l, 4)
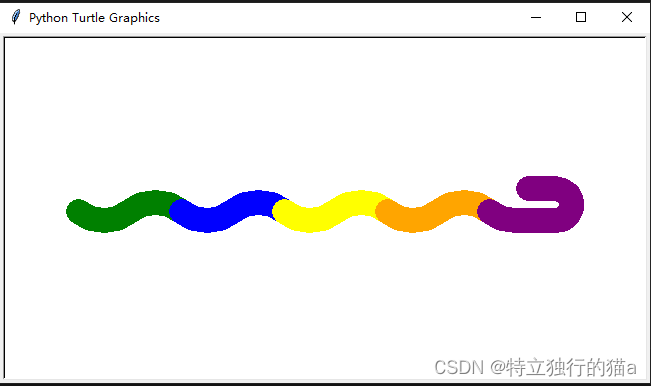
done()彩色大蟒蛇
import turtle
turtle.setup(650, 350,200,200)
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(-250)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.pensize(25)
colors=['green','blue','yellow','orange','pink','purple']
turtle.seth(-40)
for i in range(4):
turtle.color(colors[i])#选择索引从0~3的颜色
turtle.circle(40, 80)#上半弧度
turtle.circle(-40, 80)#下半弧度
turtle.color(colors[5])
turtle.circle(40, 80/2)
turtle.fd(40)
turtle.circle(16, 180)
turtle.fd(40 * 2/3)
turtle.done()
画小猪佩奇
# coding=utf-8
import turtle as t
t.pensize(4)
t.hideturtle()
t.colormode(255)
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.setup(840, 500)
t.speed(10)
# 鼻子
t.pu()
t.goto(-100, 100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-30)
t.begin_fill()
a = 0.4
for i in range(120):
if 0 <= i < 30 or 60 <= i < 90:
a = a + 0.08
t.lt(3) # 向左转3度
t.fd(a) # 向前走a的步长
else:
a = a - 0.08
t.lt(3)
t.fd(a)
t.end_fill()
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(25)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(10)
t.pd()
t.pencolor(255, 155, 192)
t.seth(10)
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(5)
t.color(160, 82, 45)
t.end_fill()
t.pu()
t.seth(0)
t.fd(20)
t.pd()
t.pencolor(255, 155, 192)
t.seth(10)
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(5)
t.color(160, 82, 45)
t.end_fill()
# 头
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(41)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(180)
t.circle(300, -30)
t.circle(100, -60)
t.circle(80, -100)
t.circle(150, -20)
t.circle(60, -95)
t.seth(161)
t.circle(-300, 15)
t.pu()
t.goto(-100, 100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-30)
a = 0.4
for i in range(60):
if 0 <= i < 30 or 60 <= i < 90:
a = a + 0.08
t.lt(3) # 向左转3度
t.fd(a) # 向前走a的步长
else:
a = a - 0.08
t.lt(3)
t.fd(a)
t.end_fill()
# 耳朵
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-7)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(70)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(100)
t.circle(-50, 50)
t.circle(-10, 120)
t.circle(-50, 54)
t.end_fill()
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(30)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(100)
t.circle(-50, 50)
t.circle(-10, 120)
t.circle(-50, 56)
t.end_fill()
# 眼睛
t.color((255, 155, 192), "white")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-95)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(15)
t.end_fill()
t.color("black")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-3)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(3)
t.end_fill()
t.color((255, 155, 192), "white")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-25)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(40)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(15)
t.end_fill()
t.color("black")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-3)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(3)
t.end_fill()
# 腮
t.color((255, 155, 192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-95)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(65)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(30)
t.end_fill()
# 嘴
t.color(239, 69, 19)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(15)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-80)
t.circle(30, 40)
t.circle(40, 80)
# 身体
t.color("red", (255, 99, 71))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-78)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(-130)
t.circle(100, 10)
t.circle(300, 30)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(230)
t.seth(90)
t.circle(300, 30)
t.circle(100, 3)
t.color((255, 155, 192), (255, 100, 100))
t.seth(-135)
t.circle(-80, 63)
t.circle(-150, 24)
t.end_fill()
# 手
t.color((255, 155, 192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-40)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-27)
t.pd()
t.seth(-160)
t.circle(300, 15)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(15)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.seth(-10)
t.circle(-20, 90)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(30)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(237)
t.pd()
t.seth(-20)
t.circle(-300, 15)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.seth(-170)
t.circle(20, 90)
# 脚
t.pensize(10)
t.color((240, 128, 128))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-75)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-180)
t.pd()
t.seth(-90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(-180)
t.color("black")
t.pensize(15)
t.fd(20)
t.pensize(10)
t.color((240, 128, 128))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(90)
t.pd()
t.seth(-90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(-180)
t.color("black")
t.pensize(15)
t.fd(20)
# 尾巴
t.pensize(4)
t.color((255, 155, 192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(70)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(95)
t.pd()
t.seth(0)
t.circle(70, 20)
t.circle(10, 330)
t.circle(70, 30)
t.done()画钟表
# -*- coding:utf-8 –*-
# 用turtlr画时钟
# 以自定义shape的方式实现
import turtle as t
import datetime as d
def skip(step): # 抬笔,跳到一个地方
t.penup()
t.forward(step)
t.pendown()
def drawClock(radius): # 画表盘
t.speed(0)
t.mode("logo") # 以Logo坐标、角度方式
t.hideturtle()
t.pensize(7)
t.home() # 回到圆点
for j in range(60):
skip(radius)
if (j % 5 == 0):
t.forward(20)
skip(-radius - 20)
else:
t.dot(5)
skip(-radius)
t.right(6)
def makePoint(pointName, len): # 钟的指针,时针、分针、秒针
t.penup()
t.home()
t.begin_poly()
t.back(0.1 * len)
t.forward(len * 1.1)
t.end_poly()
poly = t.get_poly()
t.register_shape(pointName, poly) # 注册为一个shape
def drawPoint(): # 画指针
global hourPoint, minPoint, secPoint, fontWriter
makePoint("hourPoint", 100)
makePoint("minPoint", 120)
makePoint("secPoint", 140)
hourPoint = t.Pen() # 每个指针是一只新turtle
hourPoint.shape("hourPoint")
hourPoint.shapesize(1, 1, 6)
minPoint = t.Pen()
minPoint.shape("minPoint")
minPoint.shapesize(1, 1, 4)
secPoint = t.Pen()
secPoint.shape("secPoint")
secPoint.pencolor('red')
fontWriter = t.Pen()
fontWriter.pencolor('gray')
fontWriter.hideturtle()
def getWeekName(weekday):
weekName = ['星期一', '星期二', '星期三', '星期四', '星期五', '星期六', '星期日']
return weekName[weekday]
def getDate(year, month, day):
return "%s-%s-%s" % (year, month, day)
def realTime():
curr = d.datetime.now()
curr_year = curr.year
curr_month = curr.month
curr_day = curr.day
curr_hour = curr.hour
curr_minute = curr.minute
curr_second = curr.second
curr_weekday = curr.weekday()
t.tracer(False)
secPoint.setheading(360 / 60 * curr_second)
minPoint.setheading(360 / 60 * curr_minute)
hourPoint.setheading(360 / 12 * curr_hour + 30 / 60 * curr_minute)
fontWriter.clear()
fontWriter.home()
fontWriter.penup()
fontWriter.forward(80)
# 用turtle写文字
fontWriter.write(getWeekName(curr_weekday), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
fontWriter.forward(-160)
fontWriter.write(getDate(curr_year, curr_month, curr_day), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
t.tracer(True)
print(curr_second)
t.ontimer(realTime, 100) # 每隔100毫秒调用一次realTime()
def main():
t.tracer(False)
drawClock(160)
drawPoint()
realTime()
t.tracer(True)
t.mainloop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()画狮子头
import turtle as t
def hair(): # 画头发
t.penup()
t.goto(-50, 150)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('#a2774d')
t.begin_fill()
for j in range(10): # 重复执行10次
t.setheading(60 - (j * 36)) # 每次调整初始角度
t.circle(-50, 120) # 画120度的弧
t.end_fill()
def face(): # 画脸
t.penup()
t.goto(0, 100)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('#f2ae20')
t.begin_fill()
t.setheading(180)
t.circle(85)
t.end_fill()
# 下巴
t.circle(85, 120)
t.fillcolor('white')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(85, 120)
t.setheading(135)
t.circle(100, 95)
t.end_fill()
def ears(dir): # 画眼睛,dir用来设置方向,左右眼对称
t.penup()
t.goto((0 - dir) * 30, 90)
t.setheading(90)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('#f2ae20')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(dir * 30)
t.end_fill()
t.penup()
t.goto((0 - dir) * 40, 85)
t.setheading(90)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('white')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(dir * 17)
t.end_fill()
def nose(): # 画鼻子
t.penup()
t.goto(20, 0)
t.setheading(90)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('#a2774d')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(20)
t.end_fill()
def eye(dir): # 画耳朵,dir用来设置方向,左右耳对称
t.penup()
t.goto((0 - dir) * 30, 20)
t.setheading(0)
t.pendown()
t.fillcolor('black')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(10)
t.end_fill()
def mouth(): # 画嘴巴
t.penup()
t.goto(0, 0)
t.setheading(-90)
t.pendown()
t.forward(50)
t.setheading(0)
t.circle(80, 30)
t.penup()
t.goto(0, -50)
t.setheading(180)
t.pendown()
t.circle(-80, 30)
hair()
ears(1)
ears(-1)
face()
eye(1)
eye(-1)
mouth()
nose()
t.done()画朵小红花
import turtle as t
t.speed(0)
#花柄
t.penup()
t.goto(0,-150)
t.pendown()
t.pensize(2)
t.setheading(90)
t.color('brown')
t.fd(300)
#花瓣
t.pensize(1)
t.color('black','red')
t.begin_fill()
for i in range(10):
t.left(45)
t.circle(80,60)
t.left(120)
t.circle(80,60)
t.end_fill()
#叶子
for i in range(2):
t.penup()
t.goto(0,10-50*i)
x=20+80*i
t.setheading(x)
t.pendown()
t.color('brown','green')
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(60,60)
t.left(120)
t.circle(60,60)
t.end_fill()
t.hideturtle()浪漫樱花
from turtle import *
from random import *
from math import *
def tree(n, l):
pd () # 下笔
# 阴影效果
t = cos ( radians ( heading () + 45 ) ) / 8 + 0.25
pencolor ( t, t, t )
pensize ( n / 3 )
forward ( l ) # 画树枝
if n > 0:
b = random () * 15 + 10 # 右分支偏转角度
c = random () * 15 + 10 # 左分支偏转角度
d = l * (random () * 0.25 + 0.7) # 下一个分支的长度
# 右转一定角度,画右分支
right ( b )
tree ( n - 1, d )
# 左转一定角度,画左分支
left ( b + c )
tree ( n - 1, d )
# 转回来
right ( c )
else:
# 画叶子
right ( 90 )
n = cos ( radians ( heading () - 45 ) ) / 4 + 0.5
ran = random ()
# 这里相比于原来随机添加了填充的圆圈,让樱花叶子看起来更多一点
if (ran > 0.7):
begin_fill ()
circle ( 3 )
fillcolor ( 'pink' )
# 把原来随机生成的叶子换成了统一的粉色
pencolor ( "pink" )
circle ( 3 )
if (ran > 0.7):
end_fill ()
left ( 90 )
# 添加0.3倍的飘落叶子
if (random () > 0.7):
pu ()
# 飘落
t = heading ()
an = -40 + random () * 40
setheading ( an )
dis = int ( 800 * random () * 0.5 + 400 * random () * 0.3 + 200 * random () * 0.2 )
forward ( dis )
setheading ( t )
# 画叶子
pd ()
right ( 90 )
n = cos ( radians ( heading () - 45 ) ) / 4 + 0.5
pencolor ( n * 0.5 + 0.5, 0.4 + n * 0.4, 0.4 + n * 0.4 )
circle ( 2 )
left ( 90 )
pu ()
# 返回
t = heading ()
setheading ( an )
backward ( dis )
setheading ( t )
pu ()
backward ( l ) # 退回
bgcolor ( 0.956, 0.9255, 0.9882 ) # 设置背景色(把灰色换成淡紫色)
ht () # 隐藏turtle
speed ( 0 ) # 速度 1-10渐进,0 最快
tracer ( 0, 0 )
pu () # 抬笔
backward ( 50 )
left ( 90 ) # 左转90度
pu () # 抬笔
backward ( 300 ) # 后退300
tree ( 12, 100 ) # 递归7层
done ()引用出处
海龟绘图 - 廖雪峰的官方网站
python---turtle库(详解)_python turtle_超越ct的博客-CSDN博客
python: turtle绘制有趣的小图像合集_turtle画图作品-CSDN博客
Python Turtle 画图:黑洞里的繁星(附源代码)_turtle绘图代码-CSDN博客
Python海龟turtle基础知识大全与画图集合_python海龟编程代码大全-CSDN博客
Python — — turtle 常用代码_python海龟编程代码大全-CSDN博客
Python海龟画图集合_香自寒来-华为云开发者联盟