k8s - container
1、容器的生命周期:
(1) 简介:
Kubernetes 会跟踪 Pod 中每个容器的状态,就像它跟踪 Pod 总体上的阶段一样。 可以使用容器生命周期回调,在容器生命周期中的特定状态点触发事件。
● 容器生命周期回调:
在容器的生命周期中,可以利用容器生命周期回调来安排特定时间点执行某些任务或触发事件,例如在容器停止时进行清理操作。
(2) 容器状态:
① 种类:
容器的状态有三种: Waiting (等待)、Running (运行中) 和 Terminated (已终止)。
要检查 Pod 中容器的状态,可以使用 kubectl describe pod
② 状态含义:
● Waiting:如果容器并不处在 Running 或 Terminated 状态之一,它就处在 Waiting 状态。 处于 Waiting 状态的容器仍在运行它完成启动所需要的操作。
当使用 kubectl 来查询包含 Waiting 状态的容器的 Pod 时,可以看到一个 Reason 字段,其中给出了容器处于等待状态的原因。
● Running:Running 状态表明容器正在执行状态并且没有问题发生。 如果配置了 postStart 回调,那么该回调已经执行且已完成。
如果 kubectl 来查询包含 Running状态的容器的 Pod 时,可以看到关于容器进入 Running 状态的信息。
● Terminated:处于 Terminated 状态的容器已经开始执行或者正常结束或者因为某些原因失败。
如果使用 kubectl 来查询包含 Terminated 状态的容器的 Pod 时, 可以看到容器进入此状态的原因、退出代码以及容器执行期间的起止时间。
如果容器配置了 preStop 回调,则该回调会在容器进入 Terminated 状态之前执行。
2、容器生命周期回调:
(1) 两个回调:
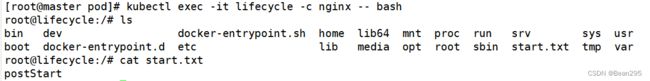
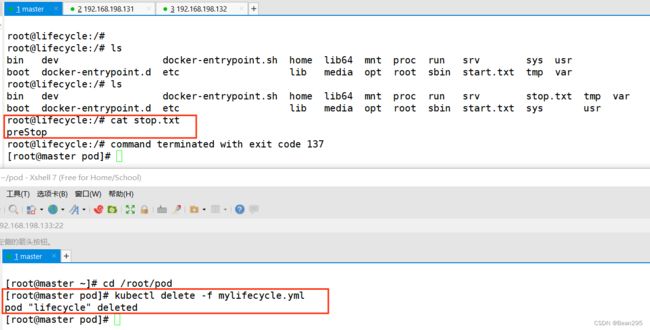
① postStart:postStart 是一个容器的生命周期事件,用于在容器完全启动之后运行的命令或操作。可以利用 postStart 执行容器启动后的初始化工作,例如准备环境、加载数据、连接外部服务等,确保容器已经启动并且可以处理请求。
② preStop:与 postStart 相对,preStop 是容器停止之前的生命周期事件。当收到停止信号时,在容器正式停止之前,Kubernetes 会调用 preStop ,允许容器在终止之前执行一些清理工作或保存状态。
(2) 示例:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: lifecycle
labels:
app: lifecycle
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","echo postStart >> /start.txt"]
#-c:执行命令 在容器创建后输出 postStart 到 start.txt
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","echo preStop >> /stop.txt && sleep 30"]
#在容器停止前输出 preStop 到 stop.txt,等待30秒后再停止容器
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always3、容器重启策略:
(1) 简介:
Pod 的 spec 中包含一个 restartPolicy 字段,其作用在于控制在容器终止后 Kubernetes 如何处理容器的重启,取值包括 Always(总是重启)、OnFailure(容器异常退出重启) 和 Never ,默认值是 Always 。
restartPolicy 适用于 Pod 中的所有容器。
(2) 示例:
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always4、自定义容器启动命令:
(1) 简介:
k8s中可以修改容器启动默认执行命令以及传递相关参数。推荐使用 command 修改启动命令,args 为启动命令传递参数。
(2) 示例:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: redis
labels:
app: redis
spec:
containers:
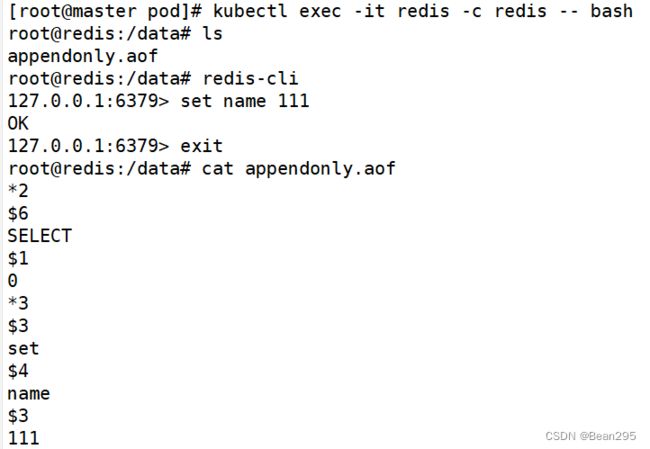
- name: redis
image: redis:5.0.10
command: ["redis-server"]
args: ["--appendonly yes"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always5、容器探针:
(1) 概念:
probe 是由 kubelet 对容器执行的定期诊断。 要执行诊断,kubelet 既可以在容器内执行代码,也可以发出⼀个网络请求。(用于定期对容器进行健康检查)
(2) 探针类型:
① livenessProbe (存活探针):指示容器是否正在运行。如果存活态探测失败,则 kubelet 会杀死容器,容器将根据其重启策略决定是否重启。
② readinessProbe (就绪探针):指示容器是否准备好为请求提供服务。如果就绪态探测失败,端点控制器将从与 Pod 匹配的所有服务的端点列表中删除该 Pod 的 IP 地址。
③ startupProbe 1.7+ (启动探针):指示容器中的应用是否已经启动。如果提供了启动探针,其他探针都会被禁用,直到此探针成功为止。如果启动探测失败, kubelet 将杀死容器,容器依其重启策略进行重启。
(3) 探针机制:
① exec:在容器内执行指定命令。如果命令退出时返回码为 0 则认为诊断成功。
② grpc:使用 grpc 执行远程过程调用。 如果响应的状态是 "SERVING",则认为诊断成功。
③ httpGet:对容器的 IP 地址上指定端口和路径执行 HTTP GET 请求。如果响应的状态码大于等于 200 且小于 400,则诊断被认为是成功的。
④ tcpSocket:对容器的 IP 地址上的指定端口执行 TCP 检查。如果端口打开,则诊断被认为是成功。
(4) 探针结果:
Success:成功,容器通过了诊断。
Failure:失败,容器未通过诊断。
Unknown:未知,诊断失败,不会采取任何行动。
(5) 探针参数:
① initialDelaySeconds:初始延迟时间,等待多久后开始第一次探针检测。
② periodSeconds:探测周期,指定探针检测的时间间隔,定义了连续进行健康状态检查的频率。
③ timeoutSeconds:超时时间,探针等待容器响应的最长时间,如果在此时间内没有得到响应,则该探测被视为失败。
④ failureThreshold:失败阈值,定义了连续失败的次数,达到该次数后探测器将认定探测失败。
⑤ successThreshold:成功阈值,定义了连续成功的次数,达到该次数后探测器将认定探测成功。
(6) 探针使用:
① exec:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec: #使用 exec 机制执行命令,通过查看是否有 pid 文件来检测容器状态。
command:
- ls
- /var/run/nginx.pid
initialDelaySeconds: 5 #初始化时间 5s
periodSeconds: 4 #检测间隔时间 4s
timeoutSeconds: 1 #默认检测超时时间为 1s
failureThreshold: 3 #默认失败次数为 3次,达到 3次后重启 pod
successThreshold: 1 #默认成功次数为 1次,1次代表成功
restartPolicy: Always② tcpsocker:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 5 #初始化时间 5s
periodSeconds: 4 #检测间隔时间 4s
timeoutSeconds: 1 #默认检测超时时间为 1s
failureThreshold: 3 #默认失败次数为 3次,达到 3次后重启 pod
successThreshold: 1 #默认成功次数为 1次,1次代表成功
restartPolicy: Always6、容器资源限制:
(1) 种类:
① 内存资源限制: 内存请求 (request) 和内存限制 (limit) 分配给一个容器,保障容器拥有它请求数量的内存,但不允许使用超过限制数量的内存。
② CPU 资源限制: 为容器设置 CPU request 和 CPU limit。 给容器分配其所请求数量的 CPU 资源,容器使用的 CPU 不能超过所配置的限制。
● 请求:基础资源 ;限制:最大资源
(2) metrics-server:
① 简介:
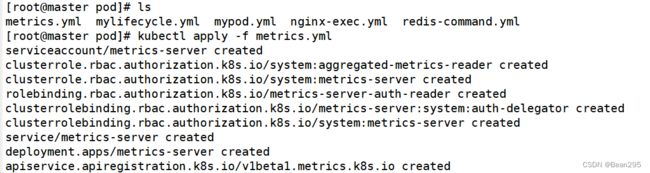
Kubernetes Metrics Server (Kubernetes指标服务器),是一个可扩展的、高效的容器资源度量源。Metrics Server 用于监控每个 Node 和 Pod 的负载。Metrics Server 从 Kubelets 收集资源指标,并通过 Metrics API 在 Kubernetes apiserver中公开。
Metrics API 可以通过kubectl top 访问,使其更容易调试自动扩缩管道。
② 安装 metrics-server:
vim components.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: system:aggregated-metrics-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/metrics
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server-auth-reader
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: extension-apiserver-authentication-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server:system:auth-delegator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:auth-delegator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:metrics-server
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
k8s-app: metrics-server
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls #修改去掉证书验证
image: dyrnq/metrics-server:v0.6.2 #修改官方无法下载
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /livez
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
periodSeconds: 10
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /readyz
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 20
periodSeconds: 10
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-dir
hostNetwork: true #必须指定这个才行
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
serviceAccountName: metrics-server
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: tmp-dir
---
apiVersion: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: APIService
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
spec:
group: metrics.k8s.io
groupPriorityMinimum: 100
insecureSkipTLSVerify: true
service:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
version: v1beta1
versionPriority: 100kubectl top pod pod名:
(3) 指定内存请求和限制:
① 简介:
为容器指定内存请求,可以在容器资源清单中包含 resources:requests 字段 ;要指定内存限制,可以包含 resources:limits。
内存资源的基本单位是字节(byte)。可以使用这些后缀之⼀,将内存表示为 纯整数或定点整数:E、P、T、G、M、K、Ei、Pi、Ti、Gi、Mi、Ki。
② 示例:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests: #请求
memory: "100Mi"
limits: #限制
memory: "200Mi"
restartPolicy: Always③ 内存请求和限制的目的:
通过为集群中运行的容器配置内存请求和限制,可以有效利用集群节点上可用的内存资源;将 Pod 的内存请求保持在较低水平,可以更好安排 Pod 调度。
● 内存限制大于内存请求的作用:
Pod 可以进行一些突发活动,从而更好的利用可用内存。
Pod 在突发活动期间,可使用的内存被限制为合理的数量。
(4) 指定CPU请求和限制:
① 简介:
CPU 资源以 CPU 单位度量。小数值是可以使用的。一个请求 0.5 CPU 的容器会获得请求 1 个 CPU 的容器的 CPU 的一半。 可以使用后缀 m 表示毫。例如 100mCPU、100 milliCPU 和 0.1 CPU 都相同。
② 示例:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
limits:
cpu: 200m
restartPolicy: Always