pytorch—to、device、cuda差异
先说结论:
.to不仅可以更改设备torch.device还可以改变数据类型torch.dtype,拓展性最好
.device只能适用于device之间的转换,扩展性好,即使没有GPU,也可以运行代码,不用做任何修改;
.cuda只能用于将设备的cpu转换到cuda,灵活性扩展性最差,如果机器不支持GPU,则需要修改代码后才能在CPU上运行;
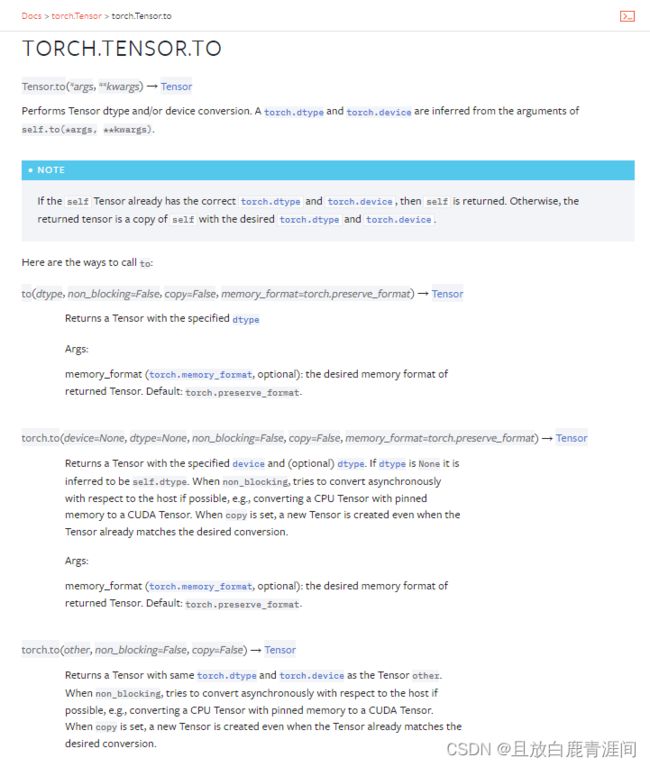
1. TORCH.TENSOR.TO
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.to.html?highlight=tensor#torch.Tensor.to
执行张量数据类型和/或所处设备的转换,dtype和device是从self.to(*args, **kwargs)中的参数推断出来的。
如果 self Tensor 已经具有正确的 torch.dtype 和 torch.device,(参数中给出的dtype和device已经是当前tensor的dtype和device),则返回 self。
否则,返回的张量是 self 的副本,具有所需的 torch.dtype 和 torch.device!!! 即返回的copy才是具有目标device的tensor!!!
import torch
print('CUDA版本:',torch.version.cuda)
print('Pytorch版本:',torch.__version__)
print('显卡是否可用:','可用' if(torch.cuda.is_available()) else '不可用')
print('显卡数量:',torch.cuda.device_count())
print('当前显卡的CUDA算力:',torch.cuda.get_device_capability(0))
print('当前显卡型号:',torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))
>>>
CUDA版本: 11.7
Pytorch版本: 1.13.1
显卡是否可用: 可用
显卡数量: 1
当前显卡的CUDA算力: (8, 6)
当前显卡型号: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Laptop GPU
tensor = torch.randn(2, 2)
tensor
>>>
tensor([[ 0.0121, 0.8552],
[-0.1244, -2.1166]])
tensor.dtype,tensor.device
>>>
(torch.float32, device(type='cpu'))
a = tensor.to(torch.float64)
tensor.dtype,a.dtype
>>>
(torch.float32, torch.float64)
# 可以用字符串形式给出
a = tensor.to('cuda:0')
tensor.device,a.device
>>>
(device(type='cpu'), device(type='cuda', index=0))
# 也可以通过torch.device给出
cuda0 = torch.device('cuda:0')
b = tensor.to(cuda0)
cuda0,tensor.device,b.device
>>>
(device(type='cuda', index=0),
device(type='cpu'),
device(type='cuda', index=0))
# 同时改变device和dtype
c = tensor.to('cuda:0',torch.float64)
c
>>>
tensor([[-0.0412, -0.6153],
[ 0.9453, -1.0264]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)
other = torch.randn((), dtype=torch.float64, device=cuda0)
d = tensor.to(other, non_blocking=True)
tensor.device,d
>>>
(device(type='cpu'),
tensor([[ 0.0121, 0.8552],
[-0.1244, -2.1166]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64))
nn.Module也可以使用.to()方法:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html?highlight=module#torch.nn.Module.to
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]])
>>> linear.to(torch.double)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> gpu1 = torch.device("cuda:1")
>>> linear.to(gpu1, dtype=torch.half, non_blocking=True)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16, device='cuda:1')
>>> cpu = torch.device("cpu")
>>> linear.to(cpu)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16)
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2, bias=None).to(torch.cdouble)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.3741+0.j, 0.2382+0.j],
[ 0.5593+0.j, -0.4443+0.j]], dtype=torch.complex128)
>>> linear(torch.ones(3, 2, dtype=torch.cdouble))
tensor([[0.6122+0.j, 0.1150+0.j],
[0.6122+0.j, 0.1150+0.j],
[0.6122+0.j, 0.1150+0.j]], dtype=torch.complex128)
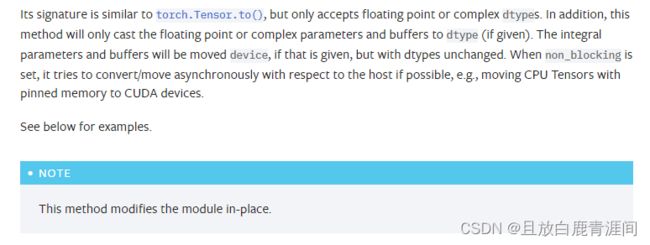
它的签名类似于 torch.Tensor.to(),但只接受浮点或复杂的数据类型。此外,此方法只会将浮点或复杂参数和缓冲区转换为 dtype(如果给定)。如果给定的话,积分参数和缓冲区将被移动设备,但数据类型不变。当设置 non_blocking 时,如果可能,它会尝试相对于主机异步转换/移动,例如,将具有固定内存的 CPU 张量移动到 CUDA 设备。
该方法对module进行就地修改!!! 也就是说,执行to方法之后,module直接就进行修改了,不用再取返回值了
2. TORCH.TENSOR.DEVICE
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensor_attributes.html#torch.device
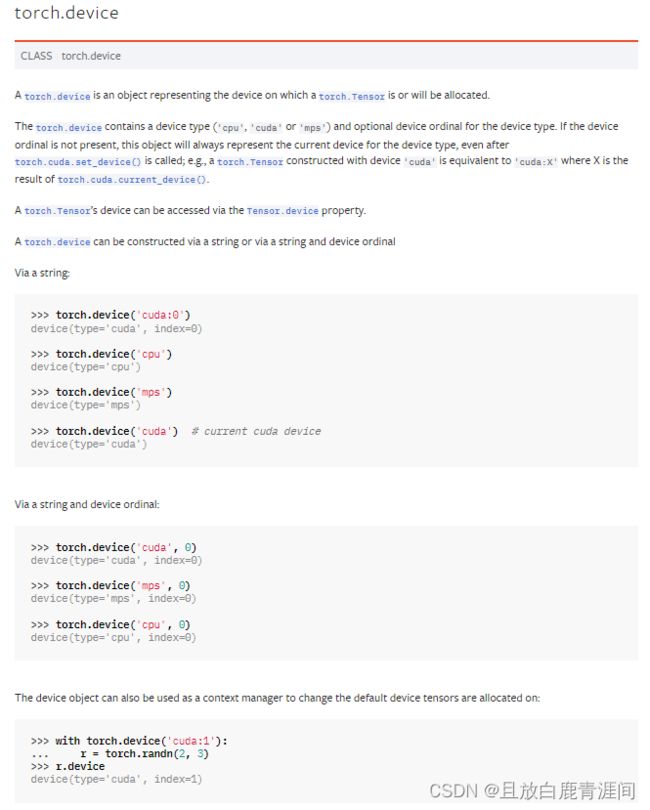
torch.device 是一个对象,表示已分配或将要分配 torch.Tensor 的设备。
torch.device 包含设备类型(“cpu”、“cuda”或“mps”)和设备类型的可选序号。如果设备序号不存在,则该对象将始终代表该设备类型的当前设备,即使在调用 torch.cuda.set_device() 之后也是如此;例如,使用设备“cuda”构造的 torch.Tensor 相当于“cuda:X”,其中 X 是 torch.cuda.current_device() 的结果。
可以通过Tensor.device属性访问torrent.Tensor的设备。
torch.device 可以通过字符串或通过字符串和设备序号构造
通过字符串:
>>> torch.device('cuda:0')
device(type='cuda', index=0)
>>> torch.device('cpu')
device(type='cpu')
>>> torch.device('mps')
device(type='mps')
>>> torch.device('cuda') # current cuda device
device(type='cuda')
通过字符串和设备序号:
>>> torch.device('cuda', 0)
device(type='cuda', index=0)
>>> torch.device('mps', 0)
device(type='mps', index=0)
>>> torch.device('cpu', 0)
device(type='cpu', index=0)
设备对象还可用作上下文管理器,用于更改张量分配的默认设备:
>>> with torch.device('cuda:1'):
... r = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> r.device
device(type='cuda', index=1)
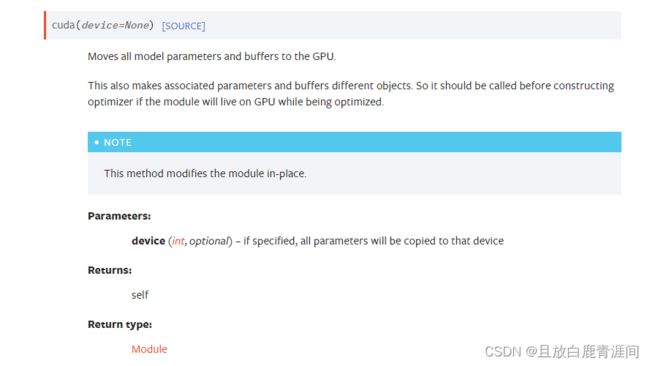
3. TORCH.TENSOR.CUDA
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.cuda.html?highlight=cuda#torch.Tensor.cuda
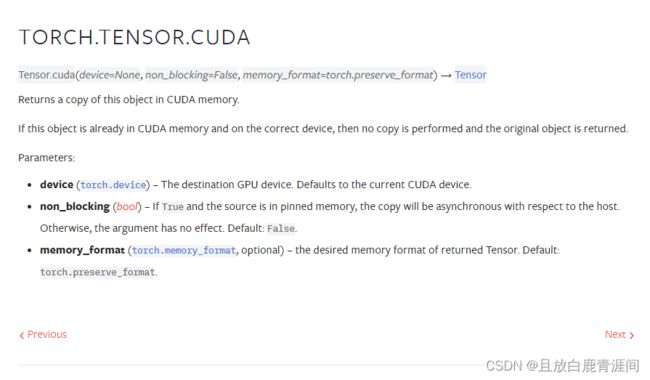
返回该对象在CUDA内存中的副本。
如果该对象已在 CUDA 内存中且在正确的设备上,则不执行复制,并返回原始对象。
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至 GPU。
这也使得相关参数和缓冲区成为不同的对象。因此,如果在优化过程中模块将在GPU上运行,则应在构建优化器之前调用它。