《代码随想录》-链表
《代码随想录》-链表
- 203.移除链表元素
- 707.设计链表
- 206.反转链表
- 24.两两交换链表中的节点
- 19.删除链表的倒数第k个节点
- 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
- 142.环形链表Ⅱ
203.移除链表元素
分析
- 链表题目都设置一个虚拟头节点dummy
- 单链表无法找到要删除的节点,只能找到待删除节点的前一个节点。迭代找待删除节点前一个或者添加一个pre指针递归寻找。
代码
- 迭代
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
dfs(dummy,dummy.next,val);
return dummy.next;
}
public void dfs(ListNode pre,ListNode root,int val){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
if(root.val == val){
pre.next = root.next;
}else{
pre = root;
}
dfs(pre,pre.next,val);
}
}
707.设计链表
代码
class MyLinkedList {
private Node head = null;
private int size = 0;
public MyLinkedList() {
head = new Node(0);
}
public int get(int index) {
Node temp = head.next;
while(temp != null && index >= 0){
if(index == 0){
return temp.val;
}else{
temp = temp.next;
index--;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
Node temp = head;
Node insert = new Node(val);
insert.next = temp.next;
temp.next = insert;
size++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
Node temp = head;
Node insert = new Node(val);
while(temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = insert;
size++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
Node insert = new Node(val);
Node temp = head;
if(index > size){
return;
}
while(temp.next != null && index >= 0){
if(index == 0){
insert.next = temp.next;
temp.next = insert;
size++;
return;
}else{
temp = temp.next;
index--;
}
}
insert.next = temp.next;
temp.next = insert;
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
Node temp = head;
while(temp.next != null && index >= 0){
if(index == 0){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
break;
}else{
temp = temp.next;
index--;
}
}
}
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
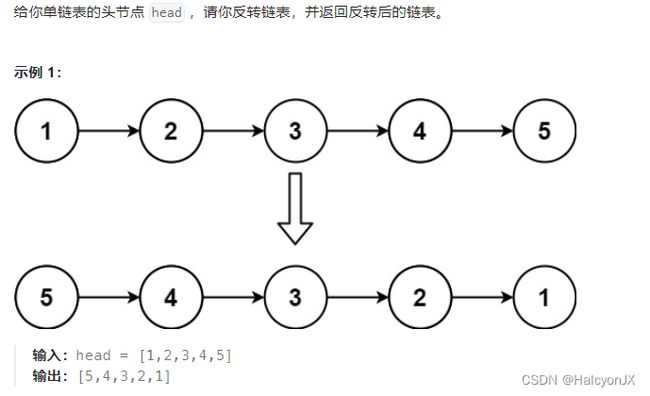
206.反转链表
代码
- 方法一(两个链表)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode newList = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = head;
ListNode next = null;
while(temp != null){
next = temp.next;
temp.next = newList.next;
newList.next = temp;
temp = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
}
- 方法二(双指针)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next = null;
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
- 方法三(递归)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null,head);
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre,ListNode cur){
if(cur == null) return pre;
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur,next);
}
}
- 方法四(从后往前递归)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
分析
- 方法一
- 直观的做法就是创建一个新的链表,每遍历一个元素就把这个元素添加到新链表的头节点之后。
- 方法二
- 不创建新的链表,设置一个前置指针
pre - 保存
cur指针的下一个节点next,不让下一个节点没有指向 cur.next = pre调转链表的方向pre和cur后移,注意pre要先移动,再令cur = next
- 不创建新的链表,设置一个前置指针
- 方法三
- 思路和方法二一样,只是换成了递归
- 方法四
- 先校验边界条件
- 递归调用反转第二个节点往后的链表
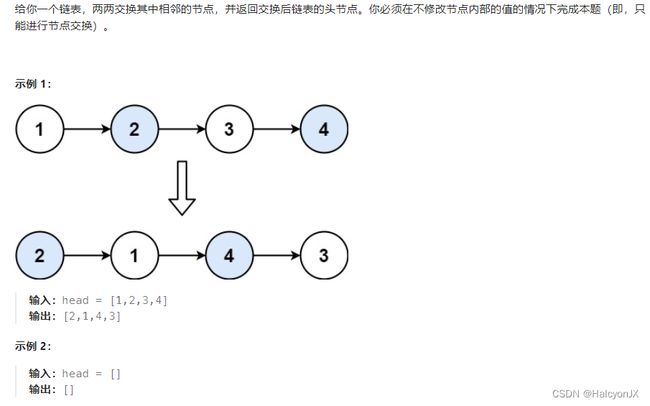
24.两两交换链表中的节点
代码
- 方法一:两个临时变量保存节点
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode temp1 = null;
ListNode temp2 = null;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
temp1 = cur.next;
temp2 = cur.next.next.next;
//进行交换
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = temp1;
cur.next.next.next = temp2;
//移动cur两位
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 方法二:一个临时变量保存节点
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode temp = null;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
temp = cur.next.next; //保存cur后的第二个节点
cur.next.next = temp.next;//cur后的第一个节点指向cur后的第三个节点
temp.next = cur.next;//cur后的第二个节点指向cur后的第一个节点
cur.next = temp;//让cur指向保存的节点,此时temp变成了cur后的第一个节点
cur = temp.next;//让cur移动两位,即temp的下一个节点就是要移动到的位置
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
//退出条件
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
//保存当前节点的下一个
ListNode next = head.next;
ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);
//进行交换
next.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return next;
}
}
分析
-
方法二
- 上图步骤一和步骤三调换,先让1指向了3,最后再让2指向
cur。 - 保存的是2节点,注意交换后2节点的位置,让
cur移动两位
- 上图步骤一和步骤三调换,先让1指向了3,最后再让2指向
-
递归
- 先设置退出条件,链表为单数或者传入链表为空时直接返回。
- 保存的
head的下一个节点,返回的newNode其实是head之后的第二个节点,可以假设整个链表只有2个节点理解。 - 交换后
next就变成了头节点,所以返回next。
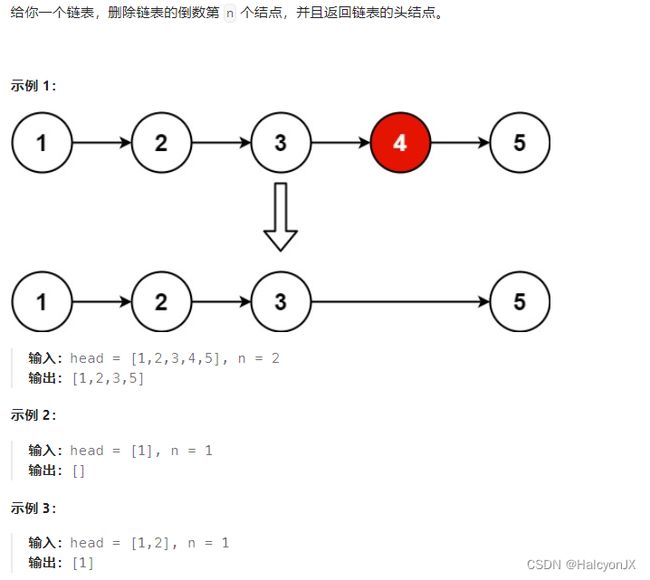
19.删除链表的倒数第k个节点
代码
- 方法一:扫描两遍
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
int size = 0; //记录链表有多少个元素
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
size++;
}
cur = dummy;//将cur返回头节点之前
for(int i = 0;i<size-n;i++){//后移找到待删除节点之前
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;//删除元素
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 方法二:扫描一遍
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
for(int i = 0;i < n + 1;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
分析
- 方法一
- 直观做法就是一次扫描记录多少个元素
- 根据节点数目得出需要移动多少次找到待删除元素
- 方法二
- 只扫描一遍的话,就需要根据
n求出待删除元素再哪个位置。 - 两个指针
fast和slow,fast从虚拟头节点开始走n步,然后fast和slow一起往后移,直到fast指向空,此时刚好slow指向待删除节点。可以画个链表试验一下。 - 由于
slow要找到待删除节点的前一个节点才能完成删除操作,所以fast先走n+1步。
- 只扫描一遍的话,就需要根据
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
代码
- 方法一(差值解法)
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
while(curA != null){
curA = curA.next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB != null){
curB = curB.next;
lenB++;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if(lenB > lenA){
int temp = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = temp;
ListNode temp1 = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = temp1;
}
int gap = lenA - lenB;
while((gap--) > 0){
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA != null){
if(curA == curB) return curA;
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
- 方式二(暴力解法)
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
for(ListNode a = headA;a != null;a = a.next){
for(ListNode b = headB;b != null;b = b.next){
if(a == b) return a;
}
}
return null;
}
}
- 方式三(栈解法)
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Stack<ListNode> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> s2 = new Stack<>();
while(headA != null){
s1.push(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while(headB != null){
s2.push(headB);
headB = headB.next;
}
ListNode ans = null;
while(!s1.isEmpty() && !s2.isEmpty()){
ListNode a = s1.pop();
ListNode b = s2.pop();
if(a == b) ans = a;
else break;
}
return ans;
}
}
- 方法四
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA,b = headB;
while(a != b){
a = (a != null ? a.next : headB);
b = (b != null ? b.next : headA);
}
return a;
}
}
分析
此题比较的是两个节点是否为同一个节点,而非节点的值是否相同
-
方法一(差值法)
-
先算出两个链表的长度,求得差值,让长链表先移动两者的差值长度,再一起移动比较节点
-
代码太长了,优化一下。
public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode a = headA,b = headB; int t1 = 0,t2 = 0; while(a != null && ++t1>0){a = a.next;} while(b != null && ++t2>0){b = b.next;} int g = Math.abs(t1 - t2); while(g-- > 0){ if(t1 > t2) headA = headA.next; else headB = headB.next; } while(headA != null && headB != null){ if(headA == headB) return headA; else{ headA = headA.next; headB = headB.next; } } return null; } }
-
-
方法二
- 暴力解法找出所有节点对比的情况
- 时间复杂度太高
-
方法三
-
从尾到首比较,当出现两个节点不同的情况就说明已经找到要返回的节点了
-
分别创建两个栈,将两个链表的节点压入栈中
-
取出栈中的节点进行比较
-
-
方法四
- 求差值是为了让两个链表的指针对齐
- 如何不用求差值让指针对齐呢?
- 两个指针到链表末尾的时候去遍历另一个链表,这样最终两个指针会对齐。
142.环形链表Ⅱ
代码
- 哈希表
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null){
if(list.contains(temp)) return temp;
else list.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
- 双指针
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head,slow = head;
boolean flag = false;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast == slow){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
fast = head;
if(!flag){
return null;
}else{
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
}
return slow;
}
}
分析
- 方法一哈希表:
- 遍历链表每个节点,并将节点记录下来,如果遇到遍历过的节点,说明有环,直接返回。
- 空间复杂度O(n)
- 方法二双指针法:
- 数学关系得出环的入口。