Centos 7安装、配置SVN
本文介绍Centos 7如何安装、配置SVN
文章目录
- 一、安装SVN
- 二、创建仓库
- 三、配置SVN
-
- 1、SVN配置项
- 2、用户管理
- 3、用户组和权限配置
- 4、关闭防火墙
- 5、启动服务
- 6、访问SVN仓库
一、安装SVN
以管理员身份运行以下命令:
[root@localhost user]# yum -y install subversion
输出:
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 subversion.x86_64.0.1.7.14-16.el7 将被 安装
--> 正在处理依赖关系 subversion-libs(x86-64) = 1.7.14-16.el7,它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_wc-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_subr-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_repos-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_ra_svn-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_ra_neon-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_ra_local-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_ra-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_fs_util-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_fs_fs-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_fs_base-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_fs-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_diff-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_delta-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libsvn_client-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libaprutil-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libapr-1.so.0()(64bit),它被软件包 subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 需要
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 apr.x86_64.0.1.4.8-7.el7 将被 安装
---> 软件包 apr-util.x86_64.0.1.5.2-6.el7 将被 安装
---> 软件包 subversion-libs.x86_64.0.1.7.14-16.el7 将被 安装
--> 解决依赖关系完成
依赖关系解决
================================================================================
Package 架构 版本 源 大小
================================================================================
正在安装:
subversion x86_64 1.7.14-16.el7 base 1.0 M
为依赖而安装:
apr x86_64 1.4.8-7.el7 base 104 k
apr-util x86_64 1.5.2-6.el7 base 92 k
subversion-libs x86_64 1.7.14-16.el7 base 922 k
事务概要
================================================================================
安装 1 软件包 (+3 依赖软件包)
总下载量:2.1 M
安装大小:7.5 M
Downloading packages:
(1/4): apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64.rpm | 104 kB 00:00
(2/4): apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64.rpm | 92 kB 00:00
(3/4): subversion-libs-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64.rpm | 922 kB 00:00
(4/4): subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64.rpm | 1.0 MB 00:00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
总计 9.9 MB/s | 2.1 MB 00:00
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
警告:RPM 数据库已被非 yum 程序修改。
正在安装 : apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64 1/4
正在安装 : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 2/4
正在安装 : subversion-libs-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 3/4
正在安装 : subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 4/4
验证中 : subversion-libs-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 1/4
验证中 : apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64 2/4
验证中 : subversion-1.7.14-16.el7.x86_64 3/4
验证中 : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 4/4
已安装:
subversion.x86_64 0:1.7.14-16.el7
作为依赖被安装:
apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-7.el7 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7
subversion-libs.x86_64 0:1.7.14-16.el7
完毕!
二、创建仓库
SVN创建仓库语法: svnadmin create 路径。
例:在/home/user/svn下创建SVN仓库
切换到普通用户(自己使用的用户即可),运行以下命令:
[user@localhost ~]$ svnadmin create /home/user/svn
SVN会自动在相应路径下创建文件夹,文件夹内会有以下几个目录和文件:
svn
|-conf
|-db
|-format
|-hooks
|-locks
|-README.txt
其中,conf文件夹下有3个文件:
conf
|-authz
|-passwd
|-svnserve.conf
其中,svnserve.conf为svn服务配置文件,passwd为用户名口令文件,authz为权限配置文件。
三、配置SVN
1、SVN配置项
svn配置项文件为conf文件夹中的svnserve.conf文件,该文件仅由一个[general]配置段组成,格式:<配置项>=<值>。
svnserve.conf默认内容如下:
### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you
### use it to allow access to this repository. (If you only allow
### access through http: and/or file: URLs, then this file is
### irrelevant.)
### Visit http://subversion.apache.org/ for more information.
[general]
### The anon-access and auth-access options control access to the
### repository for unauthenticated (a.k.a. anonymous) users and
### authenticated users, respectively.
### Valid values are "write", "read", and "none".
### Setting the value to "none" prohibits both reading and writing;
### "read" allows read-only access, and "write" allows complete
### read/write access to the repository.
### The sample settings below are the defaults and specify that anonymous
### users have read-only access to the repository, while authenticated
### users have read and write access to the repository.
# anon-access = read
# auth-access = write
### The password-db option controls the location of the password
### database file. Unless you specify a path starting with a /,
### the file's location is relative to the directory containing
### this configuration file.
### If SASL is enabled (see below), this file will NOT be used.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default password file.
# password-db = passwd
### The authz-db option controls the location of the authorization
### rules for path-based access control. Unless you specify a path
### starting with a /, the file's location is relative to the the
### directory containing this file. If you don't specify an
### authz-db, no path-based access control is done.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default authorization file.
# authz-db = authz
### This option specifies the authentication realm of the repository.
### If two repositories have the same authentication realm, they should
### have the same password database, and vice versa. The default realm
### is repository's uuid.
# realm = My First Repository
### The force-username-case option causes svnserve to case-normalize
### usernames before comparing them against the authorization rules in the
### authz-db file configured above. Valid values are "upper" (to upper-
### case the usernames), "lower" (to lowercase the usernames), and
### "none" (to compare usernames as-is without case conversion, which
### is the default behavior).
# force-username-case = none
[sasl]
### This option specifies whether you want to use the Cyrus SASL
### library for authentication. Default is false.
### This section will be ignored if svnserve is not built with Cyrus
### SASL support; to check, run 'svnserve --version' and look for a line
### reading 'Cyrus SASL authentication is available.'
# use-sasl = true
### These options specify the desired strength of the security layer
### that you want SASL to provide. 0 means no encryption, 1 means
### integrity-checking only, values larger than 1 are correlated
### to the effective key length for encryption (e.g. 128 means 128-bit
### encryption). The values below are the defaults.
# min-encryption = 0
# max-encryption = 256
配置项分为以下5项:
1.anon-access
作用:控制非鉴权用户访问版本库的权限
取值范围:“write”、“read"和"none”。"write"为可读可写,"read"为只读,"none"表示无访问权限。
缺省值:read
2.auth-access
作用:控制鉴权用户访问版本库的权限
取值范围:“write”、“read"和"none”。"write"为可读可写,"read"为只读,"none"表示无访问权限。
缺省值:write
3.password-db
作用:指定用户配置文件名。除非指定绝对路径,否则为相对于conf文件的相对路径。
缺省值:passwd
4.authz-db
作用:指定权限配置文件名,通过该文件可以实现以路径为基础的访问控制。除非指定绝对路径,否则为相对于conf文件的相对路径。
缺省值:authz
5.realm
作用:指定版本库的认证域,即在登录时提示的认证域名称。若两个版本库的认证域相同,建议使用相同的用户名口令数据文件。
缺省值:一个UUID(Universal Unique IDentifier,全局唯一标示)
修改SVN配置项文件:
[user@localhost conf]$ vim svnserve.conf
svnserve.conf推荐配置如下:
### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you
### use it to allow access to this repository. (If you only allow
### access through http: and/or file: URLs, then this file is
### irrelevant.)
### Visit http://subversion.apache.org/ for more information.
[general]
### The anon-access and auth-access options control access to the
### repository for unauthenticated (a.k.a. anonymous) users and
### authenticated users, respectively.
### Valid values are "write", "read", and "none".
### Setting the value to "none" prohibits both reading and writing;
### "read" allows read-only access, and "write" allows complete
### read/write access to the repository.
### The sample settings below are the defaults and specify that anonymous
### users have read-only access to the repository, while authenticated
### users have read and write access to the repository.
anon-access = read #修改处
auth-access = write #修改处
### The password-db option controls the location of the password
### database file. Unless you specify a path starting with a /,
### the file's location is relative to the directory containing
### this configuration file.
### If SASL is enabled (see below), this file will NOT be used.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default password file.
password-db = passwd #修改处
### The authz-db option controls the location of the authorization
### rules for path-based access control. Unless you specify a path
### starting with a /, the file's location is relative to the the
### directory containing this file. If you don't specify an
### authz-db, no path-based access control is done.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default authorization file.
authz-db = authz #修改处
### This option specifies the authentication realm of the repository.
### If two repositories have the same authentication realm, they should
### have the same password database, and vice versa. The default realm
### is repository's uuid.
# realm = My First Repository
### The force-username-case option causes svnserve to case-normalize
### usernames before comparing them against the authorization rules in the
### authz-db file configured above. Valid values are "upper" (to upper-
### case the usernames), "lower" (to lowercase the usernames), and
### "none" (to compare usernames as-is without case conversion, which
### is the default behavior).
# force-username-case = none
[sasl]
### This option specifies whether you want to use the Cyrus SASL
### library for authentication. Default is false.
### This section will be ignored if svnserve is not built with Cyrus
### SASL support; to check, run 'svnserve --version' and look for a line
### reading 'Cyrus SASL authentication is available.'
# use-sasl = true
### These options specify the desired strength of the security layer
### that you want SASL to provide. 0 means no encryption, 1 means
### integrity-checking only, values larger than 1 are correlated
### to the effective key length for encryption (e.g. 128 means 128-bit
### encryption). The values below are the defaults.
# min-encryption = 0
# max-encryption = 256
2、用户管理
SVN用户配置文件以明文存放在passwd文件中,passwd默认内容如下:
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line.
[users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
其中,[users]下面为用户名和口令,用户格式为:
用户名 = 口令
例:添加两个用户,用户1:user1,密码:123;用户2:user2,密码:abc。
首先打开passwd:
[user@localhost conf]$ vim /home/user/svn/conf/passwd
修改passwd,添加用户,修改之后的文件如下:
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line.
[users]
user1 = 123
user2 = abc
3、用户组和权限配置
SVN用户组和权限配置文件以明文存放在authz文件中,authz默认内容如下:
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve.
### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization
### files.
### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and
### (optional) repository specified by the section name.
### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to:
### - a single user,
### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section,
### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section,
### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token,
### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token,
### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard.
###
### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can
### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access
### ('').
[aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average
[groups]
# harry_and_sally = harry,sally
# harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe
# [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * =
# [repository:/baz/fuz]
# @harry_and_sally = rw
# * = r
修改authz文件,改变用户组和权限配置。
注意:
- 权限配置文件中出现的用户名必须已在用户配置文件中定义
- 对权限配置文件的修改立即生效,不必重启svn
用户组格式:
用户组 = 用户1,用户2
其中,一个用户组可以包含一个或多个用户,每个用户之间用逗号隔开。
版本库目录格式:
[版本库:/项目/目录]
@用户组名 = 权限
用户名 = 权限
其中[版本库:/项目/目录]一项,/表示根目录及以下,根目录在svnserve启动时指定。
例:将user1添加到root用户组,并设置root用户组和user用户的权限。
首先打开authz:
[user@localhost conf]$ vim /home/user/svn/conf/authz
修改authz,设置用户组并更改权限:
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve.
### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization
### files.
### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and
### (optional) repository specified by the section name.
### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to:
### - a single user,
### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section,
### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section,
### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token,
### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token,
### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard.
###
### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can
### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access
### ('').
[aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average
[groups]
root = user1
# [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * =
[/]
@root = rw
user2 = r
权限参数的取值范围:“rw”、“r"和" ”。"rw"为可读可写,“r"为只读,” "表示无访问权限。
4、关闭防火墙
开启SVN服务之前,要确保打开相应的端口,否则客户端不能访问主机,造成连接失败,可以按照下面的步骤进行操作,打开SVN服务所需端口。
1、打开“防火墙”。
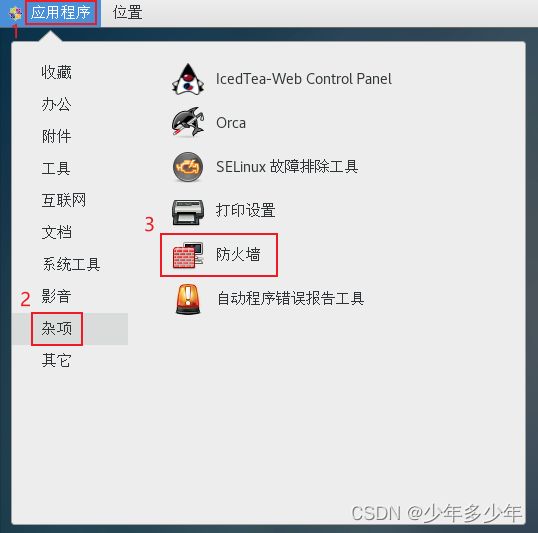
2、在“配置”处选择“永久”。
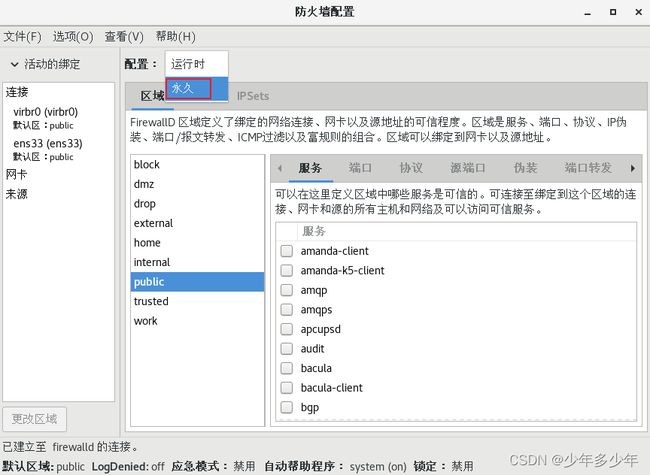
3勾选"svn",重启系统。

5、启动服务
SVN启动服务语法: svnserve -d -r 仓库目录。
例:启动路径为/home/user/svn的SVN仓库:
[user@localhost ~]$ svnserve -d -r /home/user/svn/
查看SVN进程:
[user@localhost ~]$ ps -ef|grep svn
6、访问SVN仓库
使用svn客户端 输入地址svn://ip就可以访问到SVN仓库。