LIO-SAM学习总结
# LIO-SAM学习总结目录
提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加
提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、参考资料
-
- **项目网址:
- 1、论文
- 2、知识点
-
- (1)数学基础
- 预积分
- 因子图
-
- (2)ROS基础
- (3)PCL
- (4)GTSAM
-
- 1. 设置传感器噪声模型
- 2. 添加因子
- 3. 设置初始值
- 4. 选择优化器
- (5)C++基础
- 3、标定
- 4、代码
- 二、论文和框架
- 三、传感器标定
-
- 1、IMU内参标定
- 2、IMU和激光雷达外参标定
- 四、代码介绍
-
- 代码整体框架
- 0、params.yaml
- 1、utility.h
- 2、imageProjection.cpp
-
- 各函数功能介绍
- 具体注释:
- 3、featureExtraction.cpp
-
- 各函数功能介绍
- 具体注释:
- 4、imuPreintergration.cpp
-
- TransformFusion类
- IMUPreintegration类
- 5、mapOptimization.cpp
- **具体注释:**
- 四、下载安装LIO-SAM
-
- 1、下载
- 2、编译
- 五、数据集测试、实车测试
-
- 1、跑数据集
- 2、实车测试
-
- 驱动安装
-
- 1、EAI的Dashgo D1
- 2、激光雷达驱动
- 3、IMU驱动安装
- 运行LIO-SAM
- 总结
前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
最近在学习LIO-SAM这个紧耦合的激光惯导框架,由于涉及到的内容较多,参考的资料较多,索性就写一个博客记录一下学到的知识和参考的资料,以便以后回顾和交流。内容较多,可通过目录快速跳转至各部分。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、参考资料
提示:本人刚入门slam不久,学习该框架参考了网上许多大佬的资料和博客,因此在这里也进行一个汇总,方便以后需要学习的同学查阅和学习。
**项目网址:
https://github.com/TixiaoShan/LIO-SAM**
1、论文
论文:T. Shan, B. Englot, D. Meyers, W. Wang, C. Ratti, D. Rus. LIO-SAM: Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2020.
【论文阅读38】LIO-SAM
论文学习可以直接参考上面链接中翻译后的中文版,对比LOAM对应的论文,该篇论文中别没有特别多的学习内容,主要是在Lego-LOAM的基础上加入了IMU预积分和采用因子图优化融合了激光、IMU、GPS、回环因子等。
2、知识点
(1)数学基础
预积分
预积分是LIO和VIO的核心部分。下面介绍一下SLAM中预积分的作用和推导思路。
1、为什么要使用预积分?
IMU测量的角速度和加速度进行积分可得到旋转角度和位移。如果对每个IMU数据进行积分,计算量将非常大,通常的做法是对两个激光帧(或图像帧)之间的IMU数据进行积分,从而构建相邻两帧之间的相对位姿约束。这就出现一个问题,两个激光帧之间的IMU积分需要给定第一个帧的状态估计量作为积分的初始条件。而每次迭代优化,这些状态估计量都会更新,这就需要不断重复地进行所有帧之间的IMU积分。IMU预积分就是为了解决这个问题提出的,避免了重复积分,减少了计算量。
2、IMU推导思路
首先推导得到IMU角速度和加速度的模型。由于加速度积分得到速度,速度积分得到位置。根据IMU模型推导得到R(旋转)、v(速度)、p(位置)与与角速度、加速度、IMU偏置bias、高斯白噪声之间的公式。
对第i时刻到j时刻直接的IMU数据进行积分,直接积分虽然简单,但是有一个致命的缺点:如果第i时刻的状态量经过优化更新了,则从第i+1时刻到j-1时刻的状态也要跟着更新,这时需要重新计算积分,需要耗费巨大的计算量和时间。于是使用一段时间的相对量来代替某个时刻的绝对量。因此,引入旋转、速度、位置的相对状态量,称为预积分。
后续推导过程主要分为以下几步:
一、假设零偏已知,然后将噪声项分离出来。
二、推导出预积分中的噪声递推模型。
三、当更新零偏后,推导预积分的更新的更新方式,避免重复积分。
四、求预积分中残差对状态增量的雅可比矩阵。
因子图
因子图是一种用于处理大量变量和约束关系的图形模型,被广泛应用于机器人等领域的状态估计和感知问题。在SLAM中,因子图被用来描述机器人在未知环境中的位置和地图信息。SLAM问题中,机器人需要同时进行定位和建图,因此需要在不确定性和噪声的条件下处理大量的测量和状态变量。因此,SLAM问题可以描述为一个大规模的非线性最小化问题,其中目标是最小化所有测量和状态变量的误差,从而获得最准确的地图和机器人位置。因子图可以很好地解决SLAM问题中的大规模非线性优化问题。当测量数据增加时,因子图提供了一种自适应建图的方法,能够快速完成数据的处理。此外,因子图还可以帮助机器人对测量数据的不确定性进行建模和处理,使机器人能够更准确地估计自身位置和地图信息。

因子图详细学习可参考以下链接:
1、因子图的理论基础与在机器人中的应用
2、【泡泡机器人公开课】第五十六课:gtsam_tutorial-董靖
(2)ROS基础
1、ROS中的多线程使用方法
代码中使用到的ROS多线程,可参考上述链接。
2、ROS中nav_msgs消息
(3)PCL
PCL库学习笔记——入门、基本的数据结构
代码出现is_dense这个数据不太理解。查看源码:
/** \brief True if no points are invalid (e.g., have NaN or Inf values in any of their floating point fields). */
bool is_dense = true;
上述注释代表意思:指定点云中的所有数据是有效的则为true,否则为false(True if no points are invalid (e.g., have NaN or Inf values).)
即: 点云数据中所有点均有值为true,有inf/NaN为false。通过该值可去除无效点云数据
(4)GTSAM
GTSAM是一个用于解决大规模非线性优化问题的开源C++库。它提供了处理因子图的方法,能够用于多种机器人感知和估计问题。
GTSAM官方文档链接:链接
下面介绍一下使用GTSAM构建因子图优化的大致步骤:
- 设置传感器噪声模型
- 添加因子factor
- 设置初始值
- 选择优化器进行优化
下面介绍代码中使用到GTSAM的一些函数:
1. 设置传感器噪声模型
gtsam::PreintegrationParams
boost::shared_ptr<gtsam::PreintegrationParams> p = gtsam::PreintegrationParams::MakeSharedU(imuGravity);
imuGravity为重力加速度,在参数服务器中设置的参数,用于计算相对于重力的线加速度。
其中MakeSharedU就是设置重力方向的,其中的设置和IMU的坐标轴建模方向有关
- MakeSharedU 是ENU,就是东北天,内部把imuGravity的值进行了取负。
- MakeSharedD 是NED,就是北东地,内部不改变变量的正负号。
gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3, 3)
p->accelerometerCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3, 3) * pow(imuAccNoise, 2); // acc white noise in continuous
p->gyroscopeCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3, 3) * pow(imuGyrNoise, 2); // gyro white noise in continuous
p->integrationCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3, 3) * pow(1e-4, 2); // error committed in integrating position from velocities
该函数是设置一个33单位阵。
由于需要设置传感器噪声模型,因此需要添加IMU噪声模型,角速度噪声和加速度噪声。这里的协方差矩阵使用33的单位矩阵乘以高斯白噪声imuAccNoise和imuGyrNoise的平方。
gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias
gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias prior_imu_bias((gtsam::Vector(6) << 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0).finished());
gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias()是gtsam做好的一个imu零偏,其中都是0。
gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas
gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal是gtsam中的一个噪声模型类,表示噪声协方差矩阵是一个对角矩阵的噪声模型。gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas()函数是该类中的一个方法,用来获取噪声模型中对角线元素的标准差。
在这里插入代码片
2. 添加因子
3. 设置初始值
4. 选择优化器
(5)C++基础
std::move:
详解C++移动语义std::move()
参考以上博客,简单点理解,就是将对象的状态或者所有权从一个对象转移到另一个对象,只是转移,没有内存的搬迁或者内存拷贝。
std::lock_guard:
C++11中std::lock_guard的使用
简单理解,std::lock_guard的作用就是更加方便对mutex的上锁和解锁
map
map<int, pair<pcl::PointCloud<PointType>, pcl::PointCloud<PointType>>> laserCloudMapContainer;
这段代码定义了一个名为laserCloudMapContainer的变量,它是一个
map类型的容器。
map是C++标准库中的关联容器,它提供了一种以键值对形式存储和访问元素的方式。在这里,map的键类型是int,值类型是pair。
pair是C++标准库中的一个模板类,它可以存储两个不同类型的对象。在这个代码中,pair存储了两个pcl::PointCloud类型的对象,用于表示某个整数键对应的两个点云数据。
通过使用laserCloudMapContainer[key]的形式,可以访问和操作map中特定键所对应的值。在这里,key是一个整数,可以作为索引来获取对应的点云数据对。
例如,可以通过laserCloudMapContainer[key].first和laserCloudMapContainer[key].second来分别访问两个点云数据对象。
通过使用map容器,可以方便地将整数键与两个点云数据对象进行关联和管理。
3、标定
标定是重中之中,在本系统中,主要涉及到IMU自身的内参标定和LIDAR与IMU直接的联合外参标定,在实车运行时,标定结果的好坏直接决定了最后地图会不会跑飞。
在LIO-SAM代码中的doc文件夹下有一个params.yaml文件,在该文件中可以修改IMU的bias和噪声等数据,以及IMU和LIDAR之间的旋转矩阵。
下面代码就是之前标定好的数据。
# IMU Settings IMU内参 bias和白噪声
imuAccNoise: 3.9939570888238808e-03
imuGyrNoise: 1.5636343949698187e-03
imuAccBiasN: 6.4356659353532566e-05
imuGyrBiasN: 3.5640318696367613e-05
imuGravity: 9.80511
imuRPYWeight: 0.01
# Extrinsics: T_lb (lidar -> imu) 这里应该是 imu->lidar
# lidar和imu外参标定数据 即转移矩阵
extrinsicTrans: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
extrinsicRot: [-1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0,
0, 0, -1]
extrinsicRPY: [0, -1, 0,
1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1]
根据上述标定结果进行室内实车测试,发现建图结果是一团点云,并且小车移动的同时地图跟着旋转。如下图所示:
参考以下博客:Lio_sam运行测试环节遇到的问题以及实测总结
发现本人实验所使用的小车结构和传感器安装位置和上述博客中博主的情况很类似,如下图所示:
且本人实验室的小车的地盘由于是两轮差速运动,前后两个扭角轮距地面有缝隙,因此小车在运行过程中前后老是晃动,特别是在转弯和中途停下的过程中,小车晃动特别厉害,加之雷达安装得很高,经过较长的铝型材,尾端雷达的晃动又被放大,雷达数据和IMU数据时间同步也是一个问题。因此,使用上述标定结果室内实车测试如下图:
基于上面糟糕的建图效果,下面准备采取以下几种方法来进行改进:
- 降低雷达安装高度
- 更换更合适的两个从动轮,解决小车晃动问题。
- 重新在室外低速情况下进行标定。
- 标定完成后在室外大范围场景下进行测试。
最终建图效果如下图所示:
4、代码
1、LIO-SAM代码阅读
该博客大概讲解了代码中每个函数的大概功能。
2、LIO-SAM超级详细源码流程图
该博客主要详细总结了代码流程图,学习代码时可对照着学习。
3、LIO-SAM流程及代码详解(最全)
该博客详细介绍了所有代码的注释,适合了解完算法原理和代码框架后,比对查阅学习。此外,该博主SLAM学习笔记的其他博客也是很好的学习资料。
二、论文和框架
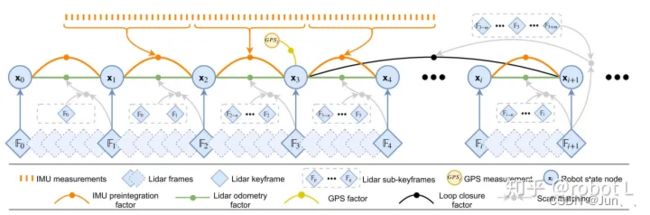
上图展示了LIO-SAM的因子图。图中主要包含四种因子。第一种是IMU预积分因子(橙色),由两个相邻关键帧之间的IMU测量积分得到。第二种是激光里程计因子(绿色),由每个关键帧和之前n个关键帧之间的帧图匹配结果得到。第三种是GPS因子(黄色),由每个关键帧的GPS测量得到。第四种是回环因子(黑色),由每个关键帧和候选回环关键帧的时序相邻的2m+1个关键帧之间的帧图匹配得到。此外,因子图优化通过iSAM2完成。
三、传感器标定
1、IMU内参标定
首先需要拿到imu的内参,使用港科大的imu_utils标定工具,使用Allan方差来标定高斯白噪声和随机游走噪声。
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53073284/article/details/123341141?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
2、IMU和激光雷达外参标定
联合标定lidar和imu的外参,使用瑞士苏黎世联邦理工大学自动驾驶实验室开发的lidar_align工具标定雷达和imu外参过程。
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53073284/article/details/123337885?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
四、代码介绍
学习具体代码前,最好保证理解了文章的大致思想,对代码框架在脑子中有一个大体的结构,区别于Cartographer代码的工程风格(代码较难学习和理解),LOAM系列代码偏向学院风,更容易大家理解,主要部分都在src文件夹下的几个.cpp中。
代码整体框架

代码主要上述图片中的各个文件组成。其中:
config文件夹:主要存放params.yaml文件,用于调参(即设置代码中一些关键参数)
include文件夹:存放utility.h头文件,主要包括一个读取参数和初始化参数的类ParamServer
launch文件夹:存放launch文件,其中最重要的是run.launch文件,用于启动该框架
msg文件夹:存放作者自定义的cloud_info.msg文件(作者自定义的消息格式)
src文件夹:代码的核心,存放4个核心cpp文件
srv文件夹:存放ROS的srv文件
CMakeList.txt:cmake文件
下面来具体介绍每个文件的代码和实现的功能:
0、params.yaml
待补充…
1、utility.h
待补充…
2、imageProjection.cpp
本程序文件主要工作分为两大块,一个是类似于Lego-loam里的将点云投射到距离图像,另一个是去除运动畸变。
(1)输入(订阅):
- imu原始数据 (imuTopic)
- 来自IMUPreintegration,imu预积分数据(odomTopic+“_incremental”)
- 激光点云原始数据(pointCloudTopic)
(2)输出(发布):
- 完成去畸变的点云数据(“lio_sam/deskew/cloud_deskewed”)
- cloudinfo数据(“lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info”)
(3)具体函数:
-
主函数
主函数肯定是最重要的,看代码一般也从主函数开始看起。不过这个.cpp文件的主函数较简单,主要是初始化ros节点和实例化一个ImageProjection对象,具体的功能程序在ImageProjection类中进行封装。 -
ImageProjection类
ImageProjection是该模块的核心。 主要是封装了程序执行过程中的一系列变量和函数,这里不展开具体介绍了,详细代码注释会放在该部分最后,请自行查看。
下面开始介绍ImageProjection类中的每个函数:
各函数功能介绍
1. ImageProjection()构造函数
ImageProjection()构造函数主要用于初始化。初始化ROS订阅的话题和发布的话题。其中allocateMemory()函数用于给一些变量分配内存。resetParameters函数用于重置部分参数数据。这两个函数就不做具体介绍了,主要涉及智能指针。
2. imuHandler回调函数
imuHandler回调函数主要功能是接收订阅的IMU数据,并利用标定好的外参数据(IMU到Lidar的旋转矩阵)将IMU数据从IMU坐标系转化到Lidar坐标系。然后将数据存储到imuQueue队列中。 注意:deskewFlag(0)应该是初始化deskewFlag这个变量为0的意思。
3. cloudHandler回调函数
cloudHandler这个函数应该是类中最重要的函数。
cachePointCloud(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
该函数主要用于根据激光雷达类型,转化数据格式,判断数据是否有效,去除无效点云数据,缓存点云数据
deskewInfo()
该函数作用是确保当前获取的IMU数据在时间上处在激光雷达数据起始点云和结束点云之间。并且将初始时刻的IMU姿态角和IMU里程计设为当前激光帧的初始姿态角和初始位姿。主要是为了后续去运动畸变,获取IMU数据转化得到的去运动畸变的参数。该函数中主要包含以下两个函数:
——imuDeskewInfo
a、选取出IMU数据定义为有效当前激光数据帧对应的IMU数据(当前帧IMU数据中时间大于最早激光点云数据时间-0.01s的IMU数据)
b、遍历筛选出来的有效数据,获取这些IMU数据转化得到的姿态角数据 Roll Pitch Yaw
c、对这些IMU数据进行积分,获得积分后的数据imuRotX imuRotY imuRotZ
——odomDeskewInfo
a、选取出时间上大于当前激光帧起始时间的最早的里程计数据作为startOdom,并获取该startOdom的姿态角
b、用当前激光帧起始时刻的imu里程计,初始化lidar位姿,后面用于mapOptmization
c、
if (int(round(startOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])) != int(round(endOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])))
这句代码意思是// 如果起止两个时刻对应imu里程计的方差不等,返回
为啥呢???
d、通过imu里程计的位姿xyzrpy得到imu里程计初始坐标系转换到大地坐标系的旋转矩阵transBegin。
通过imu里程计的位姿xyzrpy得到imu里程计终止坐标系转换到大地坐标系的旋转矩阵transEnd
通过这两个矩阵transBegin.inverse() * transEnd; 得到起始时刻里程计的相对变换矩阵transBt
由transBt 提取XYZ以及欧拉角 用于后续去运动畸变
projectPointCloud()
该函数主要的作用是遍历激光点云数据,并使用IMU数据去激光点云数据的运动畸变。该函数中还有一个deskewPoint函数,主要用于根据IMU数据去激光雷达数据的运动畸变。
——deskewPoint
cloudExtraction()
该函数的作用主要是保存有效激光点云数据,并且由于特征提取的时候不考虑每一行的前5个和最后5个,因此设置startRingIndex和endRingIndex这两个索引从第五个和倒数第五个。
publishClouds()
发布用户自定义的cloudInfo激光数据(经过数据预处理的激光点云数据)
resetParameters()
该函数用于重置部分存储数据的变量,方便下一次处理数据
4. odometryHandler回调函数
里程计回调函数 存储数据到队列中
具体注释:
#include "utility.h"
#include "lio_sam/cloud_info.h"
struct VelodynePointXYZIRT
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D
PCL_ADD_INTENSITY;
uint16_t ring;
float time;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
} EIGEN_ALIGN16;
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT (VelodynePointXYZIRT,
(float, x, x) (float, y, y) (float, z, z) (float, intensity, intensity)
(uint16_t, ring, ring) (float, time, time)
)
struct OusterPointXYZIRT {
PCL_ADD_POINT4D;
float intensity;
uint32_t t;
uint16_t reflectivity;
uint8_t ring;
uint16_t noise;
uint32_t range;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
} EIGEN_ALIGN16;
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT(OusterPointXYZIRT,
(float, x, x) (float, y, y) (float, z, z) (float, intensity, intensity)
(uint32_t, t, t) (uint16_t, reflectivity, reflectivity)
(uint8_t, ring, ring) (uint16_t, noise, noise) (uint32_t, range, range)
)
// Use the Velodyne point format as a common representation
using PointXYZIRT = VelodynePointXYZIRT;
const int queueLength = 2000;
class ImageProjection : public ParamServer //继承ParamServer
{
private:
std::mutex imuLock; // 多线程编程上锁和解锁
std::mutex odoLock;
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloud; // 激光数据订阅和发布对象
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloud;
ros::Publisher pubExtractedCloud;
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudInfo;
ros::Subscriber subImu;
std::deque<sensor_msgs::Imu> imuQueue;
ros::Subscriber subOdom;
std::deque<nav_msgs::Odometry> odomQueue;
std::deque<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> cloudQueue;
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 currentCloudMsg;
double *imuTime = new double[queueLength];
double *imuRotX = new double[queueLength];
double *imuRotY = new double[queueLength];
double *imuRotZ = new double[queueLength];
int imuPointerCur;
bool firstPointFlag;
Eigen::Affine3f transStartInverse;
pcl::PointCloud<PointXYZIRT>::Ptr laserCloudIn;
pcl::PointCloud<OusterPointXYZIRT>::Ptr tmpOusterCloudIn;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr fullCloud;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr extractedCloud;
int deskewFlag;
cv::Mat rangeMat;
bool odomDeskewFlag;
float odomIncreX;
float odomIncreY;
float odomIncreZ;
lio_sam::cloud_info cloudInfo;
double timeScanCur;
double timeScanEnd;
std_msgs::Header cloudHeader;
vector<int> columnIdnCountVec;
public:
ImageProjection():
deskewFlag(0)
{
//订阅话题进入回调函数 imu数据 激光点云.
// imuTopic:topic name;
// 2000:queue size;
// &ImageProjection::imuHandler:callback function 回调函数
// this: 调用这个class里的返回函数,可以使用第四个参数,例如有个对象叫listener,
// 调用该对象内部的回调函数,则传入&listener,这里调用自己的,则传入this指针
// ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay() :被用于指定hints,确定传输层的作用话题的方式:无延迟的TCP传输方式
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu>(imuTopic, 2000, &ImageProjection::imuHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 订阅/odometry_incremental 来自IMUPreintegration,imu预积分 进入回调函数处理数据
subOdom = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>(odomTopic+"_incremental", 2000, &ImageProjection::odometryHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 订阅激光雷达数据 并进入回调函数
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pointCloudTopic, 5, &ImageProjection::cloudHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 发布去畸变的点云
pubExtractedCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("lio_sam/deskew/cloud_deskewed", 1);
// 发布激光点云数据
pubLaserCloudInfo = nh.advertise<lio_sam::cloud_info> ("lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info", 1);
// 分配内存
allocateMemory();
// 重置部分参数数据
resetParameters();
//setVerbosityLevel用于设置控制台输出的信息。 L_DEBUG会输出DEBUG信息;
pcl::console::setVerbosityLevel(pcl::console::L_ERROR);
}
/* 给变量分配内存 */
void allocateMemory()
{
//根据params.yaml中给出的N_SCAN Horizon_SCAN参数值分配内存
//用智能指针的reset方法在构造函数里面进行初始化
laserCloudIn.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointXYZIRT>());
tmpOusterCloudIn.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<OusterPointXYZIRT>());
fullCloud.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
extractedCloud.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
fullCloud->points.resize(N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN);
cloudInfo.startRingIndex.assign(N_SCAN, 0);
cloudInfo.endRingIndex.assign(N_SCAN, 0);
cloudInfo.pointColInd.assign(N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN, 0);
cloudInfo.pointRange.assign(N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN, 0);
resetParameters();//重置部分参数数据
}
/* 重置部分参数数据 */
void resetParameters()
{
laserCloudIn->clear();
extractedCloud->clear();
// reset range matrix for range image projection
rangeMat = cv::Mat(N_SCAN, Horizon_SCAN, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(FLT_MAX));
imuPointerCur = 0;
firstPointFlag = true;
odomDeskewFlag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < queueLength; ++i)
{
imuTime[i] = 0;
imuRotX[i] = 0;
imuRotY[i] = 0;
imuRotZ[i] = 0;
}
columnIdnCountVec.assign(N_SCAN, 0);
}
~ImageProjection(){}
/* IMU回调函数 先通过标定的外参旋转矩阵R将IMU数据从IMU坐标系转到Lidar坐标系 然后存储IMU数据到队列 */
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuMsg)
{
// IMU数据转到Lidar坐标系下
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImu = imuConverter(*imuMsg);
// 存储IMU数据到队列imuQueue
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
imuQueue.push_back(thisImu);
// debug IMU data
// cout << std::setprecision(6);
// cout << "IMU acc: " << endl;
// cout << "x: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.x <<
// ", y: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.y <<
// ", z: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.z << endl;
// cout << "IMU gyro: " << endl;
// cout << "x: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.x <<
// ", y: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.y <<
// ", z: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.z << endl;
// double imuRoll, imuPitch, imuYaw;
// tf::Quaternion orientation;
// tf::quaternionMsgToTF(thisImu.orientation, orientation);
// tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(imuRoll, imuPitch, imuYaw);
// cout << "IMU roll pitch yaw: " << endl;
// cout << "roll: " << imuRoll << ", pitch: " << imuPitch << ", yaw: " << imuYaw << endl << endl;
}
/* 里程计回调函数 存储数据到队列中 */
void odometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odometryMsg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
odomQueue.push_back(*odometryMsg);
}
/* 接收激光雷达点云数据回调函数 */
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
// 根据激光雷达类型,转化数据格式,去除无效点云数据,缓存点云数据
if (!cachePointCloud(laserCloudMsg))
return;
// 将两帧lidar数据之间的IMU数据用于获取对应的IMU姿态角 并且将IMU里程计作为当前两帧之间的初始位姿
if (!deskewInfo())
return;
// 遍历激光点云数据,并使用IMU数据去激光点云数据的运动畸变 存储点云的深度
projectPointCloud();
// 该函数的作用主要是保存有效激光点云数据,
// 并且由于特征提取的时候不考虑每一行的前5个和最后5个,因此设置startRingIndex和endRingIndex这两个索引从第五个和倒数第五个
cloudExtraction();
// 发布用户自定义的cloudInfo激光数据(经过数据预处理的)
publishClouds();
/* 重置部分参数数据 */
resetParameters();
}
/* 根据激光雷达类型,转化数据格式,去除无效点云数据,缓存点云数据 */
bool cachePointCloud(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
// cache point cloud
cloudQueue.push_back(*laserCloudMsg);// 添加当前激光数据帧到队列
if (cloudQueue.size() <= 2)
return false;
// convert cloud
currentCloudMsg = std::move(cloudQueue.front());// 从队列中获取激光点云数据
cloudQueue.pop_front(); // 获取点云数据后,将队列最前面的数据剔除
if (sensor == SensorType::VELODYNE || sensor == SensorType::LIVOX)// 判断激光雷达类型(VELODYNE、LIVOX)
{
// 如果是VELODYNE、LIVOX类型的激光雷达 将点云数据从ROS数据转化为PCL数据格式
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *laserCloudIn);//
}
else if (sensor == SensorType::OUSTER)// 如果是 OUSTER激光雷达
{
// Convert to Velodyne format
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *tmpOusterCloudIn);// 转化数据格式
laserCloudIn->points.resize(tmpOusterCloudIn->size()); // 重置数据数量
laserCloudIn->is_dense = tmpOusterCloudIn->is_dense; // is_dense用于去除无效点云
// 遍历一帧有效激光数据中的所有点云 将OUSTER雷达点云数据存到laserCloudIn中
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmpOusterCloudIn->size(); i++)
{
auto &src = tmpOusterCloudIn->points[i];
auto &dst = laserCloudIn->points[i];
dst.x = src.x;
dst.y = src.y;
dst.z = src.z;
dst.intensity = src.intensity; // 激光雷达的反射强度
dst.ring = src.ring; // 通道
dst.time = src.t * 1e-9f; // 时间戳
}
}
else // 如果均不是枚举的激光雷达数据类型 则报错
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Unknown sensor type: " << int(sensor));
ros::shutdown();
}
// get timestamp 获取时间戳
cloudHeader = currentCloudMsg.header;
timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec(); // 当前激光点云的时间戳
//可以看出lasercloudin中存储的time是一帧中距离起始点的相对时间,timeScanEnd是该帧点云的结尾时间
timeScanEnd = timeScanCur + laserCloudIn->points.back().time;
// check dense flag 根据is_dense去除无效点云
if (laserCloudIn->is_dense == false)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud is not in dense format, please remove NaN points first!");
ros::shutdown();
}
// check ring channel
//由于static关键字,只检查一次,检查ring这个field是否存在. veloodyne和ouster都有;
//ring代表线数,0是最下面那条
static int ringFlag = 0;
if (ringFlag == 0)
{
ringFlag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)currentCloudMsg.fields.size(); ++i)
{
if (currentCloudMsg.fields[i].name == "ring")
{
ringFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (ringFlag == -1)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud ring channel not available, please configure your point cloud data!");
ros::shutdown();
}
}
// check point time
// 检查是否存在time通道
if (deskewFlag == 0)
{
deskewFlag = -1;
// 这里的fields代表每个点云数据的成员变量
for (auto &field : currentCloudMsg.fields)
{
if (field.name == "time" || field.name == "t")
{
deskewFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (deskewFlag == -1)
ROS_WARN("Point cloud timestamp not available, deskew function disabled, system will drift significantly!");
}
return true; // 上述步骤都通过,代表该帧点云数据有效
}
bool deskewInfo()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
// make sure IMU data available for the scan
// 确保IMU数据在时间上处于激光数据之间,否则直接退出
// 即IMU数据需要再两帧激光数据之间
if (imuQueue.empty() || imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur || imuQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Waiting for IMU data ...");
return false;
}
// 当前帧对应imu数据处理
// 1、遍历当前激光帧起止时刻之间的imu数据,初始时刻对应imu的姿态角RPY设为当前帧的初始姿态角
// 2、用角速度、时间积分,计算每一时刻相对于初始时刻的旋转量,初始时刻旋转设为0
// 注:imu数据都已经转换到lidar系下了
// imu去畸变参数计算
imuDeskewInfo();
// 当前帧对应imu里程计处理
// 1、遍历当前激光帧起止时刻之间的imu里程计数据,初始时刻对应imu里程计设为当前帧的初始位姿
// 2、用起始、终止时刻对应imu里程计,计算相对位姿变换,保存平移增量
// 注:imu数据都已经转换到lidar系下了
// 里程计去畸变参数计算
odomDeskewInfo();
return true;
}
void imuDeskewInfo()
{
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = false; // imuAvailable为IMU数据有效标志位
while (!imuQueue.empty()) // IMU数据队列不为空
{
// 判断IMU数据时间戳是否大于当前帧激光点云数据的时间戳timeScanCur
// 如果IMU数据时间小于激光雷达时间-0.01 删除该imu数据
if (imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
imuQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
// 如果IMU队列没有数据 直接退出
if (imuQueue.empty())
return;
imuPointerCur = 0;
// 遍历当前IMU队列 将有效IMU数据积分
for (int i = 0; i < (int)imuQueue.size(); ++i)
{
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImuMsg = imuQueue[i]; // 获取IMU数据
double currentImuTime = thisImuMsg.header.stamp.toSec();// 获取IMU数据时间戳
// get roll, pitch, and yaw estimation for this scan
// 从IMU数据中得到姿态角 Roll Pitch Yaw三个数据
if (currentImuTime <= timeScanCur) //
imuRPY2rosRPY(&thisImuMsg, &cloudInfo.imuRollInit, &cloudInfo.imuPitchInit, &cloudInfo.imuYawInit);
// 如果当前IMU数据时间戳 > 激光数据最后一帧的时间戳则剔除
if (currentImuTime > timeScanEnd + 0.01)
break;
// 如果是第一个IMU有效数据 初始化旋转角
if (imuPointerCur == 0){
imuRotX[0] = 0;
imuRotY[0] = 0;
imuRotZ[0] = 0;
imuTime[0] = currentImuTime;
++imuPointerCur;
continue;
}
// get angular velocity
// 获取IMU加速度数据
double angular_x, angular_y, angular_z;
imuAngular2rosAngular(&thisImuMsg, &angular_x, &angular_y, &angular_z);
// integrate rotation
// IMU数据积分
// 当前IMU数据与上一帧IMU数据之间的时间间隔 = 当前IMU时间戳 - 上一帧IMU时间戳
double timeDiff = currentImuTime - imuTime[imuPointerCur-1];
imuRotX[imuPointerCur] = imuRotX[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_x * timeDiff; // X(t) = X_(t-1) + x * △t
imuRotY[imuPointerCur] = imuRotY[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_y * timeDiff; // y z 同理
imuRotZ[imuPointerCur] = imuRotZ[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_z * timeDiff;
imuTime[imuPointerCur] = currentImuTime; // 存储当前IMU数据的时间戳 用于下一个IMU数据积分
++imuPointerCur; // IMU有效数据计数位+1
}
--imuPointerCur;// ?
// 没有合规的imu数据
if (imuPointerCur <= 0)
return;
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = true; // 处理完IMU数据 将标志位设置为true
}
void odomDeskewInfo()
{
// 同理 odomAvailable为odom数据有效标志位
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = false;
// 和IMU数据一样 只有lidar数据帧起止之间的odom数据才是有效的
while (!odomQueue.empty())
{
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
odomQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
// 无数据 退出
if (odomQueue.empty())
return;
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur)
return;
// get start odometry at the beinning of the scan
// 获取当前lidar数据起止间隔之中最早的IMU odom数据
nav_msgs::Odometry startOdomMsg;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
startOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&startOdomMsg) < timeScanCur)
continue;
else
break;
}
// 提取imu里程计姿态角
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
// Initial guess used in mapOptimization
// 用当前激光帧起始时刻的imu里程计,初始化lidar位姿,后面用于mapOptmization
cloudInfo.initialGuessX = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x;
cloudInfo.initialGuessY = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y;
cloudInfo.initialGuessZ = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z;
cloudInfo.initialGuessRoll = roll;
cloudInfo.initialGuessPitch = pitch;
cloudInfo.initialGuessYaw = yaw;
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = true;
// get end odometry at the end of the scan
odomDeskewFlag = false;
// 如果当前激光帧结束时刻之后没有imu里程计数据,返回
if (odomQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
return;
// 提取当前激光帧结束时刻的imu里程计
nav_msgs::Odometry endOdomMsg;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
endOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&endOdomMsg) < timeScanEnd)
continue;
else
break;
}
// 如果起止两个时刻对应imu里程计的方差不等,返回
// round函数:四舍五入
if (int(round(startOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])) != int(round(endOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])))
return;
// Eigen::Affine3f为仿射变换矩阵 即旋转+平移
//通过imu里程计的位姿xyzrpy得到imu里程计初始坐标系转换到大地坐标系的旋转矩阵transBegin
Eigen::Affine3f transBegin = pcl::getTransformation(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
//通过imu里程计的位姿xyzrpy得到imu里程计终止坐标系转换到大地坐标系的旋转矩阵transEnd
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Affine3f transEnd = pcl::getTransformation(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
// 起止时刻imu里程计的相对变换
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transBegin.inverse() * transEnd;
// 给定的转换中,提取XYZ以及欧拉角,通过tranBt 获得增量值 后续去畸变用到 ?????
float rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre;
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(transBt, odomIncreX, odomIncreY, odomIncreZ, rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre);
odomDeskewFlag = true;
}
/* 通过IMU数据差值计算当前激光点云时刻对应的旋转量 */
void findRotation(double pointTime, float *rotXCur, float *rotYCur, float *rotZCur)
{
*rotXCur = 0; *rotYCur = 0; *rotZCur = 0;
int imuPointerFront = 0;
// 寻找大于当前激光点云时间的最前面的IMU数据
while (imuPointerFront < imuPointerCur)
{
if (pointTime < imuTime[imuPointerFront])
break;
++imuPointerFront;
}
//如果计数为0或该次imu时间戳小于了当前时间戳(异常退出)
if (pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront] || imuPointerFront == 0)
{
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront];
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront];
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront];
} else {
// 前后时刻插值计算当前时刻的旋转增量
//此时front的时间是大于当前pointTime时间,back=front-1刚好小于当前pointTime时间,前后时刻插值计算
int imuPointerBack = imuPointerFront - 1;
//算一下该点时间戳在本组imu中的位置
double ratioFront = (pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack]) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
double ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - pointTime) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
double ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - pointTime) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
//这三项作为函数返回值,以形参指针的方式返回
//按前后百分比赋予旋转量
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
}
void findPosition(double relTime, float *posXCur, float *posYCur, float *posZCur)
{
*posXCur = 0; *posYCur = 0; *posZCur = 0;
// If the sensor moves relatively slow, like walking speed, positional deskew seems to have little benefits. Thus code below is commented.
// if (cloudInfo.odomAvailable == false || odomDeskewFlag == false)
// return;
// float ratio = relTime / (timeScanEnd - timeScanCur);
// *posXCur = ratio * odomIncreX;
// *posYCur = ratio * odomIncreY;
// *posZCur = ratio * odomIncreZ;
}
/* 去运动畸变函数
利用当前帧起止时刻之间的imu数据计算旋转增量,
imu里程计数据计算平移增量,进而将每一时刻激光点位置变换到第一个激光点坐标系下,进行运动补偿
*/
PointType deskewPoint(PointType *point, double relTime)
{
//这个来源于上文的时间戳通道和imu可用判断,没有或是不可用则返回点
if (deskewFlag == -1 || cloudInfo.imuAvailable == false)
return *point;
// relTime=points[i].time 即激光点云时间戳数据
// lasercloudin中存储的time是一帧中距离起始点的 相对时间
// 在cloudHandler的cachePointCloud函数中,timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec();,即当前帧点云的初始时刻
//二者相加即可得到当前点的准确时刻
double pointTime = timeScanCur + relTime;
//根据时间戳插值获取imu计算的旋转量与位置量(注意imu计算的相对于起始时刻的旋转增量)
float rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur;
findRotation(pointTime, &rotXCur, &rotYCur, &rotZCur);
// ????
float posXCur, posYCur, posZCur;
findPosition(relTime, &posXCur, &posYCur, &posZCur);
//这里的firstPointFlag来源于resetParameters函数,而resetParameters函数每次ros调用cloudHandler都会启动
if (firstPointFlag == true)
{
// 第一个点的位姿增量(0),求逆 ??? 为啥要这么搞
transStartInverse = (pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur)).inverse();
firstPointFlag = false;//改成false以后,同一帧激光数据的下一次就不执行了
}
// transform points to start
//扫描当前点时lidar的世界坐标系下变换矩阵
Eigen::Affine3f transFinal = pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur);
//扫描该点相对扫描本次scan第一个点的lidar变换矩阵=
//第一个点时lidar世界坐标系下变换矩阵的逆×当前点时lidar世界坐标系下变换矩阵
//Tij=Twi^-1 * Twj
//注:这里准确的来说,不是世界坐标系,
//根据代码来看,是把imu积分:
//从imuDeskewInfo函数中,在当前激光帧开始的前0.01秒的imu数据开始积分,
//把它作为原点,然后获取当前激光帧第一个点时刻的位姿增量transStartInverse,
//和当前点时刻的位姿增量transFinal,根据逆矩阵计算二者变换transBt。
//因此相对的不是“世界坐标系”,
//而是“当前激光帧开始前的0.01秒的雷达坐标系(在imucallback函数中已经把imu转换到了雷达坐标系了)
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transStartInverse * transFinal;
PointType newPoint;
//根据lidar位姿变换 Tij,修正点云位置: Tij * Pj ????
newPoint.x = transBt(0,0) * point->x + transBt(0,1) * point->y + transBt(0,2) * point->z + transBt(0,3);
newPoint.y = transBt(1,0) * point->x + transBt(1,1) * point->y + transBt(1,2) * point->z + transBt(1,3);
newPoint.z = transBt(2,0) * point->x + transBt(2,1) * point->y + transBt(2,2) * point->z + transBt(2,3);
newPoint.intensity = point->intensity;
return newPoint;
}
void projectPointCloud()
{
int cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();// 获取输入点云数量
// range image projection
// 遍历激光点云
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i)
{
// 获取激光点云数据
PointType thisPoint;
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
thisPoint.intensity = laserCloudIn->points[i].intensity;
// 计算点云的距离并根据该距离判断是否在激光点云最小范围和最大范围之间
float range = pointDistance(thisPoint);
if (range < lidarMinRange || range > lidarMaxRange)
continue;
// 获取激光点云的通道数 并判断该通道数是否小于激光雷达总线数N_SCAN
int rowIdn = laserCloudIn->points[i].ring;
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
if (rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0)
continue;
int columnIdn = -1;
if (sensor == SensorType::VELODYNE || sensor == SensorType::OUSTER)
{
//水平角分辨率
float horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
//Horizon_SCAN=1800,每格0.2度
static float ang_res_x = 360.0/float(Horizon_SCAN);
columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2;
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
}
else if (sensor == SensorType::LIVOX)
{
columnIdn = columnIdnCountVec[rowIdn];
columnIdnCountVec[rowIdn] += 1;
}
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
if (rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) != FLT_MAX)
continue;
//去畸变 运动补偿 这里需要用到雷达信息中的time 这个field
thisPoint = deskewPoint(&thisPoint, laserCloudIn->points[i].time);
//图像中填入欧几里得深度
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
// 转换成一维索引,存校正之后的激光点
int index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
}
}
void cloudExtraction()
{
// count为有效激光点云数据
int count = 0;
// extract segmented cloud for lidar odometry
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
{
//提取特征的时候,每一行的前5个和最后5个不考虑
// 将startRingIndex(记录每根扫描线起始第5个激光点在一维数组中的索引)设为5
cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] = count - 1 + 5;
for (int j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
{
if (rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) != FLT_MAX)
{
// mark the points' column index for marking occlusion later
// 记录激光点云对应的Horizon_SCAN方向上的索引
cloudInfo.pointColInd[count] = j;
// save range info
// 保存激光点云距离(range)数据
cloudInfo.pointRange[count] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
// save extracted cloud
// 保存有效激光点云到extractedCloud
extractedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
// size of extracted cloud
// 有效激光点云数量++
++count;
}
}
// 提取特征的时候,每一行的最后5个不考虑
cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] = count -1 - 5;
}
}
/* 发布用户自定义的cloudInfo激光数据(经过数据预处理的) */
void publishClouds()
{
cloudInfo.header = cloudHeader;
cloudInfo.cloud_deskewed = publishCloud(pubExtractedCloud, extractedCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
pubLaserCloudInfo.publish(cloudInfo);
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lio_sam"); //初始化ROS节点 lio_sam
ImageProjection IP; //创建对象IP
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m----> Image Projection Started.\033[0m");
ros::MultiThreadedSpinner spinner(3); // 使用3个线程
spinner.spin(); // 等待 直到节点shutdowmn
return 0;
}
3、featureExtraction.cpp
该文件的程序较为简单,主要作用就是特征点云的提取(角点和平面点)。
(1)输入(订阅):
- 已经去除运动畸变的自定义激光数据cloud_info
(2)输出(发布):
- 提取的角点数据
- 提取的平面点数据
- 自定义激光数据cloud_info
(3)具体函数:
- 主函数
初始化ros节点和实例化一个featureExtraction对象,具体的功能程序在featureExtraction类中进行封装。
各函数功能介绍
1. FeatureExtraction()构造函数
该构造函数主要是初始化ros的订阅和发布,以及完成其他一些变量的初始化工作。
2. laserCloudInfoHandler
这个回调函数是该文件的核心。特征提取的主要步骤都在回调函数中完成,ros订阅到激光数据cloud_info之后,进入回调函数,在回调函数中先转化点云数据格式,然后计算点云的曲率并排序,最后根据曲率提取角点和平面点。
calculateSmoothness()
该函数作用是计算激光点云的曲率。关键就是下面的代码:
// 曲率= 前五个点云和后五个点云的实际距离分别都减去当前点云的实际距离之和
float diffRange = cloudInfo.pointRange[i-5] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i-4]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i-3] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i-2]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i-1] - cloudInfo.pointRange[i] * 10
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+1] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i+2]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+3] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i+4]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+5];
markOccludedPoints()
该函数作用是标记被遮挡的点和与激光束平行的面上的点。主要是根据激光点云的实际距离和pointColInd来去除与激光束平行的面上的点云和前后遮挡的点云
extractFeatures()
该函数是核心,根据曲率大小提取角点和平面点。将一条扫描线扫描一周的点云数据,划分为6段,每段分开提取有限数量的特征,保证特征均匀分。每段只取20个角点,如果单条扫描线扫描一周是1800个点,则划分6段,每段300个点,从中提取20个角点。曲率小的点云和未处理的点云都被当做平面点处理。
publishFeatureCloud()
该函数的作用是发布提取到的角点和平面点。
具体注释:
#include "utility.h"
#include "lio_sam/cloud_info.h"
struct smoothness_t{
float value;
size_t ind;
};
struct by_value{
bool operator()(smoothness_t const &left, smoothness_t const &right) {
return left.value < right.value;
}
};
class FeatureExtraction : public ParamServer
{
public:
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloudInfo;
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudInfo;
ros::Publisher pubCornerPoints;
ros::Publisher pubSurfacePoints;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr extractedCloud;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr cornerCloud;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfaceCloud;
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointType> downSizeFilter;
lio_sam::cloud_info cloudInfo;
std_msgs::Header cloudHeader;
std::vector<smoothness_t> cloudSmoothness;
float *cloudCurvature;
int *cloudNeighborPicked;
int *cloudLabel;
/* 构造函数 */
FeatureExtraction()
{
// 订阅自定义激光数据cloud_info
subLaserCloudInfo = nh.subscribe<lio_sam::cloud_info>("lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info", 1, &FeatureExtraction::laserCloudInfoHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 发布cloudinfo数据
pubLaserCloudInfo = nh.advertise<lio_sam::cloud_info> ("lio_sam/feature/cloud_info", 1);
// 发布角点点云数据
pubCornerPoints = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("lio_sam/feature/cloud_corner", 1);
// 发布平面点点云数据
pubSurfacePoints = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("lio_sam/feature/cloud_surface", 1);
// 初始化变量数据
initializationValue();
}
/* 变量初始化 */
void initializationValue()
{
cloudSmoothness.resize(N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN);
downSizeFilter.setLeafSize(odometrySurfLeafSize, odometrySurfLeafSize, odometrySurfLeafSize);
extractedCloud.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
cornerCloud.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
surfaceCloud.reset(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
cloudCurvature = new float[N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN];
cloudNeighborPicked = new int[N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN];
cloudLabel = new int[N_SCAN*Horizon_SCAN];
}
/* 激光数据回调函数 */
void laserCloudInfoHandler(const lio_sam::cloud_infoConstPtr& msgIn)
{
//msgIn即为回调函数获取的去畸变点云信息
cloudInfo = *msgIn; // new cloud info
cloudHeader = msgIn->header; // new cloud header
// 点云数据格式转换
pcl::fromROSMsg(msgIn->cloud_deskewed, *extractedCloud); // new cloud for extraction
/* 计算当前激光帧中每个点的曲率 */
calculateSmoothness();
/* 标记被遮挡的点和与激光束平行的面上的点 */
markOccludedPoints();
/* 特征提取 提取角点和平面点 */
extractFeatures();
/* 发布提取到的特征点云数据 */
publishFeatureCloud();
}
/* 计算当前激光帧中每个点的曲率 */
void calculateSmoothness()
{
int cloudSize = extractedCloud->points.size();// 有效激光点云数量
// 遍历当前帧有效激光点云(前五个和最后五个不提取特征,排查在外)
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 5; i++)
{
// 计算曲率
// pointRange = sqrt(p.x*p.x + p.y*p.y + p.z*p.z);
// 曲率= 前五个点云和后五个点云的实际距离分别都减去当前点云的实际距离之和
float diffRange = cloudInfo.pointRange[i-5] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i-4]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i-3] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i-2]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i-1] - cloudInfo.pointRange[i] * 10
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+1] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i+2]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+3] + cloudInfo.pointRange[i+4]
+ cloudInfo.pointRange[i+5];
// 平方
cloudCurvature[i] = diffRange*diffRange;//diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 0;
cloudLabel[i] = 0;
// cloudSmoothness for sorting
// 存储曲率的平方
cloudSmoothness[i].value = cloudCurvature[i];
cloudSmoothness[i].ind = i;
}
}
/* 标记被遮挡的点和与激光束平行的面上的点 */
void markOccludedPoints()
{
int cloudSize = extractedCloud->points.size();
// mark occluded points and parallel beam points
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 6; ++i)
{
// 1、occluded points 被遮挡的点
// 当前点和下一个点的range(实际深度)值
float depth1 = cloudInfo.pointRange[i];
float depth2 = cloudInfo.pointRange[i+1];
// 计算当前点云和下一个点云之间的pointColInd数据差值
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(cloudInfo.pointColInd[i+1] - cloudInfo.pointColInd[i]));
// 两个点在同一扫描线上,且距离相差大于0.3,认为存在遮挡关系
//(也就是这两个点不在同一平面上,如果在同一平面上,距离相差不会太大,即一个在前一个在后,存在遮挡关系)
// 远处的点会被遮挡,标记一下该点以及相邻的5个点,后面不再进行特征提取
if (columnDiff < 10){
// 10 pixel diff in range image
if (depth1 - depth2 > 0.3){ // 当前点比下一个点云更远 则前五个点云剔除
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 5] = 1;// 设为1 表示该点云被标记为遮挡的点
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}else if (depth2 - depth1 > 0.3){ // 下一个点云比当前点云更远 则后五个点云剔除
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 6] = 1;
}
}
// 2、parallel beam 平行于激光束
// 用前后相邻点判断当前点所在平面是否与激光束方向平行
// diff1和diff2是当前点距离前后两个点的距离
float diff1 = std::abs(float(cloudInfo.pointRange[i-1] - cloudInfo.pointRange[i]));
float diff2 = std::abs(float(cloudInfo.pointRange[i+1] - cloudInfo.pointRange[i]));
// 如果当前点距离左右邻点都过远,则视其为瑕点,因为入射角可能太大导致误差较大
// 选择距离变化较大的点,并将他们标记为1
if (diff1 > 0.02 * cloudInfo.pointRange[i] && diff2 > 0.02 * cloudInfo.pointRange[i])
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}
}
/* 特征提取 提取角点和平面点 */
void extractFeatures()
{
cornerCloud->clear(); // 清空角点数据
surfaceCloud->clear(); // 清空平面点数据
// 重新分配内存
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfaceCloudScan(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfaceCloudScanDS(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
// 一条一条线遍历
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; i++)
{
surfaceCloudScan->clear(); // 清空数据
// 将一条扫描线扫描一周的点云数据,划分为6段,每段分开提取有限数量的特征,保证特征均匀分布
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
// 每段点云的起始、结束索引;startRingIndex为扫描线起始第5个激光点在一维数组中的索引
//注意:所有的点云在这里都是以"一维数组"的形式保存
//startRingIndex和 endRingIndex 在imageProjection.cpp中的 cloudExtraction函数里被填入
//假设 当前ring在一维数组中起始点是m,结尾点为n(不包括n),那么6段的起始点分别为:
// m + [(n-m)/6]*j j从0~5
// 化简为 [(6-j)*m + nj ]/6
// 6段的终止点分别为:
// m + (n-m)/6 + [(n-m)/6]*j -1 j从0~5,-1是因为最后一个,减去1
// 化简为 [(5-j)*m + (j+1)*n ]/6 -1
//这块不必细究边缘值到底是不是划分的准(例如考虑前五个点是不是都不要,还是说只不要前四个点),
//只是尽可能的分开成六段,首位相接的地方不要。因为庞大的点云中,一两个点其实无关紧要。
int sp = (cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (6 - j) + cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] * j) / 6;
int ep = (cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (5 - j) + cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] * (j + 1)) / 6 - 1;
if (sp >= ep)
continue;
// 根据曲率大小对选取出来的点从小到大进行排序
std::sort(cloudSmoothness.begin()+sp, cloudSmoothness.begin()+ep, by_value());
int largestPickedNum = 0;
// 按照曲率从大到小遍历 寻找角点
for (int k = ep; k >= sp; k--)
{
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
// 如果该点没有被标记为无效点云 且该点云的曲率大于阈值edgeThreshold 则认为是角点cornerCloud
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 && cloudCurvature[ind] > edgeThreshold)
{
largestPickedNum++; // 计数增加
// 每段只取20个角点,如果单条扫描线扫描一周是1800个点,则划分6段,每段300个点,从中提取20个角点
// 大于20个点云则跳出for循环
if (largestPickedNum <= 20){
cloudLabel[ind] = 1;
cornerCloud->push_back(extractedCloud->points[ind]);
} else {
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;// 被标记为角点
// 同一条扫描线上后5个点标记一下,不再处理,避免特征聚集 ????
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++)
{
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l] - cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l - 1]));
//大于10,说明距离远,则不作标记 ???
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
// 同理
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--)
{
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l] - cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
// 按照曲率从小到大遍历 寻找平面点 过程和寻找角点的过程一样
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++)
{
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 && cloudCurvature[ind] < surfThreshold)
{
cloudLabel[ind] = -1;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l] - cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l - 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l] - cloudInfo.pointColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
// 平面点和未被处理的点(<=0),都认为是平面点,加入平面点云集合
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++)
{
if (cloudLabel[k] <= 0){ // <=0代表平面点和未处理的点云
surfaceCloudScan->push_back(extractedCloud->points[k]);
}
}
}
//用surfaceCloudScan来装数据,然后放到downSizeFilter里,
//再用downSizeFilter进行.filter()操作,把结果输出到*surfaceCloudScanDS里。
//最后把DS装到surfaceCloud中。DS指的是DownSample。
//同样角点(边缘点)则没有这样的操作,因为角点数量较少,直接就用cornerCloud来装点云。
surfaceCloudScanDS->clear();// 清空数据
// 平面点数量较多 需要降采样
downSizeFilter.setInputCloud(surfaceCloudScan);
downSizeFilter.filter(*surfaceCloudScanDS);
// 存储降采样后的点云 加入平面点云集合
*surfaceCloud += *surfaceCloudScanDS;
}
}
/* 清楚变量数据 */
void freeCloudInfoMemory()
{
cloudInfo.startRingIndex.clear();
cloudInfo.endRingIndex.clear();
cloudInfo.pointColInd.clear();
cloudInfo.pointRange.clear();
}
/* 发布提取到的特征点云数据 */
void publishFeatureCloud()
{
// free cloud info memory
freeCloudInfoMemory();
// save newly extracted features
cloudInfo.cloud_corner = publishCloud(pubCornerPoints, cornerCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
cloudInfo.cloud_surface = publishCloud(pubSurfacePoints, surfaceCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
// publish to mapOptimization
pubLaserCloudInfo.publish(cloudInfo);
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 创建ros节点lio_sam
ros::init(argc, argv, "lio_sam");
// 实例化FeatureExtraction对象
FeatureExtraction FE;
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m----> Feature Extraction Started.\033[0m");// ROS打印消息
ros::spin();// 循环等待程序执行
return 0;
}
4、imuPreintergration.cpp
本程序主要封装了两个类。一个类是TransformFusion,主要作用是根据前一时刻激光里程计数据和该激光里程计时刻到现在时刻间的IMU数据来计算当前时刻IMU里程计。另一个类是IMUPreintegration,是本程序的核心,主要作用就是预积分。
先介绍简单一点的TransformFusion类。
TransformFusion类
该类的具体作用是根据上一帧得到的激光里程计和上一帧到当前帧之间的IMU数据得到当前时刻IMU里程计
(1)输入(订阅):
- 激光里程计 lio_sam/mapping/odometry。来自mapOptimization.cpp
- IMU里程计 odometry/imu_incremental 来自同个cpp文件的另一个IMUPreintegration类
(2)输出(发布):
- IMU里程计话题odomTopic
- imu里程计轨迹话题pubImuPath
(3)具体函数:
- TransformFusion构造函数
该构造函数作用主要有两点。一是将激光坐标系转到baselink坐标系。一个是创建订阅和发布变量。 - odom2affine函数
该函数的作用是将激光里程计数据转化为对应的变换矩阵Affine3f。 - lidarOdometryHandler函数
该回调函数的作用是保存最近一个激光雷达里程计的变换矩阵和时间戳。注意:这里不再和之前的回调函数一样将数据保存在一个队列中,而是保存一个数据。 - imuOdometryHandler函数
- 订阅imu里程计数据,来自IMUPreintegration
- 1、以最近一帧激光里程计位姿为基础,计算该时刻与当前时刻间imu里程计增量位姿变换,相乘得到当前时刻imu里程计位姿
- 2、发布当前时刻里程计位姿,用于rviz展示;发布imu里程计路径,注:只是最近一帧激光里程计时刻与当前时刻之间的一段。
IMUPreintegration类
(1)输入(订阅):
- 订阅IMU原始数据imuTopic
- 激光里程计数据,来自mapOptimization,用两帧之间的imu预积分量构建因子图
(2)输出(发布):
- IMU里程计 odomTopic+“_incremental”
(3)具体函数:
-
IMUPreintegration构造函数
该构造函数作用主要有两点。一是将激光坐标系转到baselink坐标系。一个是创建订阅和发布变量。 -
odom2affine函数
该函数的作用是将激光里程计数据转化为对应的变换矩阵Affine3f。 -
lidarOdometryHandler函数
该回调函数的作用是保存最近一个激光雷达里程计的变换矩阵和时间戳。注意:这里不再和之前的回调函数一样将数据保存在一个队列中,而是保存一个数据。 -
imuHandler函数
将接收到的IMU原始数据转到LIDAR坐标系下,转换后,会存入两个队列,一个imuQueOpt队列,一个imuQueImu队列。这两队列有什么区别和联系呢?这个主要在另一个回调函数odometryHandler会被处理,在那里会说明。这里我们可以先理解为,imuQueImu是真正我们要用的数据,imuQueOpt是一个中间缓存的数据结构,用来优化imu的bias之类的东西。
该函数的主要作用是上一帧(最近一帧)的激光里程计为起始,通过不断订阅到的IMU数据,通过预积分得到当前时刻激光里程计
主要步骤是:
1、将IMU数据从imu坐标系转到LIDAR坐标系下。
2、以上一帧激光里程计时刻对应的状态、偏置,施加从该时刻开始到当前时刻的imu预计分量,得到当前时刻的状态currentState
3、从currentState中获取到当前时刻imu的位姿等数据,再经过坐标变换得到激光的位姿的数据
4、将得到的激光里程计数据发布出去 -
odometryHandler函数
1、获取激光里程计数据(xyz和四元数) 将来自里程计(odometry)的位姿数据转换为GTSAM中的Pose3对象,以便在后面进行因子图优化
2、初始化
a、重置ISAM2优化器
b、删除保存imu数据的队列中旧的IMU数据,即保证IMU队列中的IMU数据都是最近接收到的激光里程计之后的数据
c、添加机器人priorPose、priorVel、priorBias先验因子到graphFactors因子图模型中,并且将当前机器人的状态prevPose_、prevVel_、prevBias_插入到graphValues因子图优化的状态变量中
d、利用定义的因子图优化器optimizer进行一次优化操作,对变量的最优估计进行计算。
3、取两帧激光里程计帧之间的IMU数据,然后往imu预积分器imuIntegratorOpt_添加IMU数据
4、利用两帧之间的IMU数据完成了预积分后,增加imu因子preint_imu到因子图模型中
5、向图中添加一个表示两个节点之间约束关系的因子imu偏置Bias因子,同时指定了初始状态和噪声模型
6、添加激光里程计位姿因子
7、插入预测变量,利用定义的因子图优化器optimizer进行一次优化操作,对变量的最优估计进行计算
8、优化后 用最新的偏置重新计算当前激光里程计时刻之后的imu预积分,这个预积分用于计算每时刻位姿
5、mapOptimization.cpp
(1)输入(订阅):
- 订阅当前激光帧点云cloud_info
- 订阅GPS里程计gpsTopic
- 订阅来自外部闭环检测程序提供的闭环数据,本程序没有提供,这里实际没用上
(2)输出(发布):
-
发布历史关键帧里程计(组成轨迹)
-
发布局部关键帧map的特征点云
-
发布激光里程计
-
发布激光里程计,它与上面的激光里程计基本一样,只是roll、pitch用imu数据加权平均了一下,z做了限制
-
发布激光里程计路径
-
发布地图保存服务
-
发布闭环匹配关键帧局部map
-
发布当前关键帧经过闭环优化后的位姿变换之后的特征点云
-
发布闭环边,rviz中表现为闭环帧之间的连线
-
发布局部map的降采样平面点集合
-
发布历史帧(累加的)的角点、平面点降采样集合
-
发布当前帧原始点云配准之后的点云
(3)具体函数:
该文件主要由mapOptimization类和main函数组成,mapOptimization在main函数中被实例化。
主函数main:
初始化ros节点lio_sam,实例化mapOptimization对象。mapOptimization类
该类主要的内容就是一个初始化构造函数和三个回调函数 -
构造函数:
该构造函数的作用是以下几点:
1.配置ISAM2的参数
2.创建订阅和发布
3.配置降采样滤波器
4.变量分配内存
laserCloudInfoHandler
该激光点云cloud_info的回调函数。该函数主要作用如下:
订阅当前激光帧点云信息,来自featureExtraction
-
1、当前帧位姿初始化
1) 如果是第一帧,用原始imu数据的RPY初始化当前帧位姿(旋转部分) 2) 后续帧,用imu里程计计算两帧之间的增量位姿变换,作用于前一帧的激光位姿,得到当前帧激光位姿 -
2、提取局部角点、平面点云集合,加入局部map
1) 对最近的一帧关键帧,搜索时空维度上相邻的关键帧集合,降采样一下 2) 对关键帧集合中的每一帧,提取对应的角点、平面点,加入局部map中 -
3、当前激光帧角点、平面点集合降采样
-
4、scan-to-map优化当前帧位姿
(1) 要求当前帧特征点数量足够多,且匹配的点数够多,才执行优化 (2) 迭代30次(上限)优化 1) 当前激光帧角点寻找局部map匹配点 a.更新当前帧位姿,将当前帧角点坐标变换到map系下,在局部map中查找5个最近点,距离小于1m,且5个点构成直线(用距离中心点的协方差矩阵,特征值进行判断),则认为匹配上了 b.计算当前帧角点到直线的距离、垂线的单位向量,存储为角点参数 2) 当前激光帧平面点寻找局部map匹配点 a.更新当前帧位姿,将当前帧平面点坐标变换到map系下,在局部map中查找5个最近点,距离小于1m,且5个点构成平面(最小二乘拟合平面),则认为匹配上了 b.计算当前帧平面点到平面的距离、垂线的单位向量,存储为平面点参数 3) 提取当前帧中与局部map匹配上了的角点、平面点,加入同一集合 4) 对匹配特征点计算Jacobian矩阵,观测值为特征点到直线、平面的距离,构建高斯牛顿方程,迭代优化当前位姿,存transformTobeMapped (3)用imu原始RPY数据与scan-to-map优化后的位姿进行加权融合,更新当前帧位姿的roll、pitch,约束z坐标 -
5、设置当前帧为关键帧并执行因子图优化
1) 计算当前帧与前一帧位姿变换,如果变化太小,不设为关键帧,反之设为关键帧 2) 添加激光里程计因子、GPS因子、闭环因子 3) 执行因子图优化 4) 得到当前帧优化后位姿,位姿协方差 5) 添加cloudKeyPoses3D,cloudKeyPoses6D,更新transformTobeMapped,添加当前关键帧的角点、平面点集合 -
6、更新因子图中所有变量节点的位姿,也就是所有历史关键帧的位姿,更新里程计轨迹
-
7、发布激光里程计
-
8、发布里程计、点云、轨迹
updateInitialGuess函数:
该函数的作用是以下几点:
1.如果是第一帧,用原始imu数据的RPY初始化当前帧位姿(旋转部分)
2.如果是后续帧,用imu里程计计算两帧之间的增量位姿变换,作用于前一帧的激光位姿,得到当前帧激光位姿
extractSurroundingKeyFrames函数:
该函数的作用是以下几点:
1.提取当前关键帧的相邻关键帧集合
2.对提取到的关键帧集合中的每一帧,提取对应的角点、平面点,加入局部map中
downsampleCurrentScan函数:
该函数的作用是以下几点:
1.降采样当前帧激光点云数据中的角点、平面点
scan2MapOptimization函数:
该函数的作用是根据现有地图与最新点云数据进行配准从而更新机器人精确位姿与融合建图,主要分为以下几点:
1.角点优化cornerOptimization函数
2.平面点优化surfOptimization函数
3.组合优化多项式系数 将角点优化和面点优化的结果合并为优化系数combineOptimizationCoeffs函数
4.Levenberg-Marquardt优化LMOptimization函数
5.对位姿进行更新transformUpdate函数
gpsHandler函数:
该回调函数作用是将gps数据存入队列。
具体注释:
#include "utility.h"
#include "lio_sam/cloud_info.h"
#include "lio_sam/save_map.h"
#include 四、下载安装LIO-SAM
1、下载
2、编译
五、数据集测试、实车测试
1、跑数据集
首先下载论文中的数据集,这里以park_dataset数据集为例。由于数据集文件较大,一般有好几个G,建议科学上网或者寻找别人已经从官网下载好保存在网盘里的。
下载完数据集后,将其放在一个文件夹内,然后运行LIO-SAM:
roslaunch lio_sam run.launch
启动LIO-SAM后,cd进入到存放数据集的文件夹中,播放数据集bag(根据电脑性能自行选择频率):
rosbag play park_dataset.bag -r 3
park_dataset数据集建图效果如下:
2、实车测试
驱动安装
在进行实车测试之前,首先需要安装一些必备的驱动。如IMU驱动、雷达驱动、机器人驱动。首先介绍一下我们实验室使用的机器人。目前测试使用:
- 机器人是EAI的Dashgo D1,需要安装机器人底盘的驱动。
- IMU使用的是LPMS-IG1九轴惯性测量模块(注意:LIO-SAM必须使用九轴IMU,否则无法正常运行),需要安装IMU驱动。
- 激光雷达使用的是速腾聚创的16线激光雷达RS-LIDAR-16,需要安装雷达的驱动。
下面介绍三个驱动的安装方式:
1、EAI的Dashgo D1
安装EAI驱动可参考CSDN上EAI官方提供的文档:https://blog.csdn.net/eaibot/category_6256249.html
官方文档描述的很清楚如何安装驱动和使用驱动,下面的命令是如何调用键盘去控制机器人运动。
cd catkin_ws
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch dashgo_driver demo.launch
rosrun dashgo_tools teleop_twist_keyboard.py
将机器人和电脑通过连接线连接后,运行上述命令,启动了机器人驱动,并且可以通过键盘控制机器人运动。
此外,由于电脑需要放在机器人上跟着机器人一起运动,因此也可以通过ssh的方式,远程控制机器人进行移动和建图。ssh的安装此处不再赘述,可自行上网查阅教程。
可通过以下命令使用另一台电脑连接到该电脑,在另一台电脑的ubuntu系统中输入以下命令,输入正确的密码后即可远程控制和建图。
ssh xxx@ip_address
这里的xxx是电脑ubuntu的设置的名称,ip_address可通过
ifconfig
命令查询本机ip地址
2、激光雷达驱动
由于LIO-SAM代码中需要使用到激光雷达数据中的ring(通道,即点云位于哪条扫描线上)和timestamp(时间戳)。但是旧版的雷达驱动中没有这两个数据,因此需要安装新版的驱动。z
-1 XYZI - x, y, z, intensity
-2 XYZIRT - x, y, z, intensity, ring, timestamp
上面1为老版数据参数,2为新版数据参数。
注意:如果要输出新版点云数据,还需要根据**切换点类型**进行配置重新编译
下面介绍如何安装新版雷达驱动,主要是下载官方github上的驱动包并按照官方的文档进行安装。
下载地址:https://github.com/RoboSense-LiDAR/rslidar_sdk
中文安装文档:https://github.com/RoboSense-LiDAR/rslidar_sdk/blob/main/README_CN.md
根据官方提供的中文文档安装驱动后,使用网线将电脑的以太网口连接上雷达,启动launch文件:
cd catkin_ws
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch rslidar_sdk start.launch
正常运行结果如下图:
3、IMU驱动安装
LPMG IG1的驱动可参考以下博客进行安装:
LPMS-IG1 IMU内参标定
同时,可根据上述博客完成IMU内参标定。
然后就是通过命令行启动IMU:
cd catkin_ws
source devel/setup.bash
rosrun openzen_sensor openzen_sensor_node
然后使用rostopic命令查看IMU数据:
rostopic echo /imu/data
正常运行结果如下图:
运行LIO-SAM
完成上述步骤后,运行以下命令启动lio-sam
cd lio_sam/
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch lio_sam run.launch
这里出现一个小bug,运行lio-sam后,代码中数据预处理环节有个地方报错:
// check dense flag 根据is_dense去除无效点云
if (laserCloudIn->is_dense == false)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud is not in dense format, please remove NaN points first!");
ros::shutdown();
}
目前原因还不清楚,目前采取的方法是先注释掉这个if语句运行LIO-SAM。
总结
未完待续......
