算法笔记—链表、队列和栈
链表、队列和栈
- 1. 链表
-
- 1.1 单链表反转
- 1.2 双链表反转
- 1.3 合并两个有序链表
- 1.4 链表相加
- 1.5 划分链表
- 2. 队列和栈
-
- 2.1 循环队列
- 2.2 栈实现队列
- 2.3 队列实现栈
- 2.4 最小栈
- 2.2 双端队列
1. 链表
1.1 单链表反转
- 力扣 反转链表
// 反转单链表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next; // next指向head.next指的位置
head.next = pre; // head.next指向pre指向的位置
pre = head; // pre指向head指向的位置
head = next; // head指向next指向的位置
}
return pre;
}
// 单链表节点定义
public static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
1.2 双链表反转
// 反转双链表
public static DoubleListNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleListNode head) {
DoubleListNode pre = null;
DoubleListNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
head.last = next;// 同时修改last指针即可
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 双链表节点
public static class DoubleListNode {
public int value;
public DoubleListNode last;
public DoubleListNode next;
public DoubleListNode(int v) {
value = v;
}
}
1.3 合并两个有序链表
- 力扣链接
// 合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return head1 == null ? head2 : head1;
}
//谁小谁做头
ListNode head = head1.val <= head2.val ? head1 : head2;
ListNode cur1 = head.next;
// 另一个链表的头结点
ListNode cur2 = head == head1 ? head2 : head1;
// 已挂好(处理好)节点的前一个
ListNode pre = head;
// 只要都没完 谁小谁挂在pre之后
while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
if (cur1.val <= cur2.val) {
pre.next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
// 若有一个链表结束 另一个剩余的挂在pre之后
pre.next = cur1 != null ? cur1 : cur2; //剩余部分
return head;
}
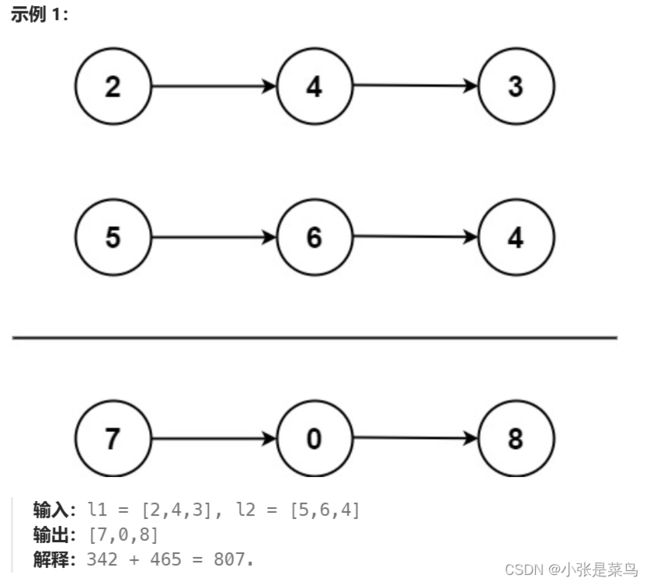
1.4 链表相加
力扣 两数相加
给你两个非空的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照逆序的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储一位数字。
// 链表两数相加 没有复用老链表
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode h1, ListNode h2) {
ListNode ans = null, cur = null; // 初始化新链表
int carry = 0; // 进位数 加法的进位只能为 0 或者 1
for (int sum, val; // 声明变量
h1 != null || h2 != null; // 循环条件
h1 = h1 == null ? null : h1.next, // 每一轮h1的跳转
h2 = h2 == null ? null : h2.next // 每一轮h2的跳转
) {
sum = (h1 == null ? 0 : h1.val)
+ (h2 == null ? 0 : h2.val)
+ carry; // 上一轮的进位
// 组建新链表
val = sum % 10; // 个位
carry = sum / 10; // 进位
if (ans == null) {
ans = new ListNode(val);
cur = ans;
} else {
cur.next = new ListNode(val);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 判断最后一位有无进位 若有则挂 1 节点
if (carry == 1) {
cur.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return ans;
}
1.5 划分链表
力扣 分隔链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
- 你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
public static ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode leftHead = null, leftTail = null;
ListNode rightHead = null, rightTail = null;
ListNode next = null;
// 终止条件
while (head != null) {
next = head.next; //记录一下下一位置 因为要断链
head.next = null;
// 小于范围
if (head.val < x) {
// set head
if (leftHead == null) {
leftHead = head;
} else {
leftTail.next = head;
}
// set tail
leftTail = head;
// 大于范围
} else {
if (rightHead == null) {
rightHead = head;
} else {
rightTail.next = head;
}
rightTail = head;
}
head = next; // 处理下一节点
}
// 默认返回左头 这里对左头进行判断
// 如果没有小于的 直接返回右头结点
if (leftHead == null){
return rightHead;
}
leftTail.next = rightHead;
return leftHead;
}
// 单链表节点
public static class ListNode {
public int val;
public Video_012.ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, Video_012.ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
2. 队列和栈
2.1 循环队列
力扣 设计循环队列
class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] queue;
public int l, r, size, limit;
// 同时在队列里的数字个数,不要超过k
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
queue = new int[k];
l = r = size = 0;
limit = k;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
queue[r] = value;
// r++, 结束了,跳回0
r = r == limit - 1 ? 0 : (r + 1);
size++;
return true;
}
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
// l++, 结束了,跳回0
l = l == limit - 1 ? 0 : (l + 1);
size--;
return true;
}
}
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return queue[l];
}
}
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
int last = r == 0 ? (limit - 1) : (r - 1);
return queue[last];
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == limit;
}
}
2.2 栈实现队列
力扣
class MyQueue {
public Stack<Integer> in;
public Stack<Integer> out;
public MyQueue() {
in = new Stack<Integer>();
out = new Stack<Integer>();
}
// 倒数据
// 从in栈,把数据倒入out栈
// 1) out空了,才能倒数据
// 2) 如果倒数据,in必须倒完
private void inToOut() {
if (out.empty()) {
while (!in.empty()) {
out.push(in.pop());
}
}
}
public void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
inToOut();
}
public int pop() {
inToOut();
return out.pop();
}
public int peek() {
inToOut();
return out.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
}
}
2.3 队列实现栈
力扣
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// O(n)
public void push(int x) {
int n = queue.size();
queue.offer(x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
2.4 最小栈
力扣
class MinStack {
public final int MAXN = 8001;
public int[] data;
public int[] min;
int size;
public MinStack() {
data = new int[MAXN];
min = new int[MAXN];
size = 0;
}
public void push(int val) {
data[size] = val;
if (size == 0 || val <= min[size - 1]) {
min[size] = val;
} else {
min[size] = min[size - 1];
}
size++;
}
public void pop() {
size--;
}
public int top() {
return data[size - 1];
}
public int getMin() {
return min[size - 1];
}
}
2.2 双端队列
力扣 设计循环双端队列
- 双向链表实现
// 双向链表实现
// 常数操作慢,但是leetcode数据量太小了,所以看不出劣势
class MyCircularDeque {
public Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();// Java自带的双向链表
public int size;
public int limit;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
size = 0;
limit = k;
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
deque.offerFirst(value);
size++;
return true;
}
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
deque.offerLast(value);
size++;
return true;
}
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
size--;
deque.pollFirst();
return true;
}
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
size--;
deque.pollLast();
return true;
}
}
public int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return deque.peekFirst();
}
}
public int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return deque.peekLast();
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == limit;
}
}
- 数组实现
// 用数组实现,常数操作快
// 但是leetcode数据量太小了,看不出优势
/*
数组长度为 k
头部加入a, l==0 a放在k-1位置, l来到k-1
l!=0 a放在l-1位置, l--
头部弹出a, l==k-1 返回a l来到0
l!=k-1 返回a l++
尾部加入a r==k-1 a放在0位置 r来到0
r!=k-1 a放在r+1位置 r++
尾部弹出a, r==0 返回a, r来到k-1
r!=0 返回a, r--
*/
class MyCircularDeque {
public int[] deque;
public int l, r, size, limit;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
deque = new int[k];
l = r = size = 0;
limit = k;
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
if (isEmpty()) {
l = r = 0;
deque[0] = value;
} else {
// 头插 l-- 插入数值 边界判断
l = l == 0 ? (limit - 1) : (l - 1);
deque[l] = value;
}
size++;
return true;
}
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
if (isEmpty()) {
l = r = 0;
deque[0] = value;
} else {
# 尾插 r++ 插入数值 边界判断
r = r == limit - 1 ? 0 : (r + 1);
deque[r] = value;
}
size++;
return true;
}
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
l = (l == limit - 1) ? 0 : (l + 1);
size--;
return true;
}
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
r = r == 0 ? (limit - 1) : (r - 1);
size--;
return true;
}
}
public int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return deque[l];
}
}
public int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return deque[r];
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == limit;
}
}