Spring MVC
文章目录
- Spring MVC 是什么
- 什么是 MVC
- 如何学习 Spring MVC
- Spring MVC 创建和连接
- 获取参数
-
- 传统方式
- 简便的方式
- 获取一个自定义类的对象
- 从 json 字符串获取对象
- 获取文件
- 获取 Cookie/Session/Header
- 参数重命名
- 非必传参数
- 获取url路径中的参数
- 请求转发和请求重定向
Spring MVC 是什么
Spring MVC 全称 Spring Web MVC,又称为 Spring Web
- Spring MVC 是一个 Web 框架
- Spring MVC 是基于 Servlet API 构建的
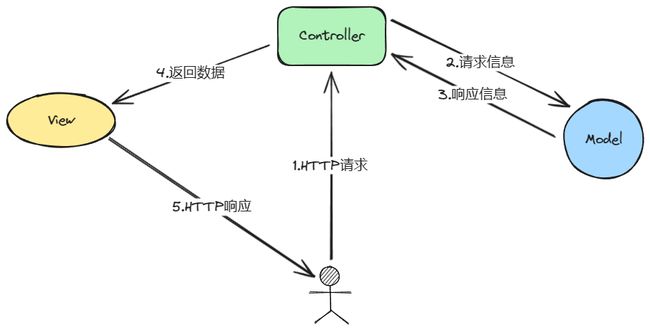
什么是 MVC
“MVC” 代表模型-视图-控制器(Model-View-Controller)。这是一种设计模式,用于构建具有良好组织结构的应用程序,以便更好地管理代码和提高可维护性。
- Model 代表应用程序中处理数据和业务逻辑的部分。在Spring MVC中,模型通常由Java对象组成,这些对象负责封装和处理数据,以及执行与应用程序相关的业务逻辑。
- View 负责渲染和显示模型的数据。在Web应用中,视图通常是用户界面的一部分,负责将模型的数据以用户友好的方式呈现出来。视图不处理业务逻辑,它只关注如何正确地显示数据。
- Controller 是模型和视图之间的中介,负责接收用户的输入,处理用户请求,并更新模型和视图。它将用户的请求路由到适当的模型处理程序,然后将模型的数据传递给适当的视图进行显示。控制器的目标是保持模型和视图之间的解耦,使应用程序更加灵活和易于扩展。
如何学习 Spring MVC
学习 Spring MVC 最关注以下 3 个功能:
- 连接:将用户(浏览器)和 Java 程序连接起来,也就是访问一个地址能够调用到我们的 Spring 程序。
- 获取参数:用户访问的时候会带一些参数,在程序中要想办法获取到参数
- 输出数据:执行业务逻辑之后,把程序执行的结果返回给用户
Spring MVC 创建和连接
在创建 Spring Boot 项目的时候,我们已经引入了 Spring Web 依赖,引入这个依赖,我们的项目就是一个 Spring MVC 项目。
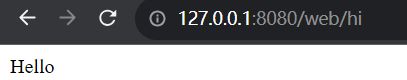
例:通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/web/hi 来返回 Hello
package com.example.spring_mvc_demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller // 类注解,在 Spring 启动的时候加载并注册
@ResponseBody // 当前类返回的非静态页面
@RequestMapping("/web") // 当使用 /web 可以访问到当前类
public class WebController {
@RequestMapping("/hi") // 当使用 /web/hi 可以访问到当前方法
public Object hi() {
return "Hello";
}
}
@ResponseBody用于标识控制器方法的返回值应该直接作为 HTTP 响应的主体部分,而不是视图解析器渲染成视图。@RequestMapping可以应用在类级别和方法级别,用于定义 URL 映射规则,将 HTTP 请求映射到相应的控制器方法上。
结果:
注意:
- 如果不加
@ResponseBody,那么返回的就是一个视图,也就是 html 文件的路径 @Controller不可替换为其他类注解(如@Service、@Component)
@RestController,相当于 @Controller + @ResponseBody
更简单的写法:
package com.example.spring_mvc_demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class WebController {
@RequestMapping("/hi") // 当使用 /hi 可以访问到当前方法
public Object hi() {
return "Hello";
}
}
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/hi 就可以看到 Hello 了。
@RequestMapping 默认支持所有请求方法,可以通过指定 method 属性使其只匹配某一种请求方法:
@RequestMapping(value = "/greet", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String greet() {
return "greet";
}
在较新的 Spring 版本中,@RequestMapping 已经被更具体的注解取代,例如 @GetMapping、@PostMapping、@PutMapping 和 @DeleteMapping,它们分别用于处理 GET、POST、PUT 和 DELETE 请求。这些注解提供了更清晰和简洁的方式来定义映射规则
如:
@RequestMapping(value = "/greet", method = RequestMethod.GET)
// 等效于
@GetMapping("/greet")
获取参数
传统方式
Spring MVC 兼容 Servlet 的用法
@RestController
public class WebController {
@GetMapping("/hi") // 当使用 /hi 可以访问到当前方法
public Object hi(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
return "Hello" + request.getParameter("name");
}
}
在 Spring MVC 中默认内置隐藏了两个参数,HttpServletRequest 和 HttpServletResponse,想要用只要声明这两个参数即可
简便的方式
直接声明要获取的参数,参数名和查询字符串的参数名一致
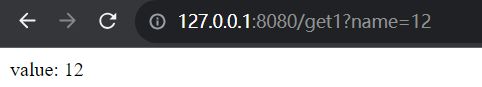
@GetMapping("/get1")
public String getParam1(String name) {
return "value: " + name;
}
结果:
参数的类型也可以写成其他的,比如 int 或 Integer,类型会自动转换
@GetMapping("/get1")
public String getParam1(Integer age) {
return "value: " + age;
}
如果查询字符串中没有指定 age 参数,那么这里会显示 null,如果 int 类型,则会报错,因为 int 无法接收 null
获取一个自定义类的对象
先定义一个类:
package com.example.spring_mvc_demo.model;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
}
然后就可以获取这个类的对象,对象的属性会自动从查询字符串中获取
@GetMapping("/get2")
public String getParam2(Student student) {
return student.toString();
}
从 json 字符串获取对象
上面的方式,传输的数据都是 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 格式,也就是查询字符串的格式。
Json 字符串是另外一种格式,要获取其解析后的对象,只要在参数的声明前加 @RequestBody 注解
@PostMapping("/login3")
public HashMap<String, Object> login3(@RequestBody Student student) {
HashMap<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("id", student.getId());
result.put("name", student.getName());
result.put("age", student.getAge());
return result;
}
我们使用 HashMap 作为返回类型,Spring 会自动将其转换为 JSON 格式作为 HTTP 响应返回给客户端
使用 Postman 构造请求并验证:
获取文件
使用 MultipartFile 类来描述一个文件,前面加上 @RequestPart 注解
@RequestPart注解,用于处理HTTP请求中的"multipart/form-data"类型的数据来支持文件上传
该注解可以传入参数,比如,@RequestPart("myfile")注解表示将请求中名为"file"的部分映射到 MultipartFile file 参数上
@PostMapping("/reg")
public String reg(@RequestPart("myfile") MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
file.transferTo(new File("d:/img.png"));
return "success";
}
使用 MultipartFile 中的方法 transferTo,将文件保存到硬盘。
获取 Cookie/Session/Header
获取 Cookie
@CookieValue 注解,用于从 HTTP 请求中提取特定 Cookie 的值,并将其映射到控制器方法的参数上。
注解中传入参数,比如 @CookieValue("cookie") 表示提取名为"cookie"的 Cookie 的值
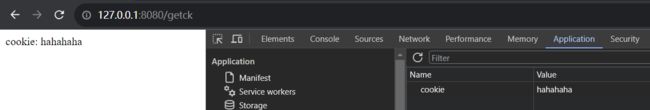
@GetMapping("/getck")
public String getCookie(@CookieValue("cookie") String cookie) {
return "cookie: " + cookie;
}
在浏览器中手动添加 cookie,可以看到服务端成功获取并返回了:
获取 Header
@RequestHeader 注解 用于从 HTTP 请求头中提取特定的信息,并将其映射到控制器方法的参数上。
传入参数指定要提取的请求头的名称。
@GetMapping("/gethead")
public String getHead(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent) {
return "User-Agent: " + userAgent;
}
session 存储和获取
@GetMapping("/setSession")
public String setSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取 HttpSession 对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 存储数据到会话中
session.setAttribute("username", "john_doe");
return "redirect:/getSession";
}
@GetMapping("/getSession")
public String getSession(HttpSession session, Model model) {
// 从会话中获取数据
String username = (String) session.getAttribute("username");
return "sessionResult: " + username;
}
和原始的 Servlet 没有区别,这里不做赘述。
参数重命名
@RequestParam 用于指定要提取的参数名称,这样,参数名和前端的查询字符串的名称就可以不一样了。
@GetMapping("/gettime")
public String getTime(@RequestParam("t") String time) {
return "time: " + time;
}
非必传参数
在Spring MVC中,你可以通过在方法参数上使用 @RequestParam 注解,并设置 required 属性为 false 来表示一个参数是非必传的。默认情况下,@RequestParam 的 required 属性是 true,即参数是必传的。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/example")
public String exampleMethod(
@RequestParam(name = "optionalParam", required = false) String optionalParam) {
// 处理参数
if (optionalParam != null) {
// 参数存在时的处理逻辑
System.out.println("Optional Parameter: " + optionalParam);
} else {
// 参数不存在时的处理逻辑
System.out.println("Optional Parameter is not provided");
}
// 其他业务逻辑
return "exampleView";
}
}
如果请求中包含了该参数,则参数值会被传递到方法中;如果请求中没有包含该参数,方法中的 optionalParam 将为 null。
获取url路径中的参数
如下代码 其中 {name} 和 {password} 是占位符,表示路径中的变量
@PathVariable 注解:用于将 URI 模板变量映射到方法的参数上。
@RequestMapping("/login4/{name}/{password}")
public String login4(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String password) {
return "name: " + name + ", password: " + password;
}
请求转发和请求重定向
区别
- 请求重定向(redirect)将请求重新定位到资源;请求转发(forward)服务端转发
- 请求重定向地址发生变化;请求转发地址不发生变化
- 请求重定向与直接访问新地址效果一样,不存在原来的外部资源不能访问;请求转发服务端转发有可能造成原外部资源不能访问
在Spring MVC中,“forward:” 和 “redirect:” 是用于控制器方法返回视图的两个关键字。
例:
@Controller
public class TestController {
// 请求转发
@RequestMapping("/hello1")
public Object hello1() {
return "forward:/login.html";
}
// 请求重定向
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public Object hello2() {
return "redirect:https://www.baidu.com";
}
}