LeetCode(58)随机链表的复制【链表】【中等】
目录
-
- 1.题目
- 2.答案
- 3.提交结果截图
链接: 随机链表的复制
1.题目
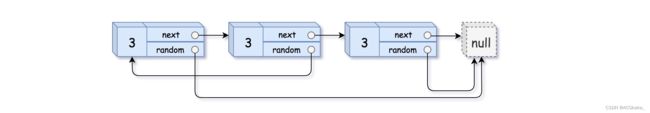
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
2.答案
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public static Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node startNode = new Node(head.val);
Node node = startNode;
while (head != null) {
node.next = new Node(head.val);
node.next.random = head.random;
map.put(head, node.next);
node = node.next;
head = head.next;
}
node = startNode.next;
while (node != null) {
node.random = map.get(node.random);
node = node.next;
}
return startNode.next;
}
}
3.提交结果截图
整理完毕,完结撒花~