真•Redis集群搭建之哨兵模式(详细)
概述:
主从切换技术的方法是︰当主服务后,需要手动把一台从服务器切换为主服务器,这就需要人工干预,费事费力,还会造成一段时间内服务不可用。这不是一种推荐的方式,更多时候,我们优先考虑哨兵模式,Redis从2.8开始正式提供了Sentinel (哨兵)架构来解决这个问题。哨兵模式是一种特殊的模式,首先Redis提供了哨兵的命令,哨兵是一个独立的进程,作为进程,它会独立运行。其原理是哨兵通过发送命令,等待Redis服务器响应,从而监控运行的多个Redis实例。
哨兵的作用:
通过发送命令,让Redis服务器返回监控其运行状态,包括主服务器和从服务器。
当哨兵监测到master宕机,会自动将slave切换成master,然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从服务器,修改配置文件,让它们切换主机。
然而一个哨兵进程对Redis服务器进行监控,可能会出现问题,为此,我们可以使用多个哨兵进行监控。各个哨兵之间还会进行监控,这样就形成了多哨兵横式。
通过哨兵让从机变主机的过程:
假设主服务器宕机,哨兵1先检测到这个结果,系统并不会马上进行failover过程,仅仅是哨兵1主观的认为主服务器不可用,这个现象成为主观下线。当后面的哨兵也检测到主服务器不可用,并且数量达到一定值时,那么哨兵之间就会进行一次投票,投票的结果由一个哨兵发起,进行failover[故障转移]操作。切换成功后,就会通过发布订阅模式,让各个哨兵把自己监控的从服务器实现切换主机,这个过程称为客观下线。
在搭建哨兵集群之前最好了解一下主从复制,因为哨兵模式是基于主从复制的,而且本次搭建也是基于我上一次的主从复制集群而搭建的:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_64284147/article/details/125630046
准备好三台服务器以搭建redis集群(三台虚拟机也行)
| 节点 | IP |
| master(服务器名:x86-Ken) | 10.0.0.37 |
| slave1(服务器名:x862-Ken) | 10.0.0.171 |
| slave2(服务器名:x863-Ken) | 10.0.0.225 |
一、配置哨兵配置文件
(1)找到官方的哨兵配置文件模板,然后打开(在解压缩后的redis压缩包里)![]()
PS:这是我打开的官方的哨兵配置文件模板,在本次搭建中用不了这么长的配置文件,有需要的同学可以了解一下或者拿走
#Example sentinel.conf
# By default protected mode is disabled in sentinel mode. Sentinel is reachable
# from interfaces different than localhost. Make sure the sentinel instance is
# protected from the outside world via firewalling or other means.
protected-mode no
# port
# The port that this sentinel instance will run on
port 26379
# By default Redis Sentinel does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid when
# daemonized.
daemonize no
# When running daemonized, Redis Sentinel writes a pid file in
# /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid by default. You can specify a custom pid file
# location here.
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Sentinel to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
logfile ""
# sentinel announce-ip
# sentinel announce-port
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
#
# The two options don't need to be used together, if only announce-ip is
# provided, the Sentinel will announce the specified IP and the server port
# as specified by the "port" option. If only announce-port is provided, the
# Sentinel will announce the auto-detected local IP and the specified port.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel announce-ip 1.2.3.4
# dir
# Every long running process should have a well-defined working directory.
# For Redis Sentinel to chdir to /tmp at startup is the simplest thing
# for the process to don't interfere with administrative tasks such as
# unmounting filesystems.
dir /tmp
# sentinel monitor
#
# Tells Sentinel to monitor this master, and to consider it in O_DOWN
# (Objectively Down) state only if at least sentinels agree.
#
# Note that whatever is the ODOWN quorum, a Sentinel will require to
# be elected by the majority of the known Sentinels in order to
# start a failover, so no failover can be performed in minority.
#
# Replicas are auto-discovered, so you don't need to specify replicas in
# any way. Sentinel itself will rewrite this configuration file adding
# the replicas using additional configuration options.
# Also note that the configuration file is rewritten when a
# replica is promoted to master.
#
# Note: master name should not include special characters or spaces.
# The valid charset is A-z 0-9 and the three characters ".-_".
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
# sentinel auth-pass
#
# Set the password to use to authenticate with the master and replicas.
# Useful if there is a password set in the Redis instances to monitor.
#
# Note that the master password is also used for replicas, so it is not
# possible to set a different password in masters and replicas instances
# if you want to be able to monitor these instances with Sentinel.
#
# However you can have Redis instances without the authentication enabled
# mixed with Redis instances requiring the authentication (as long as the
# password set is the same for all the instances requiring the password) as
# the AUTH command will have no effect in Redis instances with authentication
# switched off.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel auth-pass mymaster MySUPER--secret-0123passw0rd
# sentinel auth-user
#
# This is useful in order to authenticate to instances having ACL capabilities,
# that is, running Redis 6.0 or greater. When just auth-pass is provided the
# Sentinel instance will authenticate to Redis using the old "AUTH "
# method. When also an username is provided, it will use "AUTH ".
# In the Redis servers side, the ACL to provide just minimal access to
# Sentinel instances, should be configured along the following lines:
#
# user sentinel-user >somepassword +client +subscribe +publish \
# +ping +info +multi +slaveof +config +client +exec on
# sentinel down-after-milliseconds
#
# Number of milliseconds the master (or any attached replica or sentinel) should
# be unreachable (as in, not acceptable reply to PING, continuously, for the
# specified period) in order to consider it in S_DOWN state (Subjectively
# Down).
#
# Default is 30 seconds.
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 ACL capability is supported for
# Sentinel mode, please refer to the Redis website https://redis.io/topics/acl
# for more details.
# Sentinel's ACL users are defined in the following format:
#
# user ... acl rules ...
#
# For example:
#
# user worker +@admin +@connection ~* on >ffa9203c493aa99
#
# For more information about ACL configuration please refer to the Redis
# website at https://redis.io/topics/acl and redis server configuration
# template redis.conf.
# ACL LOG
#
# The ACL Log tracks failed commands and authentication events associated
# with ACLs. The ACL Log is useful to troubleshoot failed commands blocked
# by ACLs. The ACL Log is stored in memory. You can reclaim memory with
# ACL LOG RESET. Define the maximum entry length of the ACL Log below.
acllog-max-len 128
# Using an external ACL file
#
# Instead of configuring users here in this file, it is possible to use
# a stand-alone file just listing users. The two methods cannot be mixed:
# if you configure users here and at the same time you activate the external
# ACL file, the server will refuse to start.
#
# The format of the external ACL user file is exactly the same as the
# format that is used inside redis.conf to describe users.
#
# aclfile /etc/redis/sentinel-users.acl
# requirepass
#
# You can configure Sentinel itself to require a password, however when doing
# so Sentinel will try to authenticate with the same password to all the
# other Sentinels. So you need to configure all your Sentinels in a given
# group with the same "requirepass" password. Check the following documentation
# for more info: https://redis.io/topics/sentinel
#
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 "requirepass" is a compatibility
# layer on top of the ACL system. The option effect will be just setting
# the password for the default user. Clients will still authenticate using
# AUTH as usually, or more explicitly with AUTH default
# if they follow the new protocol: both will work.
#
# New config files are advised to use separate authentication control for
# incoming connections (via ACL), and for outgoing connections (via
# sentinel-user and sentinel-pass)
#
# The requirepass is not compatible with aclfile option and the ACL LOAD
# command, these will cause requirepass to be ignored.
# sentinel sentinel-user
#
# You can configure Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels with specific
# user name.
# sentinel sentinel-pass
#
# The password for Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels. If sentinel-user
# is not configured, Sentinel will use 'default' user with sentinel-pass to authenticate.
# sentinel parallel-syncs
#
# How many replicas we can reconfigure to point to the new replica simultaneously
# during the failover. Use a low number if you use the replicas to serve query
# to avoid that all the replicas will be unreachable at about the same
# time while performing the synchronization with the master.
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
# sentinel failover-timeout
#
# Specifies the failover timeout in milliseconds. It is used in many ways:
#
# - The time needed to re-start a failover after a previous failover was
# already tried against the same master by a given Sentinel, is two
# times the failover timeout.
#
# - The time needed for a replica replicating to a wrong master according
# to a Sentinel current configuration, to be forced to replicate
# with the right master, is exactly the failover timeout (counting since
# the moment a Sentinel detected the misconfiguration).
#
# - The time needed to cancel a failover that is already in progress but
# did not produced any configuration change (SLAVEOF NO ONE yet not
# acknowledged by the promoted replica).
#
# - The maximum time a failover in progress waits for all the replicas to be
# reconfigured as replicas of the new master. However even after this time
# the replicas will be reconfigured by the Sentinels anyway, but not with
# the exact parallel-syncs progression as specified.
#
# Default is 3 minutes.
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
# SCRIPTS EXECUTION
#
# sentinel notification-script and sentinel reconfig-script are used in order
# to configure scripts that are called to notify the system administrator
# or to reconfigure clients after a failover. The scripts are executed
# with the following rules for error handling:
#
# If script exits with "1" the execution is retried later (up to a maximum
# number of times currently set to 10).
#
# If script exits with "2" (or an higher value) the script execution is
# not retried.
#
# If script terminates because it receives a signal the behavior is the same
# as exit code 1.
#
# A script has a maximum running time of 60 seconds. After this limit is
# reached the script is terminated with a SIGKILL and the execution retried.
# NOTIFICATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel notification-script
#
# Call the specified notification script for any sentinel event that is
# generated in the WARNING level (for instance -sdown, -odown, and so forth).
# This script should notify the system administrator via email, SMS, or any
# other messaging system, that there is something wrong with the monitored
# Redis systems.
#
# The script is called with just two arguments: the first is the event type
# and the second the event description.
#
# The script must exist and be executable in order for sentinel to start if
# this option is provided.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh
# CLIENTS RECONFIGURATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script
#
# When the master changed because of a failover a script can be called in
# order to perform application-specific tasks to notify the clients that the
# configuration has changed and the master is at a different address.
#
# The following arguments are passed to the script:
#
#
#
# is currently always "start"
# is either "leader" or "observer"
#
# The arguments from-ip, from-port, to-ip, to-port are used to communicate
# the old address of the master and the new address of the elected replica
# (now a master).
#
# This script should be resistant to multiple invocations.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
# SECURITY
#
# By default SENTINEL SET will not be able to change the notification-script
# and client-reconfig-script at runtime. This avoids a trivial security issue
# where clients can set the script to anything and trigger a failover in order
# to get the program executed.
sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
# REDIS COMMANDS RENAMING
#
# Sometimes the Redis server has certain commands, that are needed for Sentinel
# to work correctly, renamed to unguessable strings. This is often the case
# of CONFIG and SLAVEOF in the context of providers that provide Redis as
# a service, and don't want the customers to reconfigure the instances outside
# of the administration console.
#
# In such case it is possible to tell Sentinel to use different command names
# instead of the normal ones. For example if the master "mymaster", and the
# associated replicas, have "CONFIG" all renamed to "GUESSME", I could use:
#
# SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG GUESSME
#
# After such configuration is set, every time Sentinel would use CONFIG it will
# use GUESSME instead. Note that there is no actual need to respect the command
# case, so writing "config guessme" is the same in the example above.
#
# SENTINEL SET can also be used in order to perform this configuration at runtime.
#
# In order to set a command back to its original name (undo the renaming), it
# is possible to just rename a command to itself:
#
# SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG CONFIG
# HOSTNAMES SUPPORT
#
# Normally Sentinel uses only IP addresses and requires SENTINEL MONITOR
# to specify an IP address. Also, it requires the Redis replica-announce-ip
# keyword to specify only IP addresses.
#
# You may enable hostnames support by enabling resolve-hostnames. Note
# that you must make sure your DNS is configured properly and that DNS
# resolution does not introduce very long delays.
#
SENTINEL resolve-hostnames no
# When resolve-hostnames is enabled, Sentinel still uses IP addresses
# when exposing instances to users, configuration files, etc. If you want
# to retain the hostnames when announced, enable announce-hostnames below.
#
SENTINEL announce-hostnames no
# When master_reboot_down_after_period is set to 0, Sentinel does not fail over
# when receiving a -LOADING response from a master. This was the only supported
# behavior before version 7.0.
#
# Otherwise, Sentinel will use this value as the time (in ms) it is willing to
# accept a -LOADING response after a master has been rebooted, before failing
# over.
SENTINEL master-reboot-down-after-period mymaster 0
(2)配置sentinel.conf文件
新建一个sentinel.conf文件(哨兵程序只会识别名为sentinel.conf的文件),然后往该文件写入以下参数(PS:以下的参数都能在以上的官方模板中找到;如果没设置redis的登录密码,则可以不需要第二段的参数;部分没配置的参数在启动哨兵时会按默认参数来启动)
#monitor表示监控
#redis_master表示被监控的主机名称
#10.0.0.37表示IP地址
#6379表示端口
#1这个数字表示哨兵判断主节点死亡的次数,即当有1个哨兵判断主节点死亡,则开始投票选举新的主节点的程序
sentinel monitor 主机名称 IP地址 1
#被监控redis的登录密码
sentinel auth-pass 主机名称 密码例:
(3)把这个配置文件复制或者上传到另外两台服务器上(为了本次搭建更贴近实际开发而使用了3个哨兵)
二、启动哨兵(前提是redis服务启动了,主从复制模式成功运行,没有弄好主从复制的就去看看我的另一篇文章再来继续搭建:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_64284147/article/details/125630046)
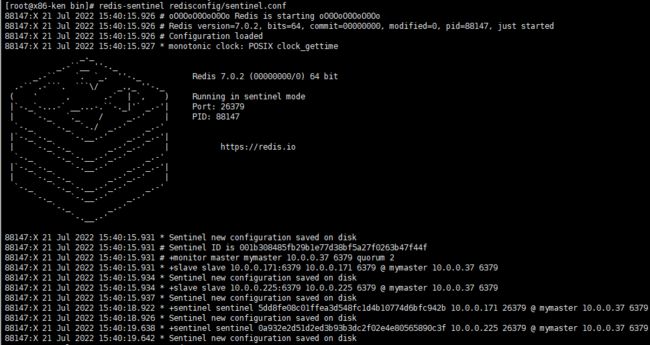
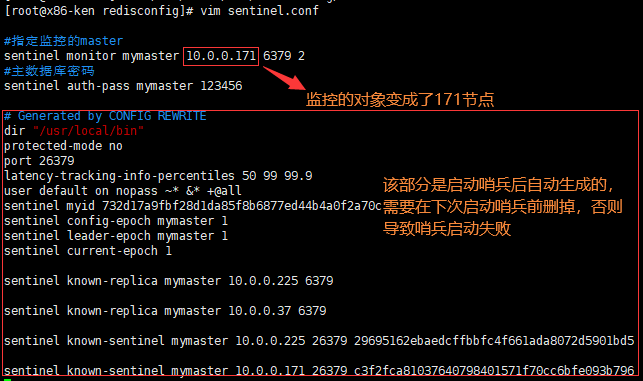
通过redis-sentinel命令根据配置文件的参数来启动每一台服务器上的哨兵(注意!!!在启动哨兵后sentinel.conf会自动生成一段参数,需要在下次启动哨兵前去掉,否则会导致启动失败;在启动哨兵前请确认安全组和防火墙是否开放了6379端口和26379端口,若没开放6379端口,会导致master和slave主观下线,若没开放26379端口,会导致各个哨兵之间不能通讯,导致在哨兵启动后显示其他哨兵sdown的情况;在配置哨兵前请确保服务器之间能互相访问)
例:
redis-sentinel redisconfig/sentinel.conf自动生成的参数:
哨兵运行效果图:
master:
slave1:
slave2:
三、测试在哨兵模式下的故障转移功能是否正常运行
(1)打印各个节点的redis的信息
master:
slave1:
slave2:
(2)在master上给字段赋值
master:
slave1:
slave2:
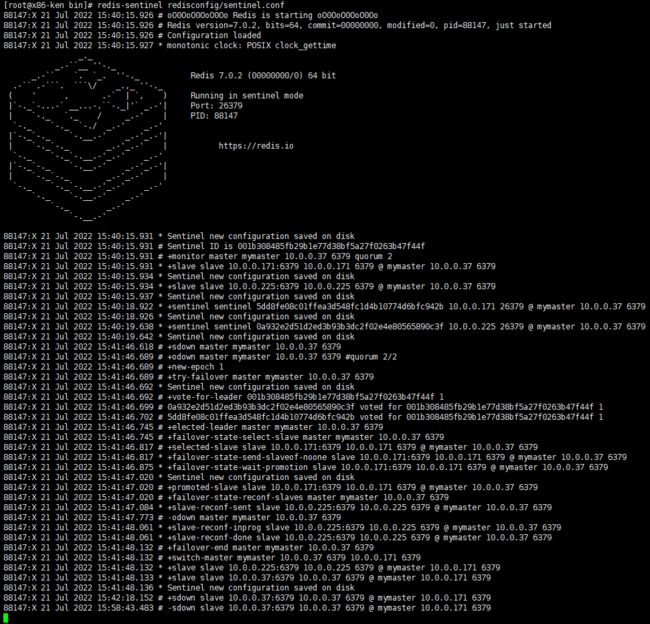
(3)关闭37节点上的redis,让角色为master的redis下线
哨兵运行的日志:
master:
slave1:
slave2:
(4)重新查看各个节点的redis的信息
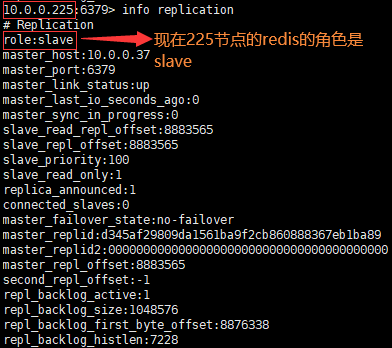
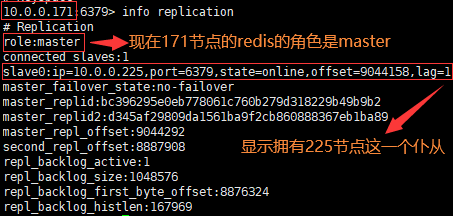
新master:
显示171节点的redis的角色变为maste,并且拥有225节点的redis这一仆从,证明哨兵模式正常运行,让171节点的redis在37节点的redis挂了后成功逆袭上位
slave:
(5)查看数据有无丢失
新master:
![]()
slave:
![]()
(6)主从复制是否正常
新 master:
显示新master能正常写入数据
slave:
显示slave能读取master的数据,并且不能写入数据
(7)让下线的master重新上线
哨兵运行的日志:
新master:
slave1:
原master的redis的打印信息:
(8)查看主从复制是否能顺利运行
显示变成仆从的37节点的redis能读取未下线前的name的数据,以及能读取下线后171变成master后存入的age的数据,并且不能写入数据
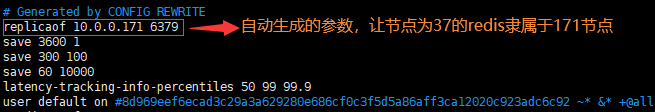
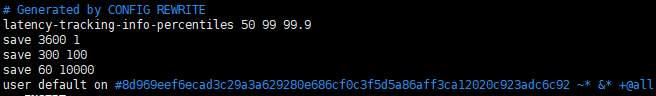
(9)查看主从切换后的redis.conf参数(生成的参数在最下面)
原master:
新master:
slave:
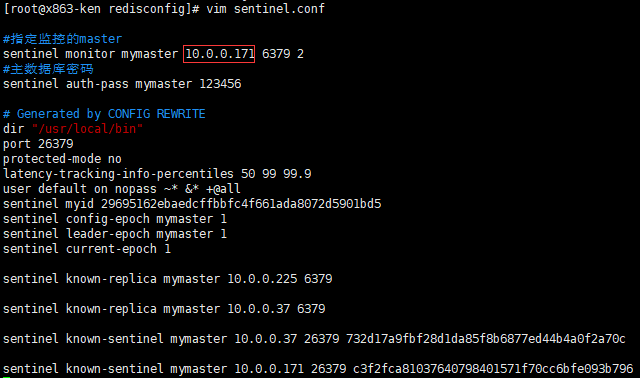
(10)查看主从切换后的sentinel.conf参数
原master:
新master:
slave:
其他:
一、在启动哨兵后,sentinel.conf会自动生成一段参数,需要在下次启动哨兵前去掉,否则下次启动时影响哨兵的运行。
二、注意在启动哨兵前,确认安全组和防火墙是否开放了26379这一个端口,若没开放,会导致各个哨兵之间不能通讯,从而发生在哨兵启动后显示其他哨兵sdown的情况
三、哨兵模式的优缺点
哨兵模式的优点:
1、哨兵模式,基于主从复制模式,所有主从模式的优点,它全都有
2、主从可以在发生故障时自动切换,数据可以转移,所以系统的可用性和健壮性会更好
缺点∶
1、Redis不好在线扩容,集群容量一旦到达数量上限,集群扩容就十分麻烦(需要大量的修改配置文件来配置主从关系)
2、实际开发中,实现哨兵模式的配置其实是很麻烦的,远不止我此次配置的两个参数这么简单