OpenCV-Python15:图像阈值处理
目录
目标
图像阈值及分割算法介绍
简单阈值算法
自适应阈值算法
Otsu`s 二值化算法
Otsu`s 二值化原理
目标
- 通过本文你将学到图像二值化、简单阈值处理、自适应阈值、Otsu`s 二值化等。
- 将学习的函数有cv2.threshold,cv2.adaptiveThreshold 等。
图像阈值及分割算法介绍
图像阈值是图像分割中常用的一种方法,通过将图像中的像素值与一个特定的阈值进行比较,将像素分为两个类别:小于阈值的像素被归为一类,大于等于阈值的像素被归为另一类。
常用的图像阈值分割算法包括:
- 全局阈值法:将图像中的所有像素都与一个全局阈值进行比较,从而将图像分为两个类别。常用的全局阈值法有基于直方图的Otsu算法和基于最大类间方差的Kapur算法。
- 自适应阈值法:将图像分为许多小的区域,在每个小区域内分别计算一个局部阈值,根据每个像素与其对应的局部阈值的比较结果进行分割。常用的自适应阈值法有基于局部平均值的均值法和基于局部中值的中值法。
- 大津阈值法(Otsu算法):通过最大化类间方差来确定最佳阈值,使得类间差异最大,类内差异最小。该方法适用于具有双峰直方图的图像。
- Kapur算法:基于最大类间方差原理,通过最大化类间熵来确定最佳阈值。相比于Otsu算法,Kapur算法对于非双峰直方图的图像更具鲁棒性。
- 均值法:将图像分成若干个小的区域,计算每个区域的像素平均值,将每个像素与其对应区域的平均值进行比较,从而确定像素的类别。
- 中值法:将图像分成若干个小的区域,计算每个区域的像素中值,将每个像素与其对应区域的中值进行比较,从而确定像素的类别。
这些图像阈值分割算法各有优劣,选择适合具体应用场景的算法可以提高分割结果的准确性和鲁棒性,下面重点介绍一下OpenCV-Python中的几种重点算法。
简单阈值算法
简单阈值算法是一种全局阈值法,与名字一样,是一种非常简单的分割算法。原理是当像素值高于阈值时,我们给这个像素赋予一个新值(可能是白色),否则我们给它赋予另外一种颜色(也许是黑色)。OpenCV中的这个算法的实现函数就是就是cv2.threshhold()。
其参数的含义如下:
1.src:输入图像,即要进行阈值分割的原始图像,通常为灰度图像。
2.thresh:阈值,用于将像素分为两个类别的分界值。根据阈值与像素值的比较结果,将像素分为两类:小于阈值的像素被归为一类,大于等于阈值的像素被归为另一类。
3.maxval:当像素值大于等于阈值时,像素所赋予的新值,通常为255。
4.type:阈值分割的类型,用于指定阈值分割的方法。常用的类型有:
cv2.THRESH_BINARY:二值化,将大于阈值的像素置为maxval,小于阈值的像素置为0。cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV:反二值化,将小于阈值的像素置为maxval,大于阈值像素置为0。cv2.THRESH_TRUNC:截断,将大于阈值的像素置为阈值,小于阈值的像素保持不变。cv2.THRESH_TOZERO:取零,将小于阈值的像素置为0,大于阈值的像素保持不变。cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV:反取零,将大于阈值的像素置为0,小于阈值的像素保持不变。
函数的返回值为:
retval:所选择的阈值。dst:阈值分割后的图像。
不同方法的测试代码如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img=cv2.imread('gradient.png',0)
ret,thresh1=cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret,thresh2=cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ret,thresh3=cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TRUNC)
ret,thresh4=cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
ret,thresh5=cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
titles = ['Original Image','BINARY','BINARY_INV','TRUNC','TOZERO','TOZERO_INV']
images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5]
for i in xrange(6):
plt.subplot(2,3,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果如下:
自适应阈值算法
自适应阈值算法是一种根据图像局部区域的统计特性来确定阈值的方法,适用于图像中存在光照不均匀或者对比度较低的情况。Opencv-Python中提供了cv2.adaptiveThreshold()函数来实现自适应阈值算法。
cv2.adaptiveThreshold()函数的参数如下:
1.src:输入图像,即要进行阈值分割的原始图像。通常为灰度图像。
2.maxval:当像素值大于等于阈值时,像素所赋予的新值。通常为255。
3.adaptiveMethod:自适应阈值算法的方法。有两种可选:
cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C:根据邻域均值确定阈值。cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C:根据邻域加权平均值确定阈值。
4.thresholdType:阈值分割的类型,用于指定阈值分割的方法。常用的类型有:
cv2.THRESH_BINARY:二值化,将大于阈值的像素置为maxval,小于阈值的像素置为0。cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV:反二值化,将小于阈值的像素置为maxval,大于阈值的像素置为0。
5.blockSize:邻域大小,用于计算局部均值或者加权平均值。
6.C:从计算得到的局部均值或者加权平均值中减去的一个常数。
代码如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('dave.jpg',0)
# 中值滤波
img = cv2.medianBlur(img,5)
ret,th1 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
#11 为Block size, 2 为C 值
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,\
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
th3 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,\
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
titles = ['Original Image', 'Global Thresholding (v = 127)',
'Adaptive Mean Thresholding', 'Adaptive Gaussian Thresholding']
images = [img, th1, th2, th3]
for i in xrange(4):
plt.subplot(2,2,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果如下:
Otsu`s 二值化算法
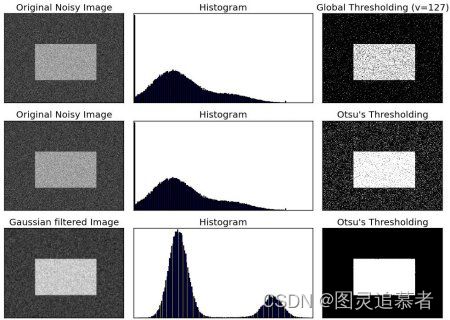
Otsu’s 二值化算法是一种自动确定阈值的方法,它可以根据图像的灰度直方图来确定一个最佳的阈值,从而将图像分割为前景和背景两部分。Opencv-Python中提供了cv2.threshold()函数来实现Otsu’s 二值化算法。
cv2.threshold()函数的参数如下:
1.src:输入图像,即要进行阈值分割的原始图像。通常为灰度图像。
2.thresh:阈值,用于将像素分为两类。在Otsu’s 二值化算法中,这个参数不需要指定。
3.maxval:当像素值大于等于阈值时,像素所赋予的新值。通常为255。
4.type:阈值分割的类型,用于指定阈值分割的方法。在Otsu’s 二值化算法中,应该使用cv2.THRESH_BINARY。
5.dst:输出图像,即阈值分割后的图像。
函数的返回值为阈值。
下面是一个示例代码,展示了如何使用Otsu’s 二值化算法对图像进行阈值分割:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('noisy2.png',0)
# global thresholding
ret1,th1 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Otsu's thresholding
ret2,th2 = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# Otsu's thresholding after Gaussian filtering
#5,5为斯核的大小0 为标准差
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)
# 值一定为0
ret3,th3 = cv2.threshold(blur,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# plot all the images and their histograms
images = [img, 0, th1,
img, 0, th2,
blur, 0, th3]
titles = ['Original Noisy Image','Histogram','Global Thresholding (v=127)',
'Original Noisy Image','Histogram',"Otsu's Thresholding",
'Gaussian filtered Image','Histogram',"Otsu's Thresholding"]
# 使用了pyplot 中画直方图的方法plt.hist, 注意的是它的参数是一维数组
# 所以使用了numpyravel 方法将多维数组换成一维也可以使用flatten 方法
#ndarray.flat 1-D iterator over an array.
#ndarray.flatten 1-D array copy of the elements of an array in row-major order.
for i in xrange(3):
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+1),plt.imshow(images[i*3],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+2),plt.hist(images[i*3].ravel(),256)
plt.title(titles[i*3+1]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+3),plt.imshow(images[i*3+2],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3+2]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果如下:
Otsu`s 二值化原理
在这一部分我们会演示怎样使用Python 来实现Otsu`s二值化算法,从而告诉大家它是如何工作的。因为是双峰图,Otsu 算法就是要找到一个阈值t, 使得同一类加权方差最小,需要满下列关系式:
![]()
其中:
其实就是在两个峰之找到一个值t将两个峰分开,并且使每一个峰内的方差最小。实现这个算法的Python 代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Jan 11 14:46:12 2014
@author: duan
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('noisy2.png',0)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)
# find normalized_histogram, and its cumulative distribution function
# 算归一化直方图
#CalcHist(image, accumulate=0, mask=NULL)
hist = cv2.calcHist([blur],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
hist_norm = hist.ravel()/hist.max()
Q = hist_norm.cumsum()
bins = np.arange(256)
fn_min = np.inf
thresh = -1
for i in xrange(1,256):
p1,p2 = np.hsplit(hist_norm,[i]) # probabilities
q1,q2 = Q[i],Q[255]-Q[i] # cum sum of classes
b1,b2 = np.hsplit(bins,[i]) # weights
# finding means and variances
m1,m2 = np.sum(p1*b1)/q1, np.sum(p2*b2)/q2
v1,v2 = np.sum(((b1-m1)**2)*p1)/q1,np.sum(((b2-m2)**2)*p2)/q2
# calculates the minimization function
fn = v1*q1 + v2*q2
if fn < fn_min:
fn_min = fn
thresh = i
# find otsu's threshold value with OpenCV function
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(blur,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
print (thresh,ret)