1.Mybtis-Plus框架基本使用
Mybatis-plus是一个mybatis的增强工具,在mybatis的基础上只做增加不做改变,简化开发
提供通用的`mapper和service` 可以在不编写任何SQL语句的情况下快速实现对单表CRUD、批量、逻辑删除、分页操作
Mybatis-plus提供优秀插件,并对idea中快速开发插件mybatisX也进行功能使用。
特性
1.耗损小,启动自动注入基本CRUD,直接面向对象,BaseMapper
2.支持Lambda形式调用,方便编写各类查询条件
3.支持主键自动生成
4.内置分页插件
1.示例1
# 构建springboot项目 依赖、配置文件
# mysql数据库连接
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#mybatis日志
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
#全局设置主键生成策略
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.id-type=auto
#扫描mybatisplus配置映射文件
mybatis-plus.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml# 测试
// 继承BaseMapper类,所有的CRUD操作编写完成
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
List selectAllByName(String name);
} 无条件查询全部
//selectList()方法的参数:封装了查询条件
//null:无任何查询条件
@Test
void testSelectList() {
List users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
} 注意:我们需要在主启动类上扫描mapper包下的所有接口@MapperScan("com.xxx.xxx")
2.示例2
# 数据库表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
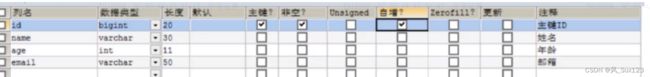
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, '[email protected]'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, '[email protected]'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, '[email protected]'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, '[email protected]'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, '[email protected]');# 依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.5.1
# 在 Spring Boot 启动类中添加 @MapperScan 注解,扫描 Mapper 文件夹:
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.baomidou.mybatisplus.samples.quickstart.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}# 编码
UserMapper中的 selectList() 方法的参数为 MP 内置的条件封装器 Wrapper
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
} # 测试
3.注解
# @TableName
描述:表名注解,标识实体类对应的表
使用位置:实体类
@Data
@TableName(value = "tb_employee")//指定表名
public class Employee {
//value与数据库主键列名一致,若实体类属性名与表主键列名一致可省略value
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)//指定自增策略
private Integer id;
//若没有开启驼峰命名,或者表中列名不符合驼峰规则,可通过该注解指定数据库表中的列名,
//exist标明数据表中,有没有对应列
@TableField(value = "last_name",exist = true)
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender;
private Integer age;
}# @TableId
描述:主键注解
使用位置:实体类主键字段
# @TableField
描述:字段注解(非主键)
# @Version
描述:乐观锁注解、标记 @Verison 在字段上
# @TableLogic
描述:表字段逻辑处理注解(逻辑删除)
# @KeySequence
描述:序列主键策略 oracle
属性:value、resultMap
# @OrderBy
描述:内置 SQL 默认指定排序,优先级低于 wrapper 条件查询@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml"}) //加载相应配置文件
public class test {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void testDataSource() throws SQLException {
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
}
}3.1mp通用crud
只需要创建 EmployeeMapper 接口, 并继承 BaseMapper 接口。接下来就使用crud方法。
// 1.插入
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml"})
public class test {
@Autowired
private EmplopyeeDao emplopyeeDao;
@Test
public void testInsert(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("东方不败");
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setGender(1);
employee.setAge(20);
emplopyeeDao.insert(employee);
//mybatisplus会自动把当前插入对象在数据库中的id写回到该实体中
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}// 2.更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(1);
employee.setLastName("更新测试");
//emplopyeeDao.updateById(employee);//根据id进行更新,没有传值的属性就不会更新
emplopyeeDao.updateAllColumnById(employee);//根据id进行更新,没传值的属性就更新为null
}// 3.查询单条
Employee employee = emplopyeeDao.selectById(1);
Employee employeeCondition = new Employee();
employeeCondition.setId(1);
employeeCondition.setLastName("更新测试");
//若是数据库中符合传入的条件的记录有多条,那就不能用这个方法,会报错
Employee employee = emplopyeeDao.selectOne(employeeCondition);
注:这个方法的sql语句就是where id = 1 and last_name = 更新测试// 4.查询多条
Map columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("last_name","东方不败");//写表中的列名
columnMap.put("gender","1");
List employees = emplopyeeDao.selectByMap(columnMap);
System.out.println(employees.size()); // 5.批量查询
List idList = new ArrayList<>();
idList.add(1);
idList.add(2);
idList.add(3);
List employees = emplopyeeDao.selectBatchIds(idList);
System.out.println(employees); // 6.分页查询
List employees = emplopyeeDao.selectPage(new Page<>(1,2),null);
System.out.println(employees); 注:selectPage方法就是分页查询,在page中传入分页信息,后者为null的分页条件,这里先让其为null,讲了条件构造器再说其用法。这个分页其实并不是物理分页,而是内存分页。也就是说,查询的时候并没有limit语句。等配置了分页插件后才可以实现真正的分页。
// 7.删除
emplopyeeDao.deleteById(1);
// 条件删除
Map columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("gender",0);
columnMap.put("age",18);
emplopyeeDao.deleteByMap(columnMap);
// 批量删除
List idList = new ArrayList<>();
idList.add(1);
idList.add(2);
emplopyeeDao.deleteBatchIds(idList); 4.测试环境
# 依赖
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter-test
3.5.1
# 通过 @MybatisPlusTest 可快速编写 Mapper 对应的测试类,实现快速测试代码5.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@MybatisPlusTest
class MybatisPlusSampleTest {
@Autowired
private SampleMapper sampleMapper;
@Test
void testInsert() {
Sample sample = new Sample();
sampleMapper.insert(sample);
assertThat(sample.getId()).isNotNull();
}
}5.主键生成策略
默认 ID_WORKER 全局唯一id
# 3.1主键自增
我们需要配置主键自增:
1.实体类字段上 @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
2.数据库字段一定要设置是自增!
3.再次测试插入即可
# 其它源码解释
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0), // 数据库id自增
NONE(1), // 未设置主键
INPUT(2), // 手动输入
ID_WORKER(3), // 默认的全局唯一id
UUID(4), // 全局唯一id uuid
ID_WORKER_STR(5); //ID_WORKER 字符串表示法
}6.更新、查询、批量查询/删除操作
所有的sql都是自动帮你动态配置的!
// 测试更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
// 通过条件自动拼接动态sql
user.setId(6L);
user.setName("关注公众号");
user.setAge(18);
// 注意:updateById 但是参数是一个对象!
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i);
}
// 测试查询
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user);
}
// 测试批量查询!
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchId(){
List users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 按条件查询之一使用map操作
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchIds(){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// 自定义要查询
map.put("name","说Java");
map.put("age",3);
List users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 测试删除
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
userMapper.deleteById(1240620674645544965L);
}
// 通过id批量删除
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchId(){
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1240620674645544961L,124062067464554496
2L));
}
// 通过map删除
@Test
public void testDeleteMap(){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","Java");
userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
} 7.自动填充
类中(时间、日期)字段 创建时间、修改时间!这些个操作一遍都是自动化完成的,我们不希望手动更新!
1、删除数据库的默认值、更新操作!
自动填充源码
2、实体类字段属性上需要增加注解
// 字段添加填充内容
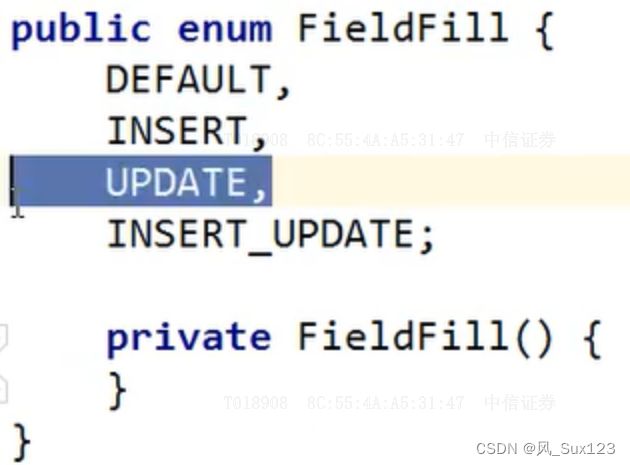
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
3、编写处理器来处理这个注解即可!
import java.util.Date;
@Slf4j
@Component // 一定不要忘记把处理器加到IOC容器中!
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
// 插入时的填充策略
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start insert fill.....");
// setFieldValByName(String fieldName, Object fieldVal, MetaObject metaObject
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
// 更新时的填充策略
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start update fill.....");
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}4、测试插入
5、测试更新、观察时间即可!
8.分页查询
1、原始的 limit 进行分页
2、pageHelper 第三方插件
3、MP 其实也内置了分页插件!
缺点
原配的分页插件,但是当数据量达到千万或者一亿条的时候,数据无法查询出来,而且爆出内存溢出的错误。
其原理是设置了一个拦截器,将数据库返回的结果集再在拦截其中做处理,达到分页的效果
1、配置拦截器组件即可
// 分页插件
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}2、直接使用Page对象即可!
// 测试分页查询
@Test
public void testPage(){
// 参数一:当前页
// 参数二:页面大小
// 使用了分页插件之后,所有的分页操作也变得简单的!
Page page = new Page<>(2,5);
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println); //获取所有记录
System.out.println(page.getTotal()); //总数
} 普通查询
@GetMapping("/test")
public Response test(){
Page producePage = new Page<>(1,2);
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("pid","price");
queryWrapper.lt("pid",5);
Page page = produceService.page(producePage, queryWrapper);
return new Response<>(page.getRecords(), ResultEnum.SUCCESS);
} lambda表达式查询
@GetMapping("/test")
public Response test(){
Page producePage = new Page<>(1,2);
Page page = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(produceService.getBaseMapper())
.select(Produce::getPid,Produce::getPrice) //查询条件
.lt(Produce::getPid,5)//id小于5
.page(producePage); //分页查询
return new Response<>(page.getRecords(), ResultEnum.SUCCESS);
} 9.逻辑删除
物理删除 :从数据库中直接移除 逻辑删除 :再数据库中没有被移除,而是通过一个变量来让他失效! deleted = 0 => deleted = 1
插入: 不作限制
查找: 追加 where条件过滤掉已删除数据,且使用 wrapper.entity 生成的 where 条件会忽略该字段
更新: 追加 where条件防止更新到已删除数据,且使用 wrapper.entity 生成的 where 条件会忽略该字段
删除: 转变为 更新
例如:
删除: update user set deleted=1 where id = 1 and deleted=0
查找: select id,name,deleted from user where deleted=0
测试一下
# 配置逻辑删除
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: flag # 全局逻辑删除的实体字段名(since 3.3.0,配置后可以忽略不配置步骤2)
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)# 1.在数据表中增加一个 deleted 字段
# 2.实体类字段上加上 @TableLogic注解
CREATE TABLE `tb_user` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
`name` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`email` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
`cre